Pencil feeding structure of pencil sharpener
A technology for pencil sharpeners and pen feeding, which is applied in sharpening devices, printing, office supplies, etc., and can solve problems such as short service life of pen feeding components, wear blocks of pen feeding components, and broken pencil tips, etc., and achieves simple structure and low wear The effect of reducing beating and convenient processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
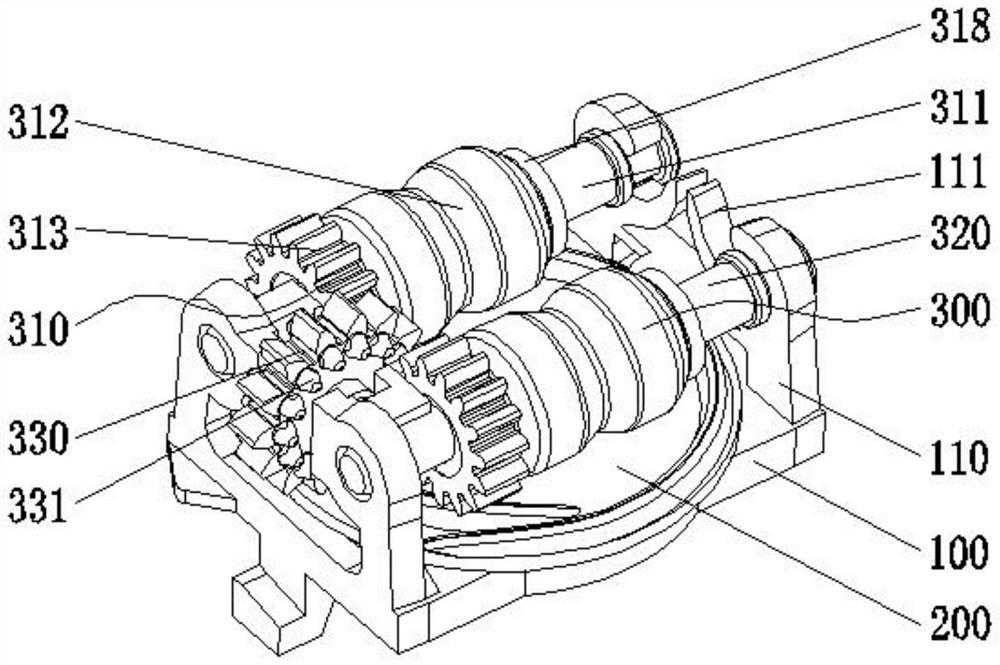
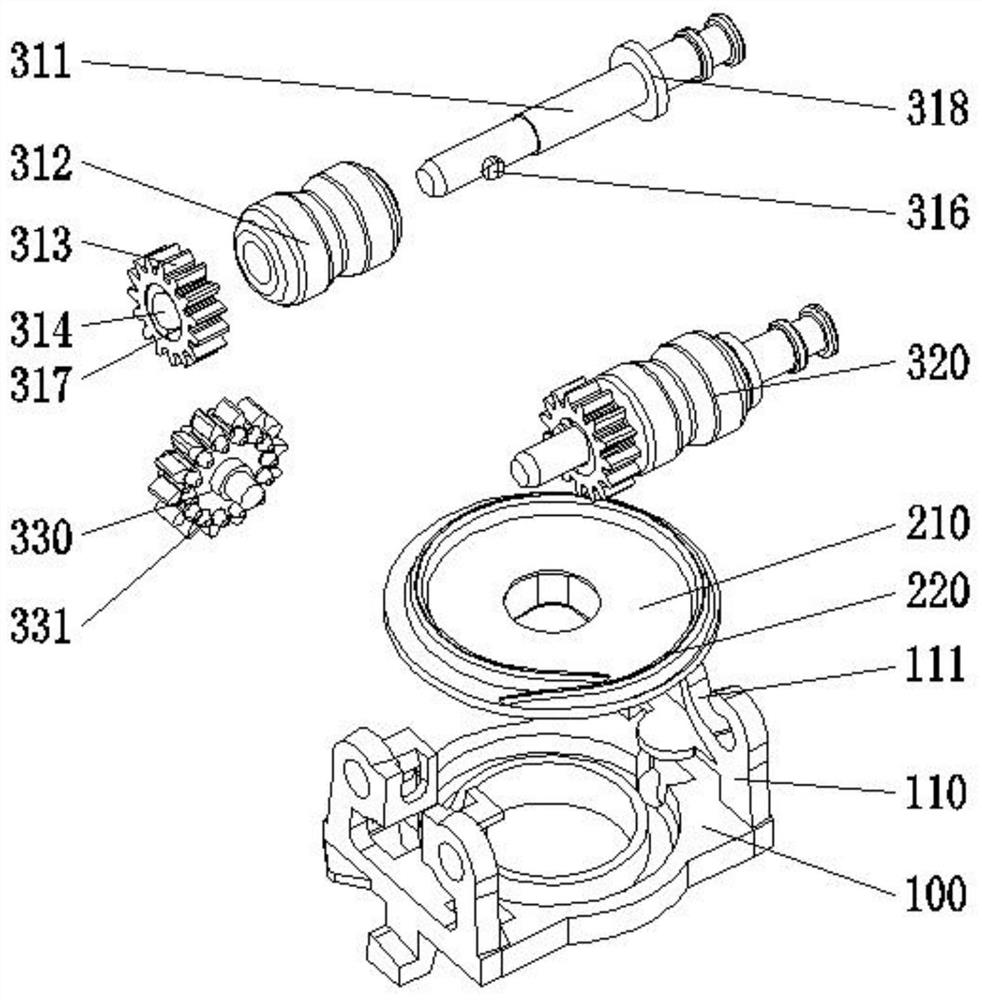
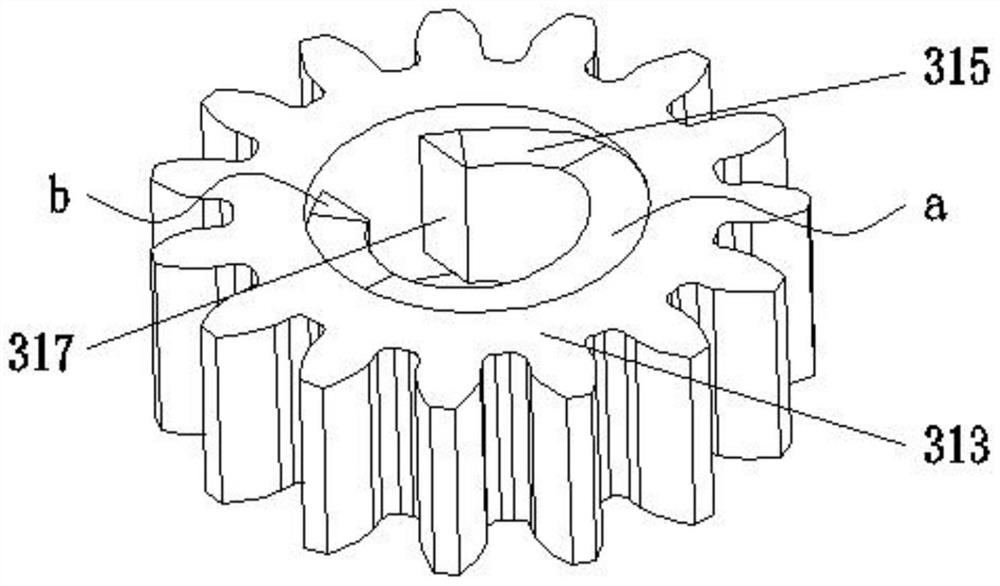
[0028] Embodiment 1: the linkage member 313 is a spur gear, the synchronous transmission member 330 is a synchronous gear, the synchronous gear is a spur gear, and the two sides of the synchronous gear are provided with convex teeth 331 for driving the spur gear to rotate. The synchronous gear is arranged at the position between the two spur gears of the installation frame 100, and the transmission is realized through gear cooperation between the driving member 200 and the pen feeding assembly 300. The teeth 331 cooperate with the linkage 313 to realize transmission.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment two, such as Figure 5 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the linkage 313 is a bevel gear, the synchronous transmission 330 is a synchronous gear, the synchronous gear is a spur gear, and both sides of the synchronous gear are provided for driving The bevel gear rotates the bevel tooth 332. The synchronous gear is set at the position between the two bevel gears on the installation frame 100. The transmission principle of this embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment, except that the synchronous gear and the linkage 313 are changed. In the meshing mode, bevel gears are used on both sides of the synchronous gear, and in the same way, the linkage 313 also uses bevel gears for meshing transmission.
[0030] The driving member 200 includes a rotating disc 210 and a helical protrusion 220 arranged on the upper surface of the rotating disc 210. The pitch of the helical protrusion 220 is equal to the tooth pitch of...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment three; as Image 6As shown, the driving member 200 includes a rotating disc 210 and two arc-shaped protrusions 230 arranged on the upper surface of the rotating disc 210. The two arc-shaped protrusions 230 are identical in shape and arranged symmetrically. The two arc-shaped protrusions The dislocation pitch of 230 is equal to the tooth pitch of the spur gear, and the drive member 200 is engaged with the synchronous gear through the dislocated arc-shaped protrusion 230; meshing, the head end and the end of the two arc-shaped protrusions 230 are coincident in the radial angle of the rotating disk 210, and the misalignment distance between the two arc-shaped protrusions 230 is equal to the tooth pitch of the synchronous gear, thereby realizing Mesh, when the rotating disk 210 rotates half a circle, the handover of the two arc-shaped protrusions 230 is in the synchronous gear to switch a tooth position. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com