Target secondary discrimination method after constant false alarm rate detection
A technology of constant false alarm detection and target, applied in the field of radar, can solve the problems of false alarm, target detection performance impact, and it is difficult to refer to the unit to improve the detection threshold.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
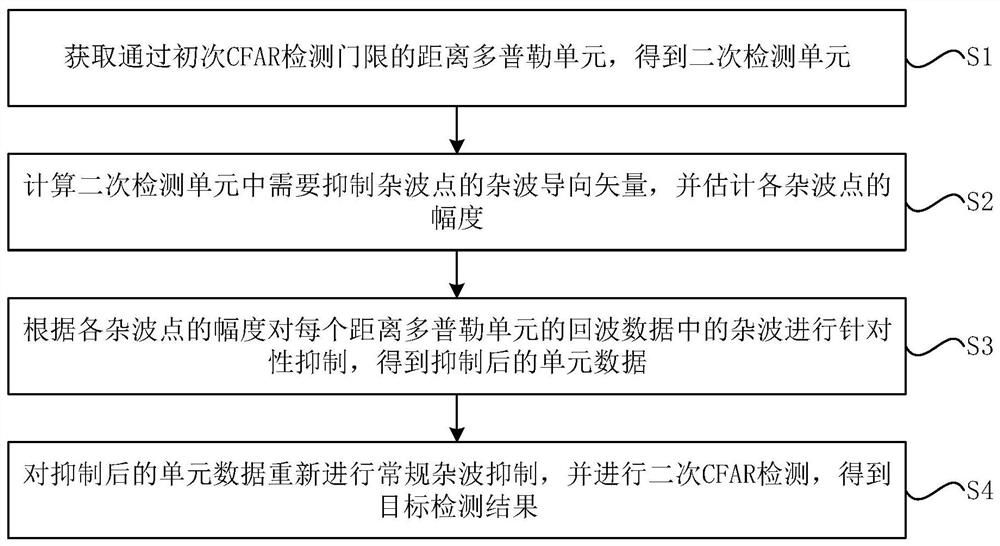
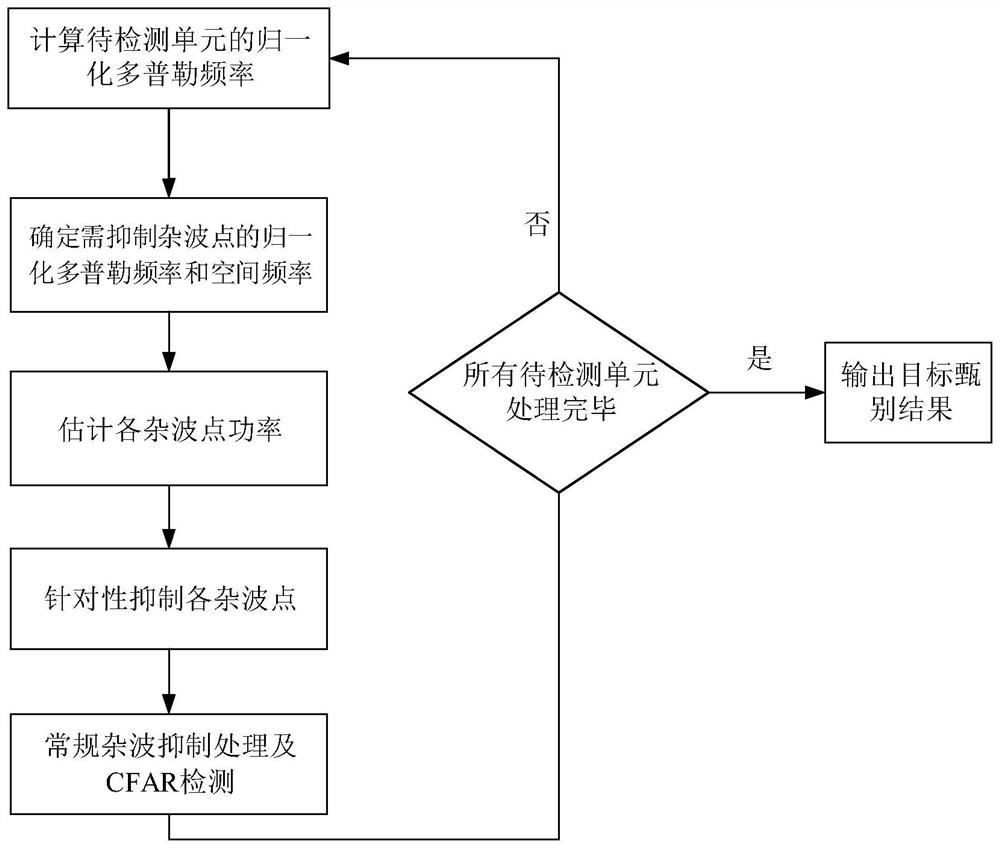
[0044] See figure 1 , figure 1 It is a flow chart of a target secondary screening method after constant false alarm detection provided by an embodiment of the present invention, including the following steps:
[0045] S1: Obtain the range Doppler unit that passes the primary CFAR detection threshold to obtain the secondary detection unit.
[0046] Specifically, the CFAR detector is firstly used to perform initial point-by-point detection on each unit in the range Doppler plane, and the position information {(I k ,J k ), k=1,2,...,K}, K secondary detection units are obtained. Among them, K is the number of range Doppler units that pass the CFAR detection threshold.
[0047] S2: Calculate the clutter steering vector of the clutter point that needs to be suppressed in the secondary detection unit, and estimate the amplitude of each clutter point, specifically including:
[0048] S21: Calculate the distance in the secondary detection unit and the normalized Doppler frequency ...
Embodiment 2
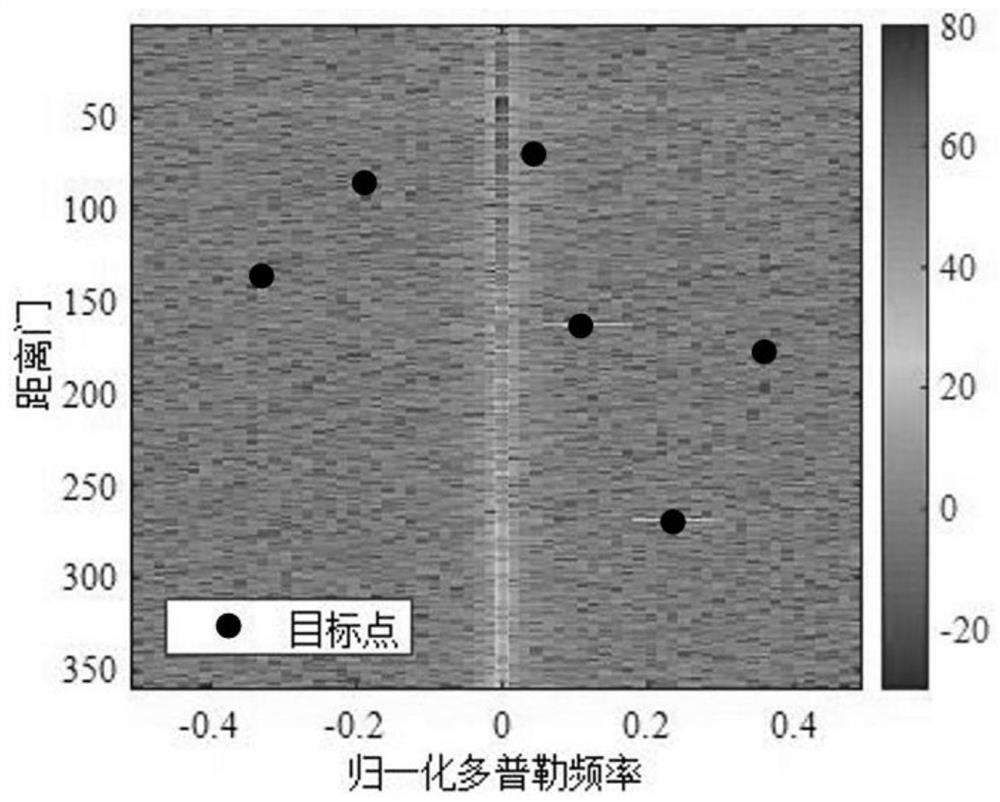
[0091] The beneficial effects of the secondary discrimination method after the constant false alarm detection provided by the above-mentioned embodiment 1 are further verified and explained through simulation experiments.
[0092] Experimental conditions:
[0093] Set the flight altitude of the carrier aircraft h a The array antenna adopts a 16×1 uniform linear array, and the array element spacing l is 0.1m. The speed direction of the aircraft is parallel to the array axis, that is, the front side-view array, and the angle between the main beam pointing and the array axis is 90°, and the elevation angle of the main beam is 0°. Carrier frequency f c 1.5GHz, wavelength λ 0 The distance sampling frequency used by the radar is 2MHz, the pulse repetition frequency is 3000Hz, and the pulse number is 64.
[0094] Experiment content:
[0095] In this simulation experiment, the target signal was added at the No. 137 range gate with a normalized Doppler frequency of -0.3281 and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com