Corn saline-alkaline tolerance related molecular marker developed based on transcription factor gene ZmNAC89 and application thereof
A technology of molecular markers and transcription factors, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragments, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems affecting production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1. Sequence Variation Analysis of Maize Transcription Factor Gene ZmNAC89
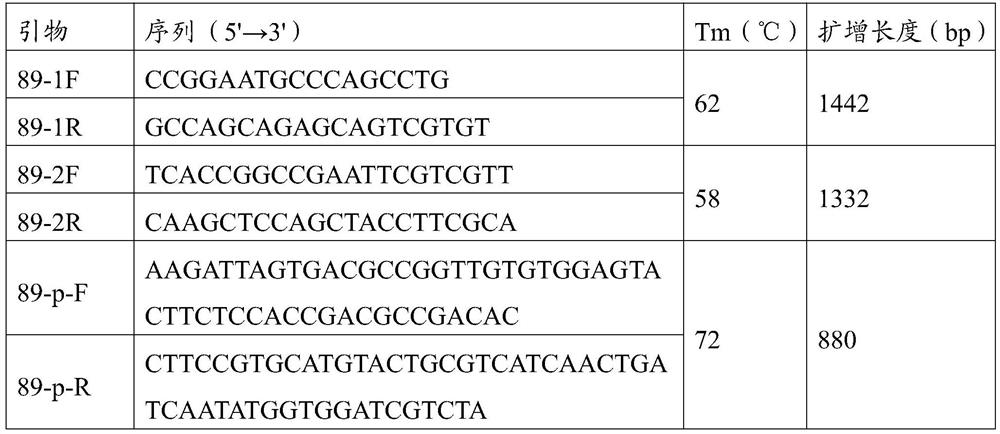
[0026] According to the MaizeGDB database (https: / / www.maizegdb.org / ) to provide the ZmNAC89 gene sequence in the maize B73 genome, primers were designed segmentally, and the gene sequence and promoter sequence were amplified from 140 maize inbred lines. The ZmNAC89 gene primers are 89-1F / R and 89-2F / R, and the promoter primer is 89-p-F / R. The primer sequences are shown in Table 1.
[0027] Table 1 ZmNAC89 gene sequence and promoter sequence cloning primers
[0028]
[0029] The sequencing results were spliced into a complete sequence using DNAMAN software, and multiple sequences were compared. The ZmNAC89 gene sequence was analyzed using DnaSPv6.0 software, and divided into different haplotypes based on the difference in SNP sites. D, Fu and Li's D* and Fu and Li's F* and other three methods were used for neutral test to preliminarily determine excellent haplotypes.
[0030] 1. H...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Association Analysis of Genetic Variation of ZmNAC89 Gene and Saline-Alkaline Tolerance
[0040] TASSEL 5.0 software was used to screen out the variant sites with a typing rate MAF>0.05, and based on the phenotype data of the natural population’s salt-alkaline tolerance identification in the previous period, the association analysis between markers and phenotypes was carried out. The general linear model GLM was used to analyze the correlation between the 16 polymorphic sites in the ZmNAC89 gene coding region sequence and the salt-alkaline tolerance phenotype indicators of the tested maize inbred lines.
[0041] The results showed that at the 0.05 level, there were 5 non-synonymous mutation SNP sites associated with the alkali resistance phenotype index (see Table 4 and Table 5). In the basic analysis, the four SNP loci, including snp124, snp145, snp253 and snp375, were significantly correlated with plant height (SL) at the same time, all of which were non-syn...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 Development of dCAPS functional markers
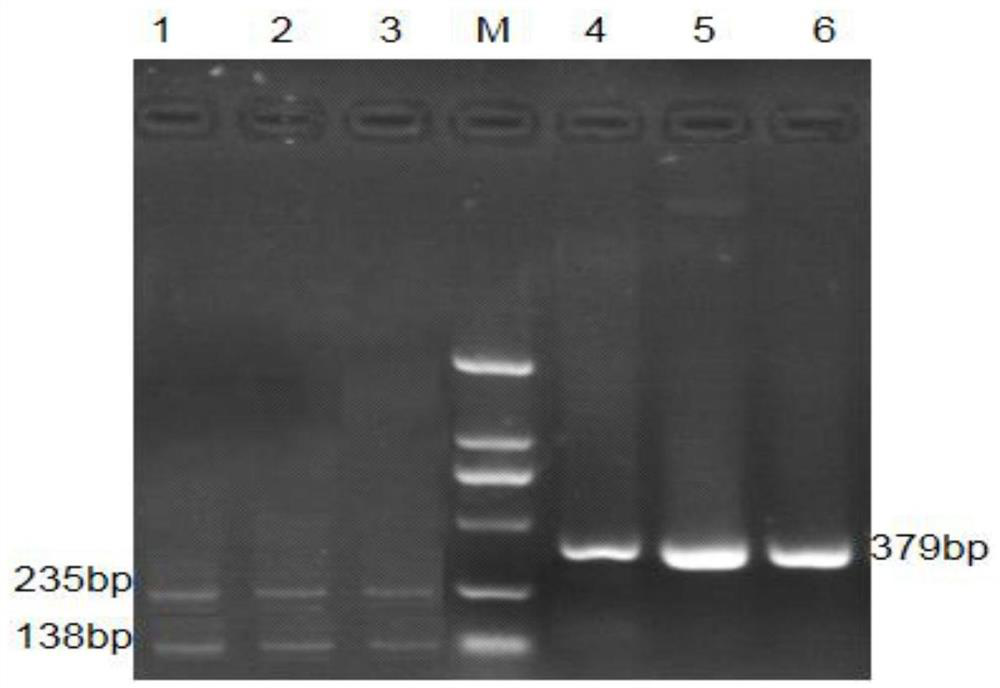
[0048] According to the results of association analysis of ZmNAC89 gene coding region, dCAPs markers were developed at snp253(T / C) and snp767(G / C) loci. Since the primers were designed based on the reverse complementary strand of the reference sequence, snp253 was transformed from T / C to A / G mutation. Utilize the online website dCAPs Finder to analyze the best enzyme cutting sites and select restriction endonucleases, develop functional markers, dCAPs marker primers and corresponding endonucleases. dCAPs labeled primers and corresponding endonucleases are shown in Table 6.
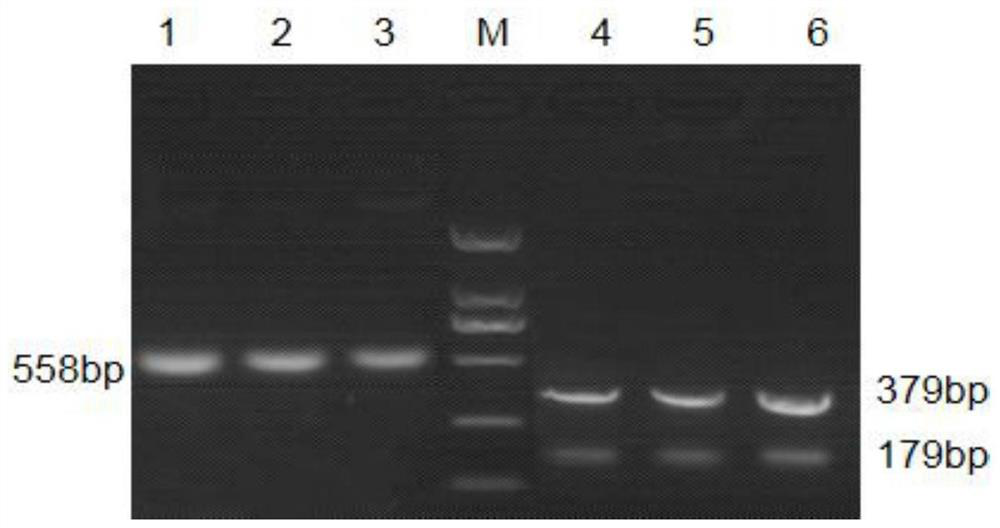
[0049] The snp253(T / C) transformed marker is named DNdCAPS253, the PCR amplified fragment is 558bp in length, the 180th base is the mutation site, and the salt-alkali-sensitive material is T, which cannot be cut by the SacII restriction endonuclease; The saline-alkaline material is C, which can be cut into two fragments of 179bp and 379bp by SacI...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com