An automatic marking device for cylindrical NdFeB magnets
An automatic marking, NdFeB technology, applied in printing devices, packaging automatic control, packaging, etc., can solve the problems of high labor intensity of employees, lower production qualification rate of cylindrical NdFeB magnets, and low marking efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
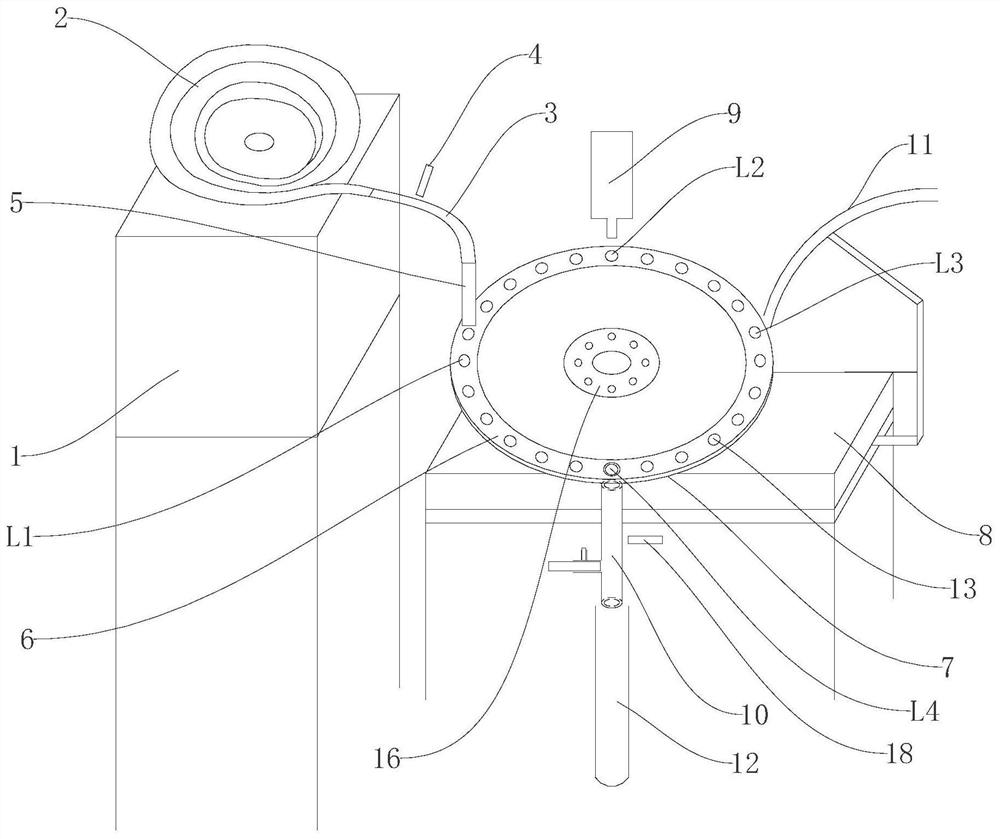
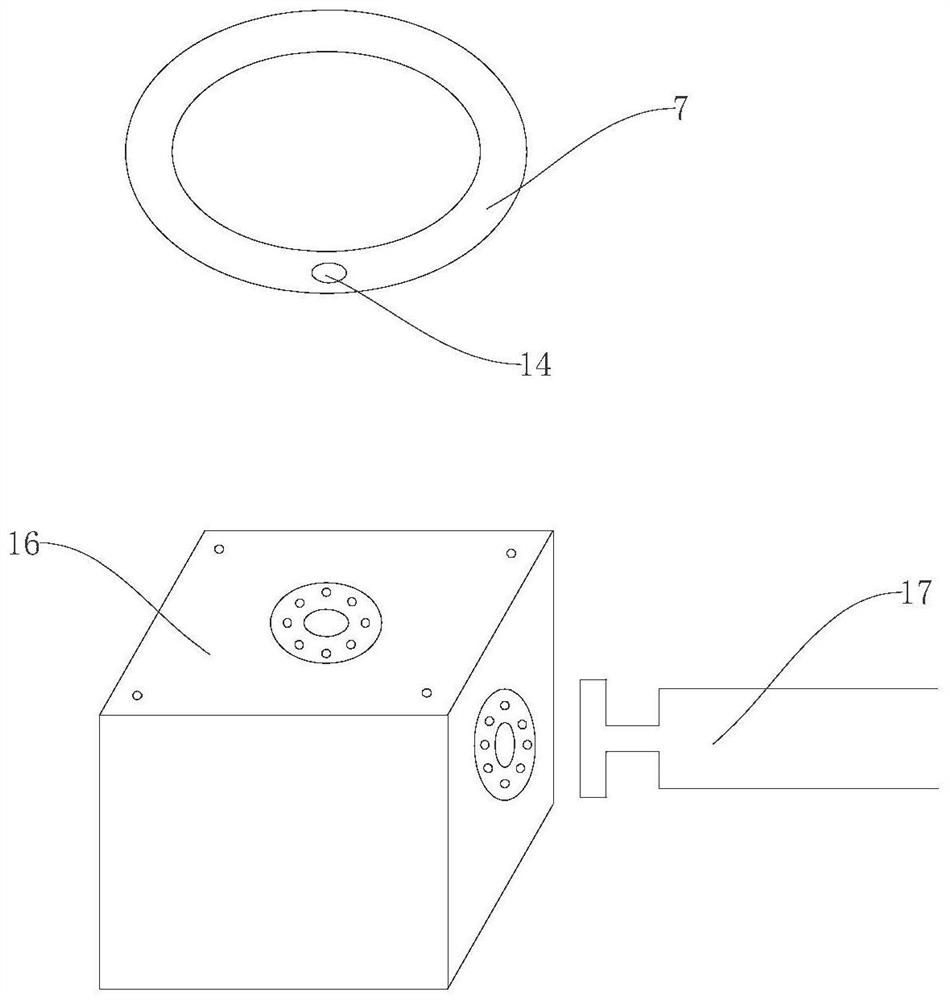
[0013] Example: such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, an automatic marking device for cylindrical NdFeB magnets includes a control module, a support table 1, a vibrating feeding tray 2, a feeding hose 3 capable of accommodating a cylindrical NdFeB magnet, and a first optical fiber Sensor 4, guiding channel 5, rotating disk 6, supporting disk 7, workbench 8, driver, inkjet printer 9, feeding pipe 10, air blowing pipe 11 and receiving hose for packing cylindrical NdFeB magnets 12. The control module is respectively connected to the vibrating feeding tray 2, the first optical fiber sensor 4, the driver and the inkjet printer 9, and can control the vibrating feeding tray 2, the driver and the inkjet printer 9 to work together. Station L1, marking station L2, drying station L3 and blanking station L4, the driver is installed on the workbench 8, the rotating disk 6 is installed on the driver, the supporting disk 7 is located below the rotating disk 6, and is fixed on the On the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com