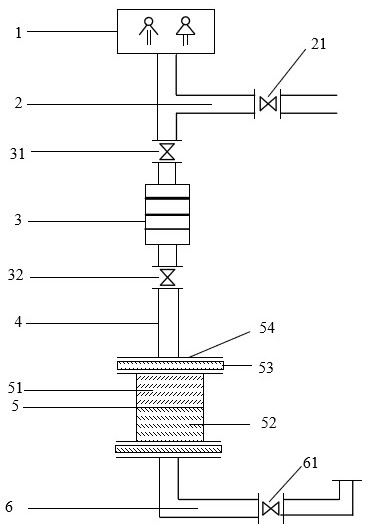
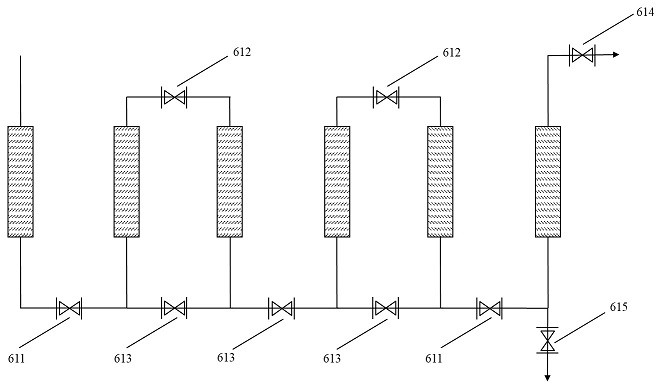
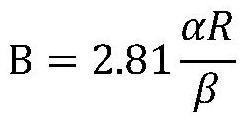Reactor, system and method for urine in-situ resource recovery
A resource recovery and reactor technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, applications, climate change adaptation, etc., can solve problems such as decreased transparency, blockage of water treatment facilities, carcinogenicity, etc., to avoid loss, efficient recovery, and simple structure. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Exploratory experiment on the filling amount of biochar and magnesia-loaded biochar
[0040] In this example, the nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium resources of urine recovery are filled with biochar and magnesia-loaded biochar, and the filling amount of biochar and magnesia-loaded biochar is determined according to the properties of urine, biochar properties, and the replacement cycle of the reactor. First, set the reactor replacement cycle to 10 days, the number of urinations per day is 0.2 person-times / day, the ammonia nitrogen adsorption capacity of biochar is 10mg / g, and the magnesium content of magnesia-loaded biochar is 15%. According to the filling amount of biochar and magnesia load The formula for calculating the filling amount of biochar is as follows;
[0041]
[0042] The filling amount of biochar obtained is 0.56kg, and the filling amount of magnesia loaded biochar is 0.09kg.
[0043] The resource recovery results are as follows: the recov...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: Biochar and magnesium oxide-loaded biochar filling experiment
[0045] The operation steps of filling the filler of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium resources recovered in urine in this embodiment are the same as in embodiment 1, and the difference from embodiment 1 is that the biochar adsorption capacity of ammonia nitrogen set in this embodiment is 4 mg / g, and the biochar is obtained The filling quantity is 1.40kg. The resource recovery results are as follows: the recovery rate of ammonia nitrogen is 99%, the recovery rate of phosphorus is 93%, and the recovery rate of potassium is 24%. The comparison of Examples 1 and 2 shows that when the adsorption capacity of biochar to ammonia nitrogen is higher, the filling amount of biochar can be reduced, thereby reducing the cost of technology application, and the recovery rate of potassium resources is higher, and the resource recovery effect is better.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3: Exploratory experiment on the filling amount of biochar and magnesium oxide-loaded biochar
[0047] The operation steps of filling the filler of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium resources of urine recovered in this embodiment are the same as in embodiment 1, and the difference from embodiment 1 is that the magnesium content of the magnesium oxide-loaded biochar set in this embodiment is 5%, and the magnesium oxide load is 5%. The filling amount of biochar is 0.27kg. The resource recovery results are as follows: the recovery rate of ammonia nitrogen is 99%, the recovery rate of phosphorus is 92%, and the recovery rate of potassium is 26%. The comparison of Examples 1 and 3 shows that when the magnesium content of the magnesia-supported biochar is high and the magnesium element content in the magnesia-supported biochar is high, the filling amount of the magnesia-supported biochar can be reduced, which is beneficial to reduce the cost of technology application...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com