Multi-core erbium-doped super-mode optical fiber for gain equalization
A gain equalization, optical fiber technology, applied in the fields of special optical fiber, signal processing, and optical fiber communication, can solve the problems of rarely reported amplifiers, increased bit error rate at the receiving end, and damage to the communication system.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] A multi-core erbium-doped supermode optical fiber for gain equalization, the optical fiber includes: nineteen cores, cladding and active doping regions; the specific structure is:
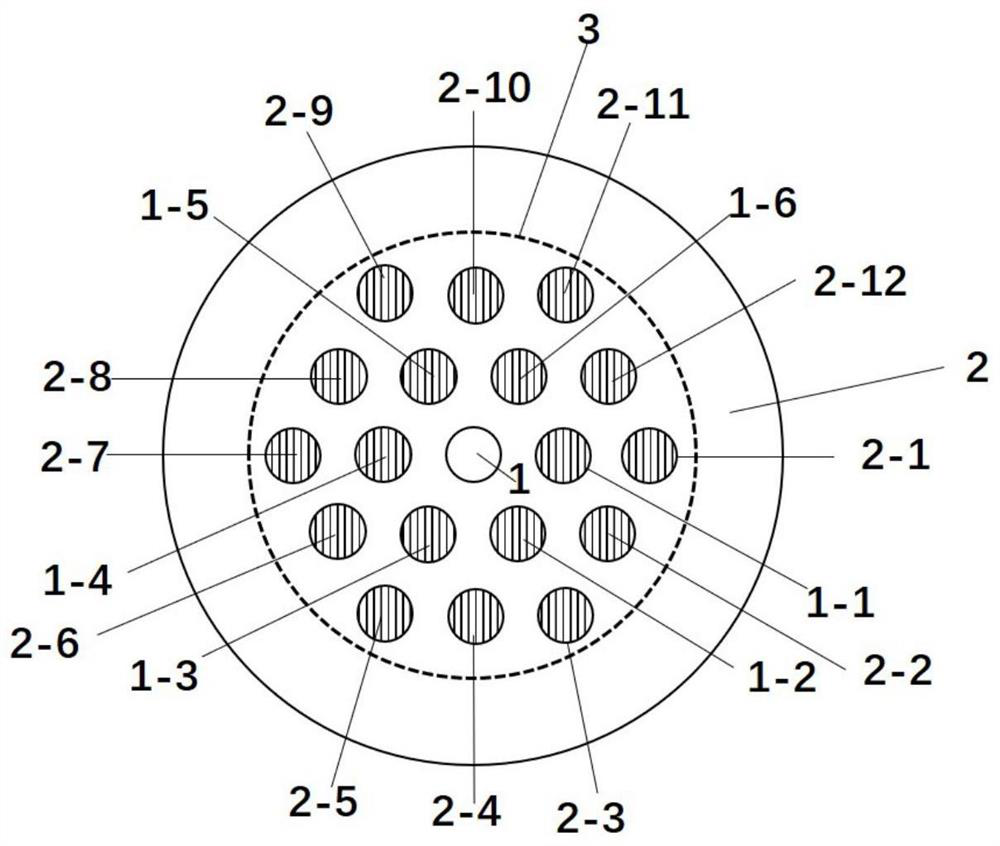
[0019] A multi-core erbium-doped supermode fiber for gain equalization is characterized in that: the multi-core erbium-doped supermode fiber contains nineteen cores, which are respectively the center core (1) and the first layer core (1 -1)~(1-6) and the second layer of cores (2-1)~(2-12), nineteen cores are evenly distributed in a regular hexagon, located in the same cladding (2), the cores The radius is between 4-6 μm, the core spacing is between 10-16 μm, and the erbium ions are in the first layer of cores (1-1)~(1-6) and the second layer of cores except the central core (1). Doping in (2-1)~(2-12).
[0020] The multi-core erbium-doped supermode fiber used for gain equalization in this embodiment adopts the first layer of single-ring doping, and the structure is as follows figure 2 sho...
Embodiment 2
[0022] A multi-core erbium-doped supermode optical fiber for gain equalization, the optical fiber includes: nineteen cores, cladding and active doping regions; the specific structure is:
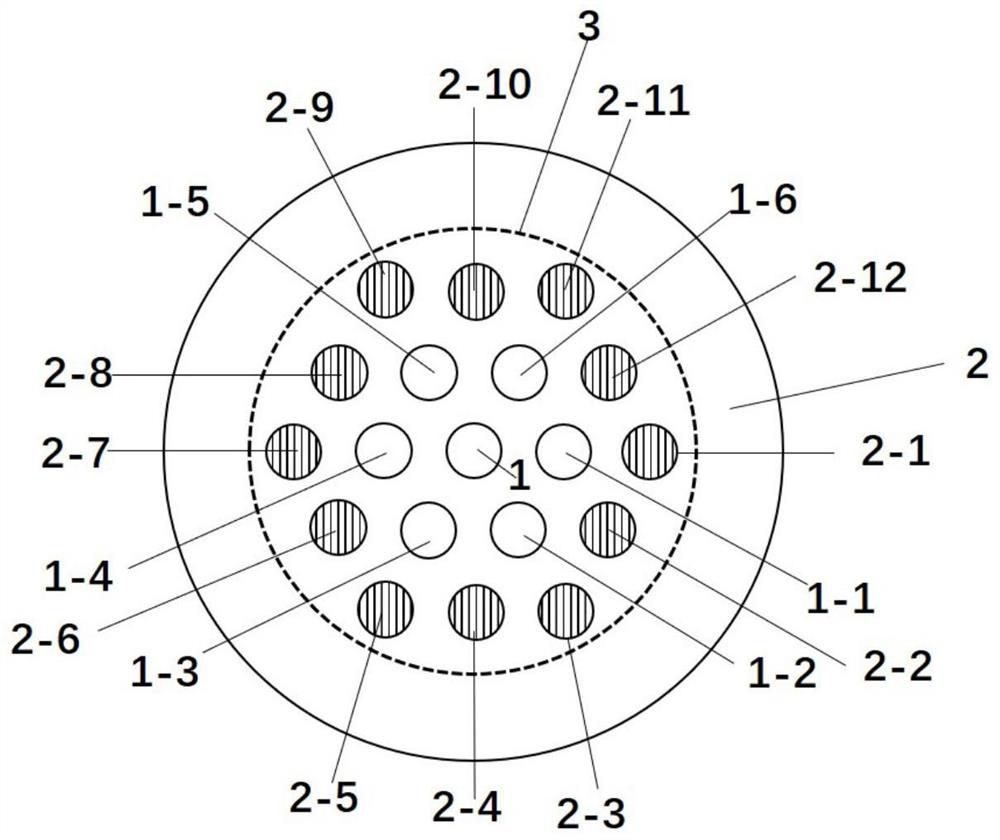
[0023] A multi-core erbium-doped supermode fiber for gain equalization is characterized in that: the multi-core erbium-doped supermode fiber contains nineteen cores, which are respectively the center core (1) and the first layer core (1 -1)~(1-6) and the second layer of cores (2-1)~(2-12), nineteen cores are evenly distributed in a regular hexagon, located in the same cladding (2), the cores The radius is between 4-6 μm, the core spacing is between 10-16 μm, and the erbium ions are in the first layer of cores (1-1)~(1-6) and the second layer of cores except the central core (1). Doping in (2-1)~(2-12).
[0024] The multi-core erbium-doped supermode fiber used for gain equalization in this embodiment adopts double trapezoidal doping, and the structure is as follows image 3 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0026] A multi-core erbium-doped supermode optical fiber for gain equalization, the optical fiber includes: nineteen cores, cladding and active doping regions; the specific structure is:
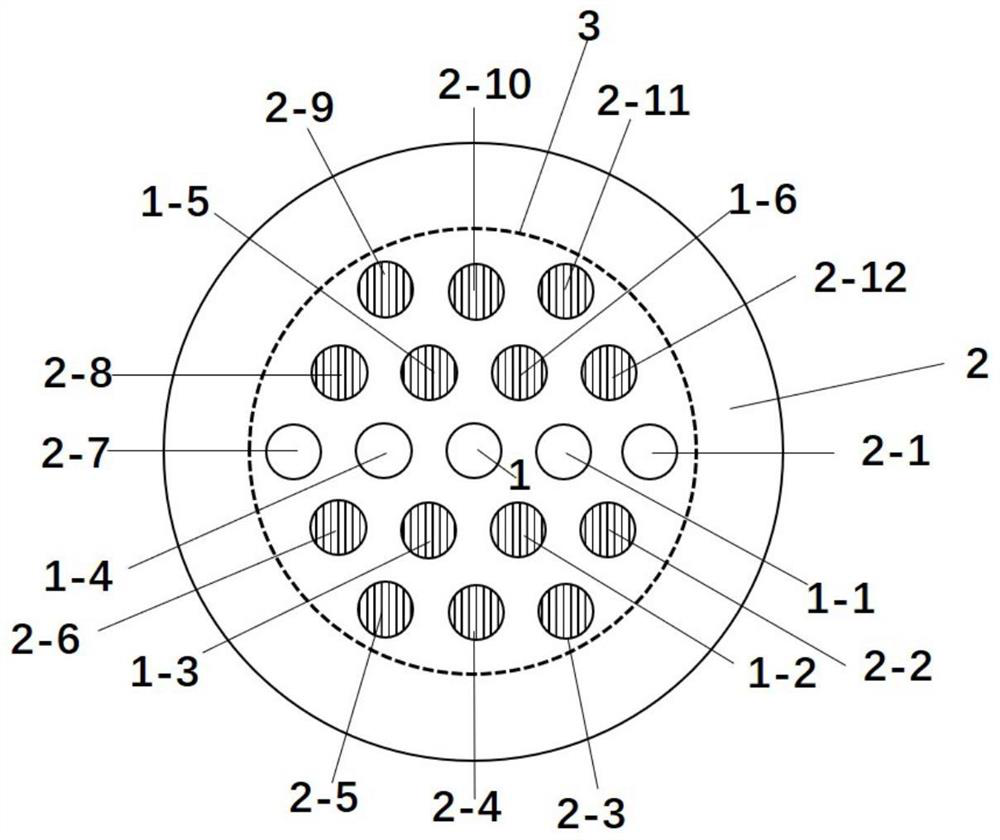
[0027] A multi-core erbium-doped supermode fiber for gain equalization is characterized in that: the multi-core erbium-doped supermode fiber contains nineteen cores, which are respectively the center core (1) and the first layer core (1 -1)~(1-6) and the second layer of cores (2-1)~(2-12), nineteen cores are evenly distributed in a regular hexagon, located in the same cladding (2), the cores The radius is between 4-6 μm, the core spacing is between 10-16 μm, and the erbium ions are in the first layer of cores (1-1)~(1-6) and the second layer of cores except the central core (1). Doping in (2-1)~(2-12).
[0028] The multi-core erbium-doped supermode fiber used for gain equalization in this embodiment adopts rectangular doping, and the structure is as follows Figure 4 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com