A shock-absorbing damper for high-piled wharf
A shock-absorbing damping and high-pile wharf technology, applied in the field of shock-absorbing dampers, can solve the problems that shock-absorbing and isolation technologies have not been widely used, and achieve the effects of reducing movement speed, reducing damage, and increasing flow resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
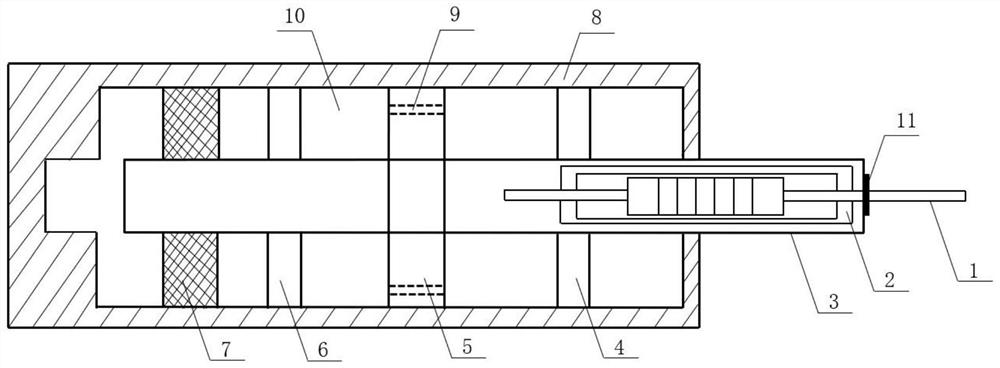
[0019] Specific implementation one: as Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, the present invention discloses a shock-absorbing damper for a high-piled wharf, including a magnetorheological damper 2, a frequency trigger switch 11 and a viscous damper 24; the magnetorheological damper 2 is arranged in the viscous damping In the main piston rod 3 of the damper 24 , and a frequency trigger switch 11 is arranged between the outer end of the main piston rod 3 and the magnetorheological damper 2 . When the present invention is subjected to a huge seismic load, the action of high-frequency seismic waves can excite the frequency trigger switch 11, so that the magnetorheological damper 2 is out of work, and the viscous damper 24 starts to work, thereby consuming seismic energy and achieving the purpose of shock absorption .
specific Embodiment approach 2
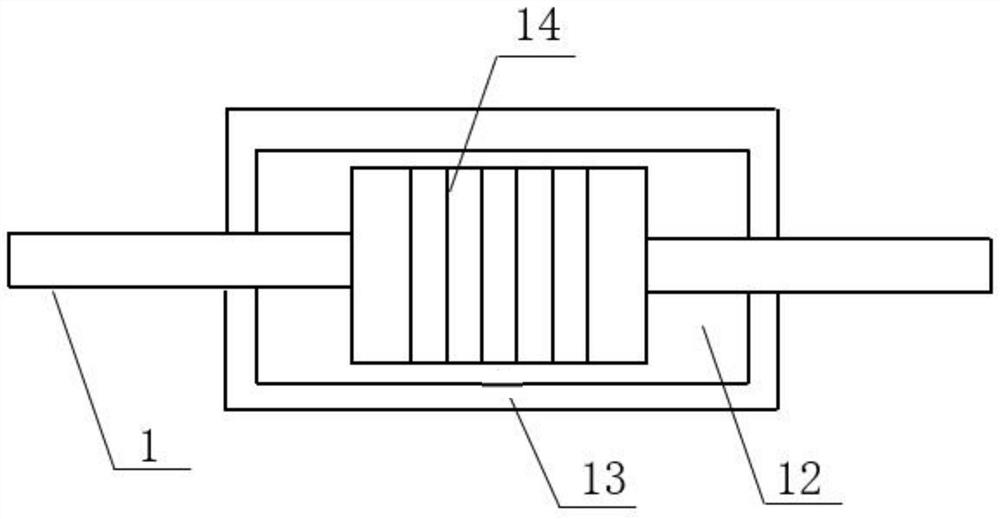
[0020] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1. The magnetorheological damper 2 includes a secondary piston rod 1, a magnetorheological liquid 12, a secondary cylinder 13 and an excitation coil 14; the The outer wall of the auxiliary piston rod 1 is preferably wound with an excitation coil 14 in the middle, the auxiliary piston rod 1 and the outer ring of the excitation coil 14 are sleeved with an auxiliary cylinder 13, the auxiliary cylinder 13 is filled with magnetorheological liquid 12, and the auxiliary piston rod is One end of 1 protrudes to the outside of the main piston rod 3 , the outer wall of the auxiliary cylinder 13 is fixedly connected with the inner wall of the main piston rod 3 , and a frequency trigger switch 11 is arranged between the main piston rod 3 and the auxiliary piston rod 1 . When the present invention is subjected to the static load of the mooring ship, the excitation coil 14 inside the magnetorheological damper 2 will g...
specific Embodiment approach 3
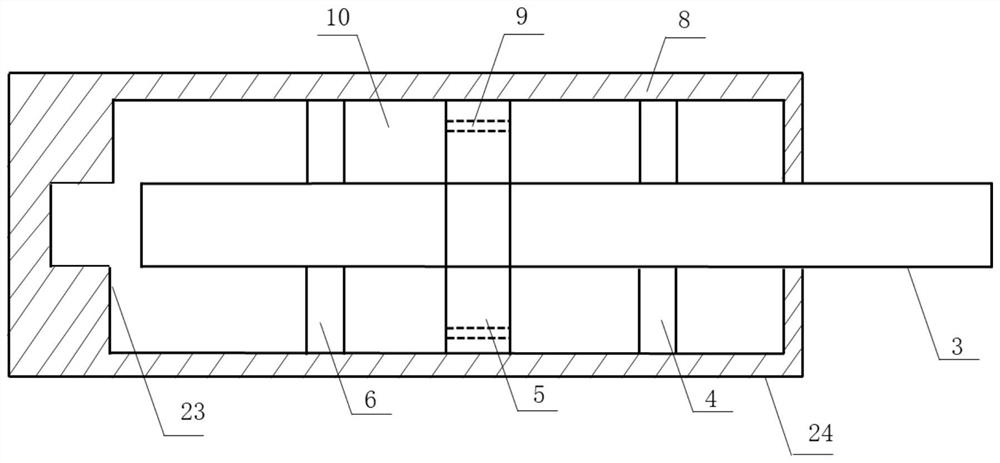
[0021] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1 or 2. The viscous damper 24 includes a main piston rod 3, a right end cover 4, a piston 5, a left end cover 6, a master cylinder 8 and Damping medium 10; the main piston rod 3 is arranged horizontally and the outer side is vertically sleeved with a right end cover 4, a piston 5 and a left end cover 6, the piston 5 is fixedly connected with the main piston rod 3, the main piston rod 3 and the right end cover 4 and The left end cover 6 is slidably connected, the right end cover 4, the piston 5 and the outer side of the left end cover 6 are sheathed with a main cylinder 8, and the outer wall of the piston 5 is fitted with the inner wall of the main cylinder 8. The right end cover 4 and the left end cover 6 It is rotatably connected with the main cylinder 8 through bearings to achieve the purpose of replacing the damping medium 10; the main cylinder 8 is provided with a damping medium 10 between the right...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com