Preparation method of ultrahigh-strength high-plasticity high-temperature-oxidation-resistant steel through hot stamping forming
A technology of hot stamping and high temperature oxidation resistance, which is applied in heat treatment equipment, heat treatment furnaces, manufacturing tools, etc., and can solve problems such as oxidation and strong plasticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
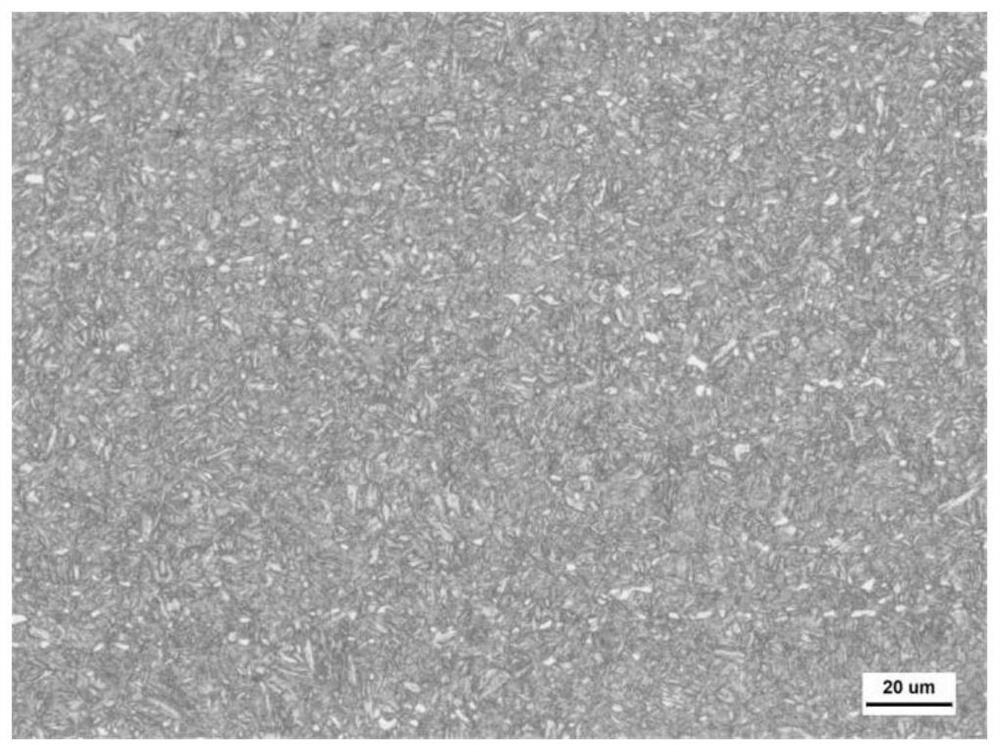
Image
Examples
Embodiment 5
[0084] Example 5: Satisfy Si / Al=1.2~2.2, and Si+Al<2.5, the average thickness of the oxide layer after the hot stamping process of the corresponding steel in Table 2 is 5.5 μm;
Embodiment 6
[0085] Embodiment 6: Satisfy Si / Al2.5, the average thickness of the oxide layer after the hot stamping process of the corresponding steel in Table 2 is 5.1 μm;
Embodiment 7
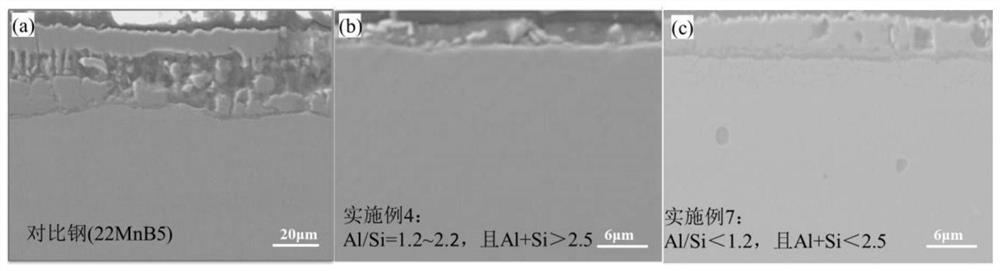
[0086] Example 7: Satisfying Si / Al figure 2 (c) provides a typical SEM picture of the oxide layer of Example 7.
[0087] Through the comparison of the oxide layer thickness in Examples 4, 5, 6 and 7, it is found that reducing the Si / Al ratio and Si+Al content will reduce the oxidation resistance, and the oxide layer thickness of the steel in Example 4 is the thinnest, and the oxidation resistance is the best, so , it is necessary to define Si / Al=1.2~2.2, and Si+Al>2.5. In summary, the steel of the present invention (satisfying: Si / Al=1.2-2.2, and Si+Al>2.5) obtains an oxide layer thickness of ≤4.2 μm after being kept at ≤950° C. for ≤5 minutes.
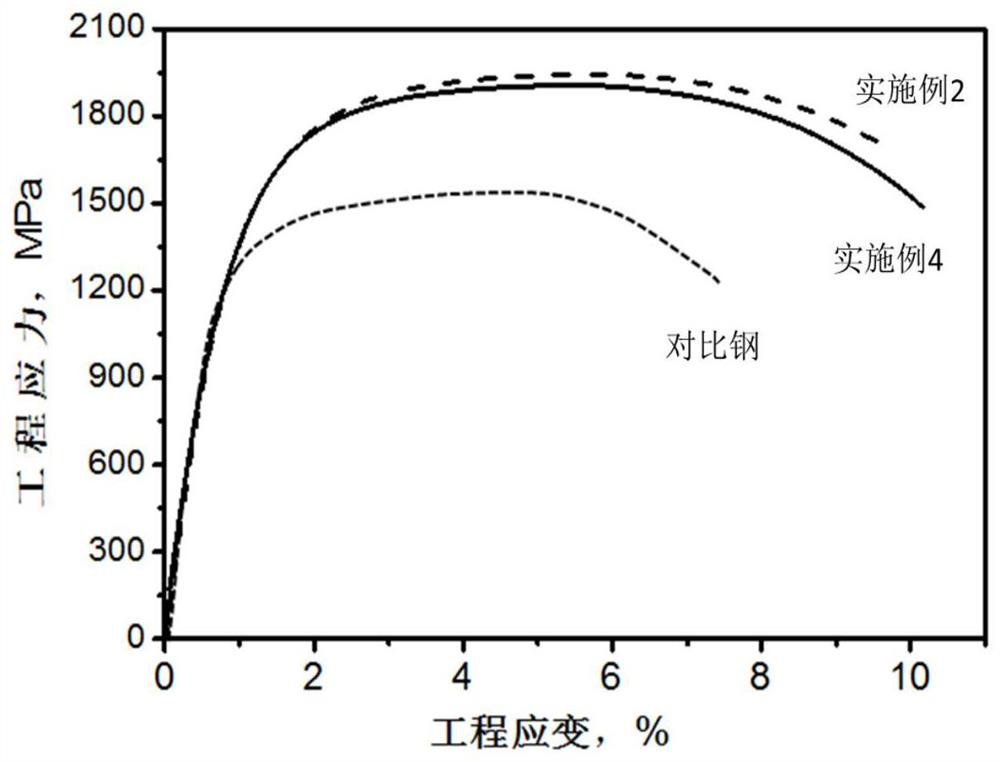
[0088] After the steel plate of embodiment 1-7 carries out heat treatment and hot stamping forming process according to table 2 process parameter, detect the yield strength, tensile strength and total elongation of implementation steel by standard tensile test, its result is as shown in table 3, and with 22MnB5 for comparison.
[00...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com