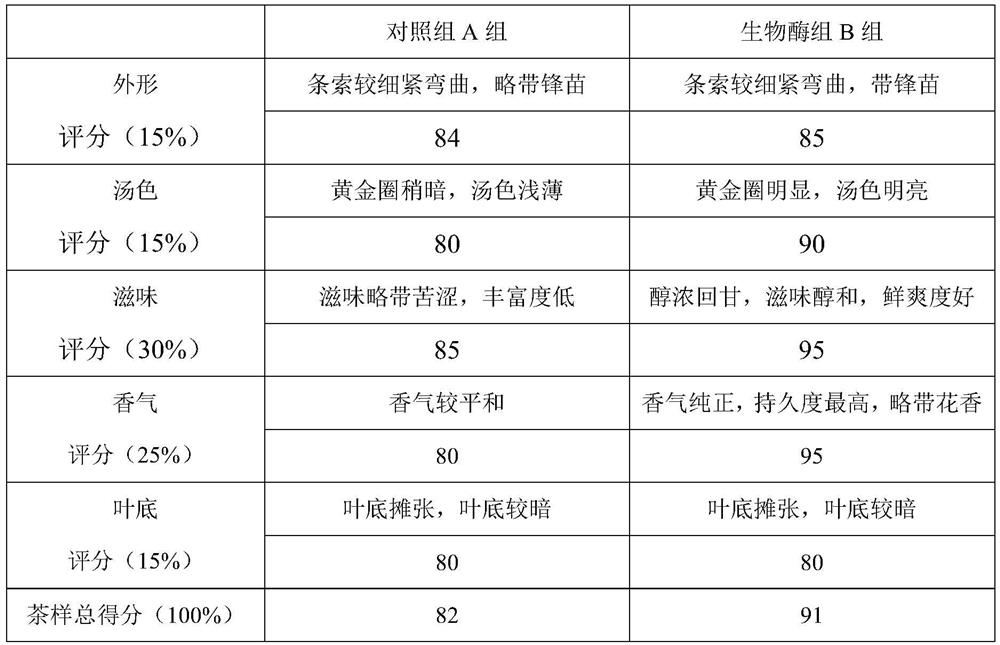
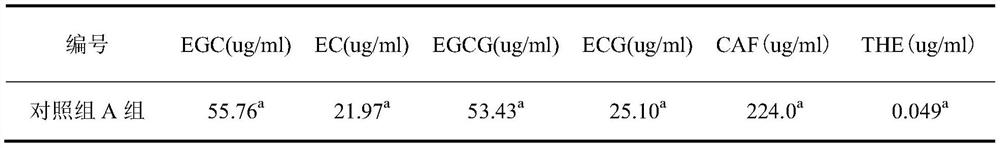
Method for fermenting tea leaves by applying tea-eating insect source biological enzyme
A biological enzyme and tea fermentation technology, applied in the field of life sciences, can solve the problems of unstable tea quality, low controllability, complicated operation, etc., and achieve the effect of improving tea quality, improving bitterness and astringency, and simple conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Preparation of tea-eating insect-derived biological enzymes. Take 200 tea inchworm larvae of the 4th instar in the container every day, and gently stimulate the mouth of the tea inchworm with one end of the capillary to make it naturally secrete saliva. Due to the capillary action of the capillary, the tension of the saliva liquid The saliva will be sucked into the capillary, and then the saliva will be injected into the centrifuge tube from the other end of the capillary with a needle tube, and then stored at low temperature. Finally, the saliva obtained was centrifuged to filter its debris, and the saliva was taken in a 20ml centrifuge tube, mixed and then centrifuged. The supernatant was obtained as the tea-eating insect-derived enzyme mother solution, and a total of nearly 100ml of the original enzyme solution was obtained.
[0024] (2) Dilute 20 ml of the tea-eating insect-derived biological enzyme mother solution taken in the step (1) to 40 ml, and store at low...
Embodiment 2
[0049] (1) Preparation of tea-eating insect-derived biological enzymes: Take 200 4-instar tea inchworm larvae in a container every day, gently stimulate the mouth of the tea inchworm with one end of the capillary to make it naturally secrete saliva, due to the capillary action of the capillary, the cohesion of the saliva liquid The saliva will be sucked into the capillary, and then the saliva will be injected into the centrifuge tube from the other end of the capillary with a needle tube, extracted continuously for 10-15 days, and stored at low temperature. Finally, the saliva obtained was centrifuged to filter its debris, and the saliva was collected in a 20ml centrifuge tube, mixed and centrifuged, and the supernatant was taken as the tea-eating insect-derived enzyme mother solution, and a total of nearly 100ml of the mother enzyme solution was obtained.
[0050] (2) Dilute 20 ml of the tea-eating insect-derived biological enzyme mother solution taken in the step (1) to 40 ml...
Embodiment 3
[0064] 1. Add exogenous food-grade tannase to process black tea
[0065] (1) Dilute 0.5 g mother liquor of tannase (500 U / g) to 40 ml with pure water, and store it at low temperature for later use.
[0066] (2) Specific steps of tea processing with tannase diluted enzyme solution
[0067] ①Fresh leaves: Fresh leaves in summer and autumn with 1-2 first buds or full leaves on the day of picking
[0068] ② Withering: Spread the fresh leaves evenly in the withering trough, and wither naturally for 21 hours to obtain withered leaves suitable for rolling.
[0069] ③ Kneading: Take 2kg of withered leaves and knead them, gently kneading for 20 minutes, and heavy kneading for 60 minutes;
[0070] ④ Spray tannase dilution: number the rolled leaves as group E, spray 40ml of diluted tannase enzyme solution (containing 0.5g of tannase stock solution) evenly on the rolled leaves with a watering can, and then ferment.
[0071] ⑤Fermentation: The conditions in the fermentation room are amb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com