A kind of construction method and application of mycoplasma bovis mouse mastitis model
A technology of Mycoplasma bovis and Mycoplasma bovis, which is applied in the field of constructing a mouse model of Mycoplasma bovis, can solve problems such as the lack of pathological damage evaluation models, obstacles in the research and development of antibiotic alternative drugs for anti-inflammatory treatment programs for dairy cow mastitis, and achieve good results. Practical application value, good repeatability and convenience, and the effect of promoting development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1. Selection of strains for infection
[0047] Mycoplasma bovis NMH7 strain is a Mycoplasma bovis isolate isolated by the inventor's research group in 2018 from a milk sample from a dairy farm in Inner Mongolia. After epidemiological and pathogenic analysis, a large amount of background information was obtained on the genotype characteristics and pathogenicity of M. bovis NMH7 strains.
[0048] The results of multi-locus sequence analysis showed that the M. bovis NMH7 strain belongs to a newly discovered genotype in my country, ST173, and its background information is included in the MLST database (https: / / pubmlst.org / bigsdb?db=pubmlst_mbovis_isolates&page=query) (details See doi: 10.1016 / j.prevetmed.2020.105106). Mycoplasma bovis NMH7 strain is documented at: https: / / pubmlst.org / bigsdb?id=2 db=pubmlst_mbovis_isolates&page=query, the ID number is 1015.
[0049]Further, the inventor tested milk samples from dairy farms across the country and found that the geno...
Embodiment 2
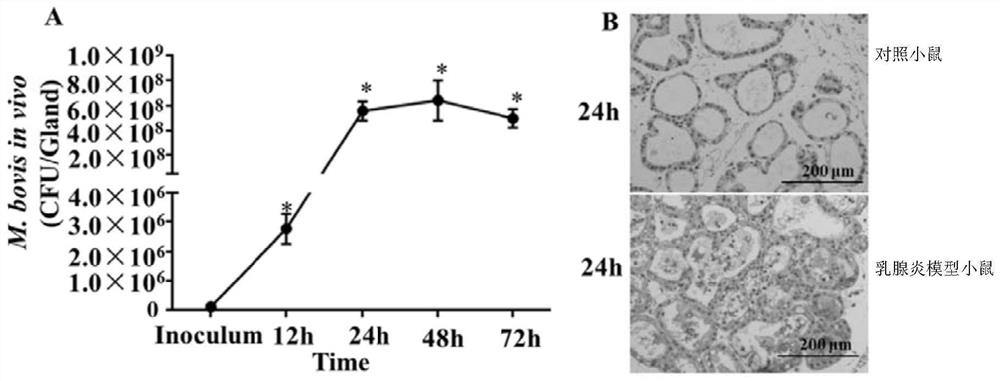
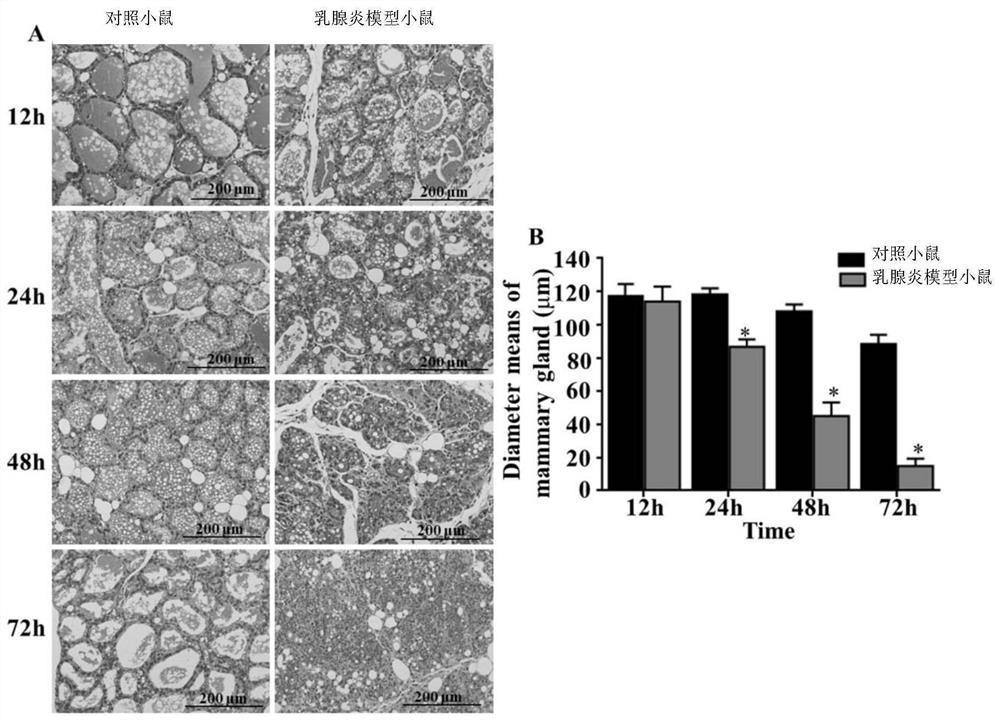
[0052] Example 2, Mycoplasma bovis infection causes mastitis in mice
[0053] 1. Construction of mastitis model mice
[0054] The infectious fluid was inoculated into lactating CD-1 mice 5 days after delivery. The method of inoculation is through the milk duct of mice. The inoculation site was the fourth pair of mammary glands of mice. The infection solution was obtained by suspending the Mycoplasma bovis NMH7 strain with sterile phosphate buffer solution, and the concentration of Mycoplasma bovis was 1 × 10 6 CFU / ml. The inoculation volume was 100 μl of infection solution per mammary gland.
[0055] 2. Control mice
[0056] Sterile phosphate buffered solution was inoculated into lactating CD-1 mice 5 days after delivery. The method of inoculation is through the milk duct of mice. The inoculation site was the fourth pair of mammary glands of mice. The inoculum volume was 100 μl sterile phosphate buffer solution per mammary gland.
[0057] 3. Detection of relevant indi...
Embodiment 3
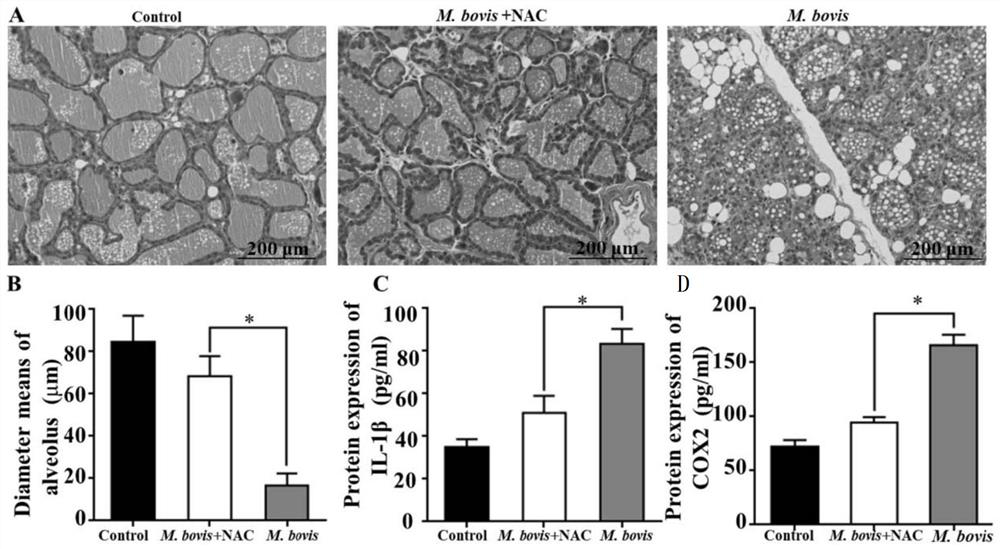
[0072] Example 3. Experiment on the protective effect of reactive oxygen species scavengers on mouse mastitis caused by Mycoplasma bovis infection
[0073] NAC (N-acetyl-L-cysteine): a reactive oxygen species scavenger, Sigma Company, USA, product number A7250.
[0074] NAC was diluted with sterile physiological saline to obtain a NAC solution with a concentration of 10 mM.
[0075] 1. Treatment of M.bovis group + NAC group
[0076] 1. Take lactating CD-1 mice 5 days after delivery, and inject NAC solution (150 mg NAC / kg body weight) intraperitoneally.
[0077] 2. Inoculate the infection solution 12 hours after completing the intraperitoneal injection. The method of inoculation is through the milk duct of mice. The inoculation site was the fourth pair of mammary glands of mice. The infection solution was obtained by suspending the Mycoplasma bovis NMH7 strain with sterile phosphate buffer solution, and the concentration of Mycoplasma bovis was 1 × 10 6 CFU / ml. The inocul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com