Method for separating cotton and micro-plastic in waste textiles and laundry wastewater and application
A technology for waste textiles and microplastics, applied in plastic recycling, recycling technology, mechanical material recycling, etc., can solve problems such as inability to separate and recycle different components, limit separation efficiency, and inability to retain microplastics with small particles. Achieve simple operation, improve separation effect, and enhance the effect of magnetic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Separation of paramagnetic cotton and polyester components in waste textiles using permanent magnets:
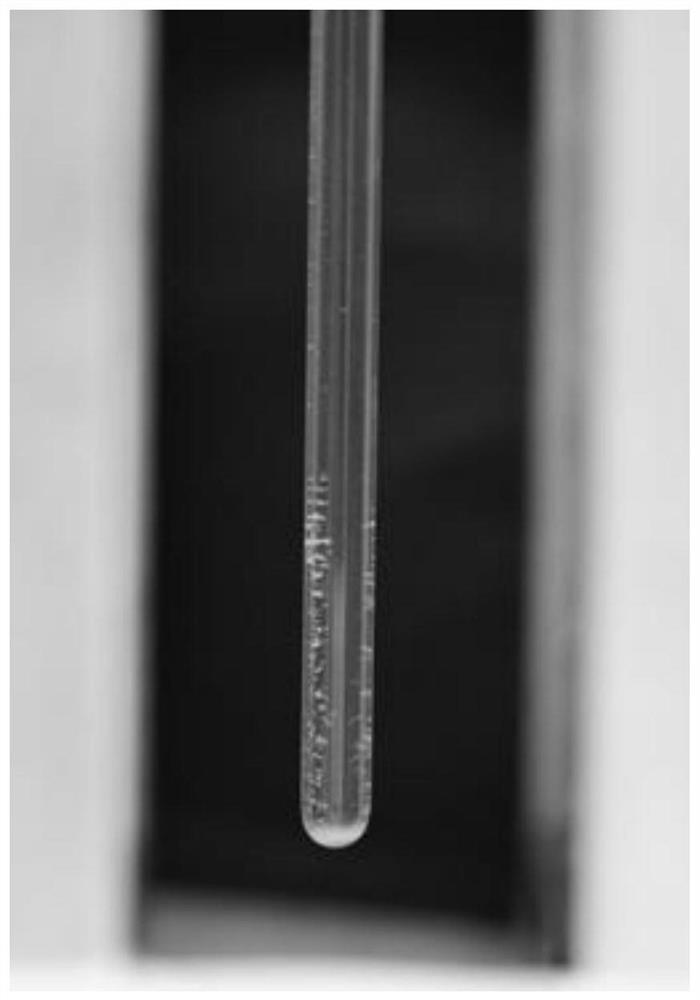
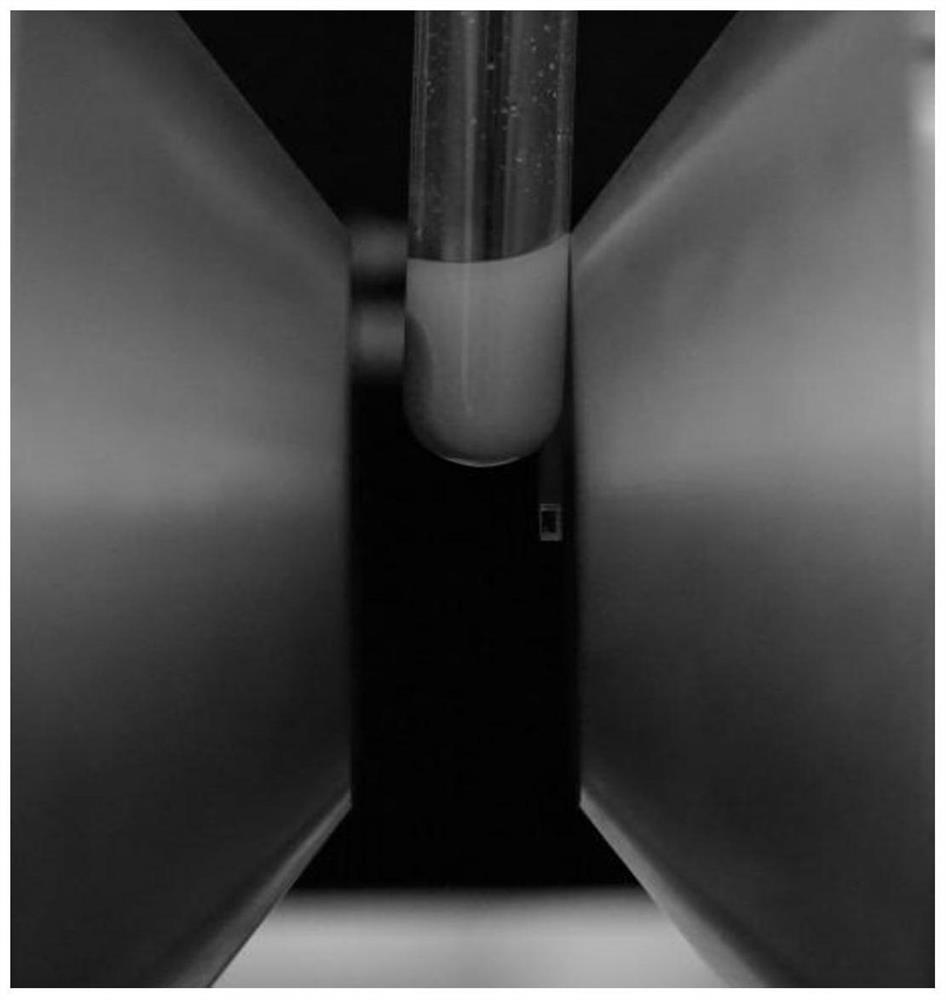
[0057] The waste textiles are pretreated and crushed into particles with a diameter less than 2 mm to obtain the pretreated waste textiles. Water is introduced into a separation pipeline with a diameter of 0.5 cm, and then the above-mentioned pretreated particles are placed in the pipeline. Put the separation pipeline vertically on the product of magnetic field strength and gradient (B▽B) Z 0~100T 2 In the magnetic field between / m.
[0058] It can be observed that the cotton component passes through the magnetic field, while the polyester component is captured by the magnetic field at a strength of 0.4-0.5T, realizing the separation of the two components, such as figure 1 shown. The infrared images of the two components after separation are shown in Figure 6 As shown, the two components were successfully separated.
Embodiment 2
[0060] Use electromagnet to separate paramagnetic cotton and polyester components in waste and old textiles. In this embodiment, the magnetic properties of paramagnetic cotton and polyester components in waste and old textiles are as follows: Figure 5 shown.
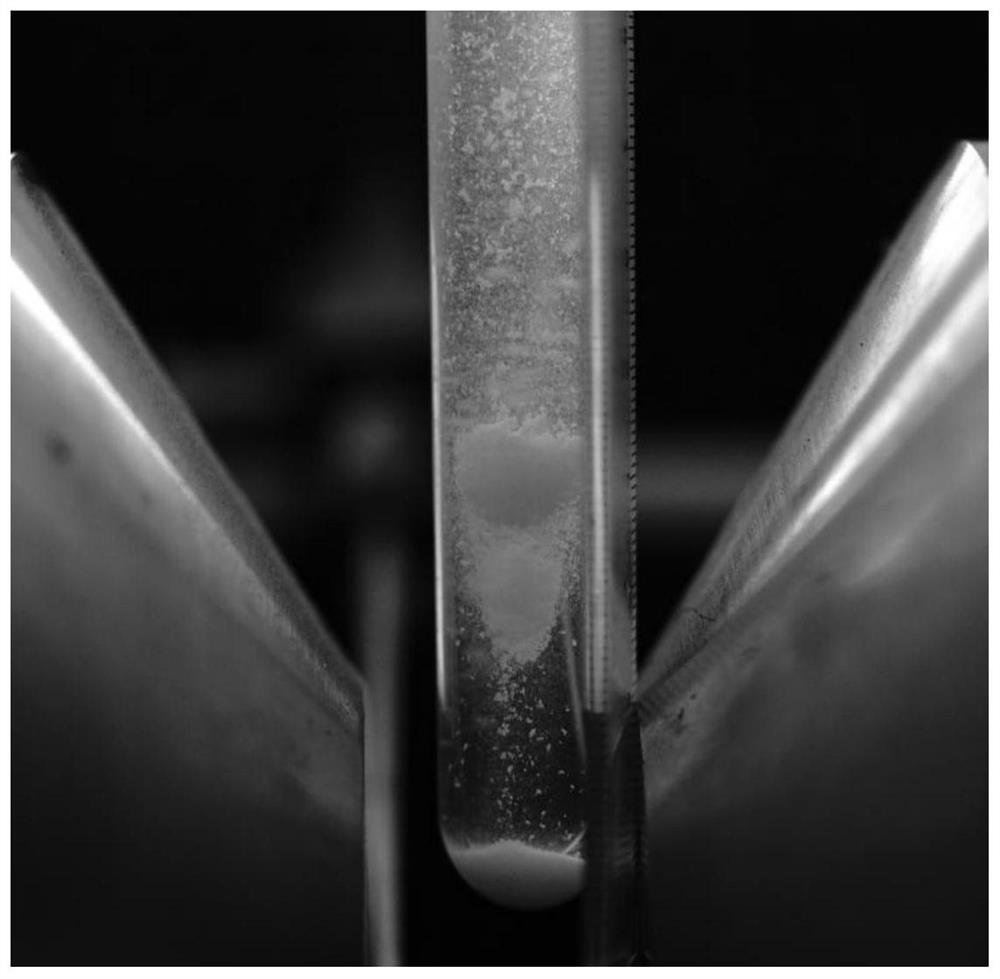
[0061] The waste textiles are pretreated and crushed into particles with a diameter less than 2 mm to obtain the pretreated waste textiles. Mix the pretreated waste textiles with water at a mass ratio of 1:10. The above mixture was placed in a separation line with a diameter of 1.5 cm. Put the separation pipeline vertically on the product of magnetic field strength and gradient (B▽B) Z 0~100T 2 In the magnetic field between / m.
[0062] It can be observed that the cotton component passes through the magnetic field, and the polyester component is captured by the magnetic field at a strength of 0.4-0.6T, realizing the separation of the two components, such as figure 2 shown. The XRD patterns of the two components a...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Separation of Antimagnetic Cotton and PET Polyester in Laundry Wastewater Using Electromagnet
[0065] Feed water and MnCl into a separation line with a diameter of 1.5 cm 2 The solution prepared according to the mass ratio of 8:1 has a solution density of 1.06g / ml. The laundry wastewater containing PET polyester and cotton particles with a particle size of less than 100 μm is passed into the pipeline to be separated. Among them, the density of PET polyester particles is 1.36g / cm 3 , the density of cotton particles is 1.40g / cm 3 .
[0066] The product of the magnetic field strength of the modulating electromagnet and the gradient (B▽B) Z at 0~100T 2 / m, place the separation line in a gradient magnetic field. It can be observed that the PET polyester component is captured by the magnetic field strength at 0.4-0.6T, and the cotton component passes through the magnetic field to realize the separation of the two components, as shown in the attached image 3 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com