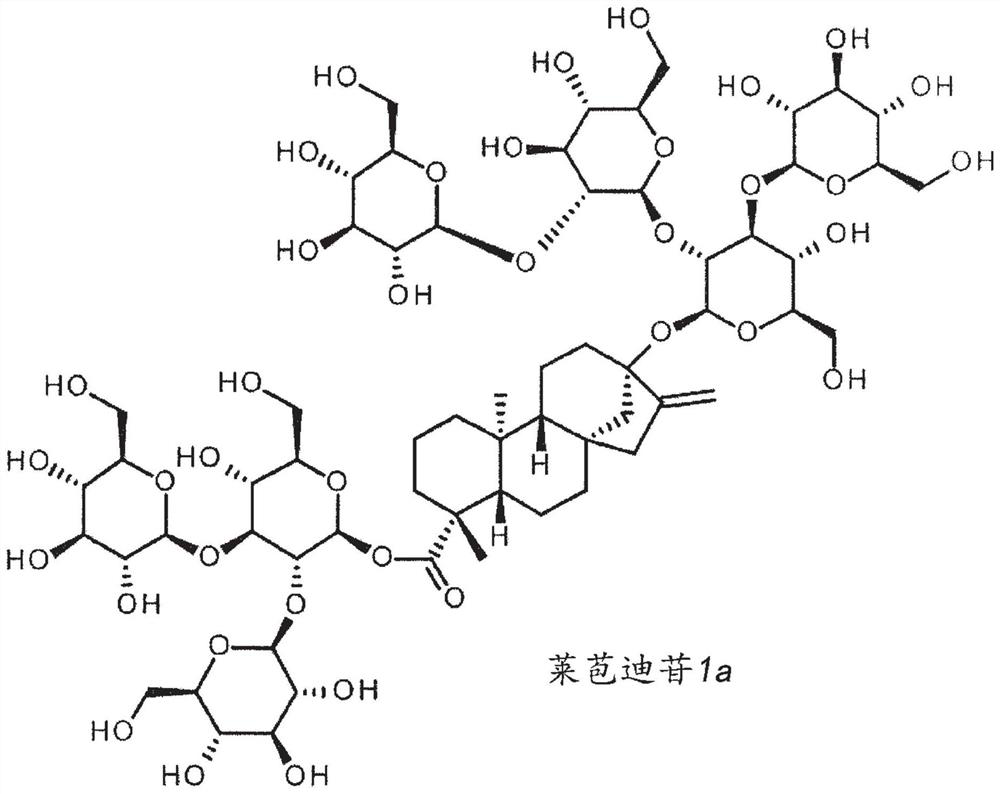
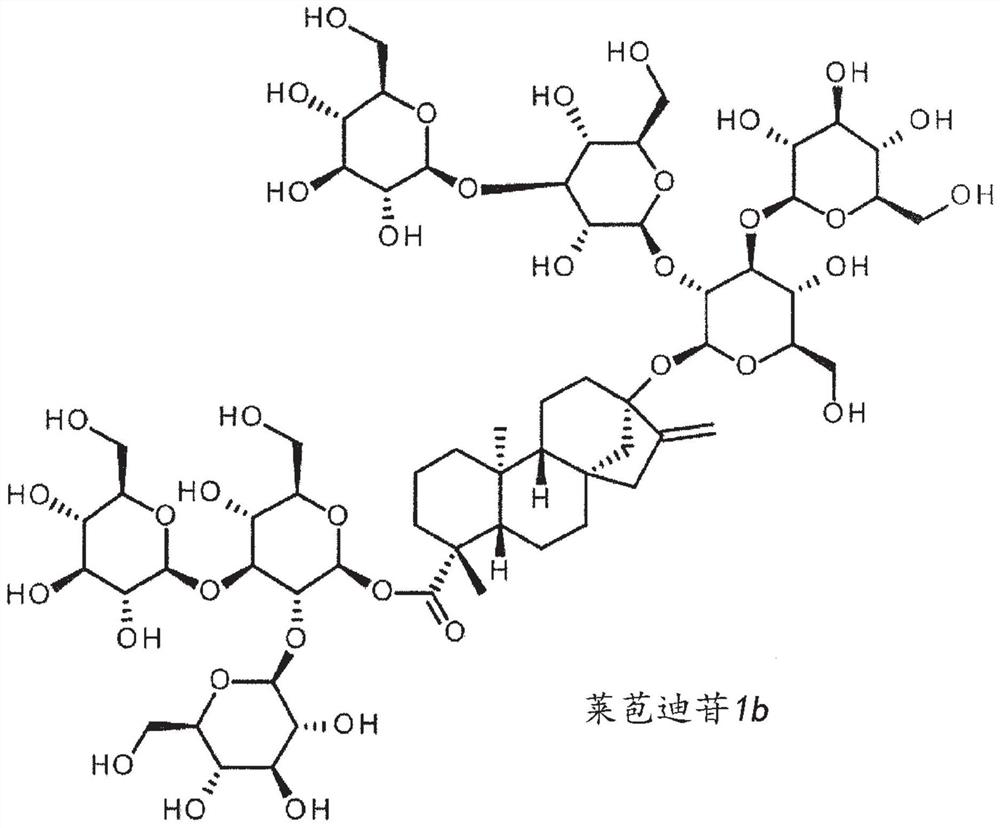
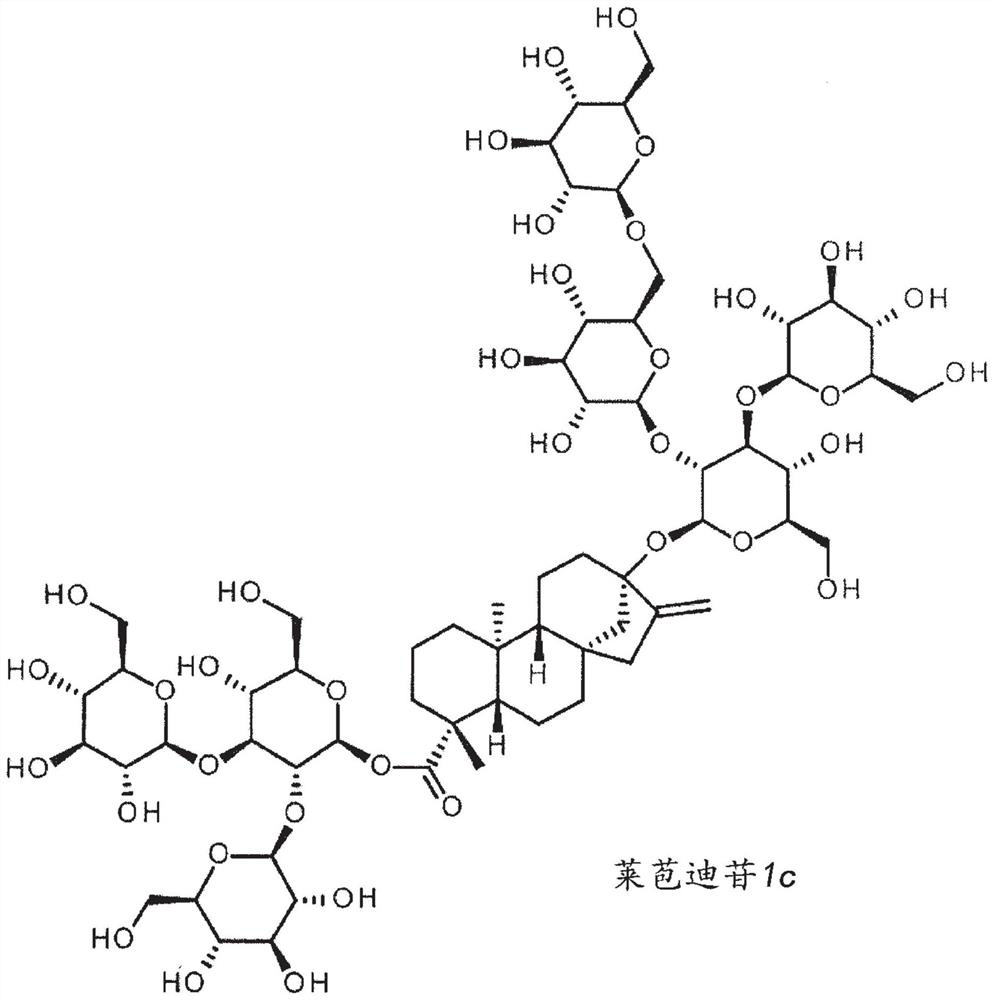
High-purity steviol glycosides
A technology of steviol glycosides and steviol, which is applied in the direction of sugar derivatives, sugar derivatives, glycosyltransferases, etc., and can solve problems such as not being suitable for commercial use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0484] Protein sequences of engineered enzymes for use in biocatalytic methods
[0485] SEQ ID 1 :
[0486] >SuSy_At, variant PM1-54-2-E05 (engineered sucrose synthase; source of WT gene: Arabidopsis)
[0487]
[0488] SEQ ID 2. :
[0489] > UGTS12, variant 0234 (engineered glucosyltransferase; source of WT gene: tomato)
[0490]
[0491] SEQ ID 3 :
[0492] > UGT76G1, variant 0042 (engineered glucosyltransferase; source of WT gene: Stevia)
[0493]
Embodiment 2
[0495] Expression and formulation of the SuSy_At variant of SEQ ID 1
[0496] The gene encoding the SuSy_At variant of SEQ ID 1 (Example 1) was cloned into the expression vector pLE1A17 (derivative of pRSF-1b, Novagen). The resulting plasmid was used to transform E. coli BL21(DE3) cells.
[0497] Cells were cultured at 37°C in ZYM505 medium (F. William Studier, "Protein Expression and Purification", Vol. 41, 2005, pp. 207-234) supplemented with kanamycin (50 mg / l). Gene expression was induced by IPTG (0.2 mM) in log phase and performed at 30° C. and 200 rpm for 16-18 hours.
[0498] by centrifugation ( 20 min, 4°C) to harvest the cells and wash with cell lysis buffer (100mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; 2mM MgCl 2 , DNA nuclease 20U / mL, lysozyme 0.5mg / mL) resuspended to an optical density of 200 (measured at 600nm (OD 600 )). Cells were then disrupted by sonication, and crude extracts were separated from cell debris by centrifugation (18000 xg, 40 min, 4°C). Sterilize the superna...
Embodiment 3
[0501] Expression and formulation of the UGTS12 variant of SEQ ID 2
[0502] The gene encoding the UGTS12 variant of SEQ ID 2 (Example 1) was cloned into the expression vector pLE1A17 (derivative of pRSF-1b, Novagen). The resulting plasmid was used to transform E. coli BL21(DE3) cells.
[0503] Cells were cultured at 37°C in ZYM505 medium (F. William Studier, "Protein Expression and Purification", Vol. 41, 2005, pp. 207-234) supplemented with kanamycin (50 mg / l). Gene expression was induced by IPTG (0.1 mM) in log phase and carried out at 30°C and 200 rpm for 16-18 hours.
[0504] Cells were harvested by centrifugation (3220×g, 20 min, 4°C) and washed with cell lysis buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0; 2 mM MgCl 2 , DNA nuclease 20U / mL, lysozyme 0.5mg / mL) resuspended to an optical density of 200 (measured at 600nm (OD 600 )). Cells were then disrupted by sonication, and crude extracts were separated from cell debris by centrifugation (18000 xg, 40 min, 4°C). Sterilize the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com