Compound polymerization inhibitor and application thereof in styrene rectification process
A technology of polymerization inhibitor and styrene, which is applied in the field of styrene composite polymerization inhibitor and its preparation, can solve problems such as the relationship is not clearly stated, and achieve the effects of reducing viscosity, stabilizing the polymerization inhibition effect, and prolonging the induction period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-9
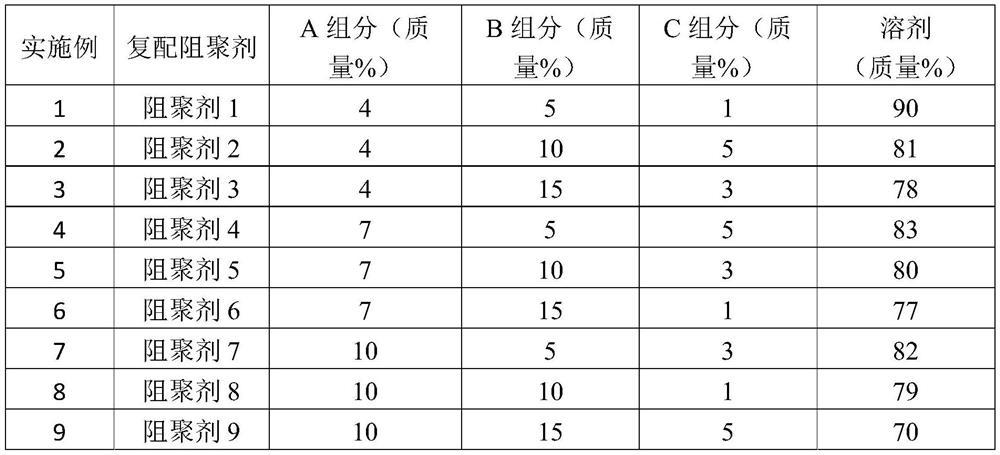
[0043] As shown in the following table 1, a series of composite polymerization inhibitors are obtained by compounding component A, component B, component C and high boiling point solvent; wherein, component A is 4-hydroxyl-2,2,6,6-tetra Methyl piperidine nitroxide radical, component B is 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-benzylidene-cyclohexa-2,5-dienone, component C is diisopropylhydroxylamine, high The boiling point solvent is glycerol monomethyl ether.
[0044] Stir each component evenly at 30-35°C to obtain a clear red liquid, which is the compounded polymerization inhibitor.
[0045] Table 1 Composite formula table of polymerization inhibitor
[0046]
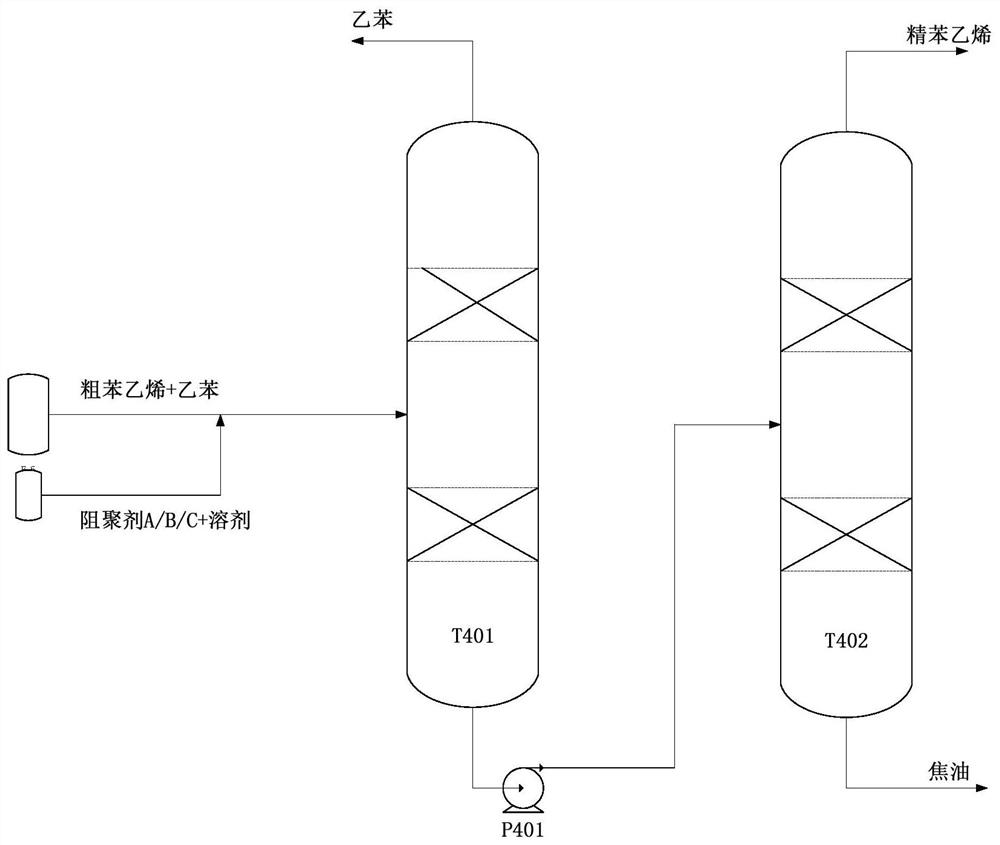
[0047] The obtained compounded polymerization inhibitor is added to styrene at a concentration of 600 ppm based on the mass of styrene, and is used for double-column continuous rectification of styrene. Distilled in figure 1 shown in the styrene distillation unit, in figure 1Among them, T401 is a styrene-ethylbenzene separation t...
Embodiment 10-17
[0071] According to the ratio of polymerization inhibitor 7, the compound polymerization inhibitor was prepared, that is, 10% of component A, 5% of component B, 3% of component C, and 82% of solvent. The results are shown in Table 4. The amount of polymerization inhibitor is calculated based on the mass of styrene.
[0072] Table 4 The influence of polymerization inhibitor dosage on the polymerization inhibition effect
[0073] experiment number Inhibitor dosage (ppm) Polymer content (ppm) Tar viscosity (cp, 150°C) Example 10 200 1450 22 Example 11 400 900 19 Example 12 600 700 17 Example 13 800 500 15 Example 14 1000 450 13 Example 15 1200 430 12 Example 16 1500 420 11 Example 17 2000 400 10
[0074] Conclusion: The greater the amount of polymerization inhibitor used, the better the effect of polymerization inhibition. The process requires that the polymer content should not exceed 500ppm, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com