Transmembrane drug delivery method based on bio-enzyme driven micron pump
A biological enzyme and drug technology, applied in the field of drug research, can solve problems such as barriers to transmembrane delivery, affect biomedical efficacy, and low effective cell release rate, and achieve the effect of promoting efficient entry and efficient transmembrane delivery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] A transmembrane drug delivery method based on a bioenzyme-driven micropump, comprising:
[0030] (1) Preparation of biomimetic self-driven micropumps: select silica microtubes, activate the microtubes with glutaraldehyde and modify the surface of the microtubes with urease to prepare microenzyme pumps.
[0031] Specifically: using polycarbonate film as a template, using ultrapure water, APTES, TEOA and TEOS to prepare silica microtubes with a diameter of 1 μm and a length of 20 μm. Add 60mg TEOA to 24mL deionized water, stir magnetically at 500rpm; add 30μL APTES to the system, stir at 500rpm for 30min, and raise the temperature of the system to 80°C; finally add 240μLTEOS and polycarbonate membrane to the above system, at 200rpm , stirred at 80°C for 4 hours. After the reaction is over, use alumina particles to polish the silica on the surface of the membrane. After the polishing is complete, rinse the alumina particles with ultrapure water; use DMF to dissolve the po...
Embodiment 2
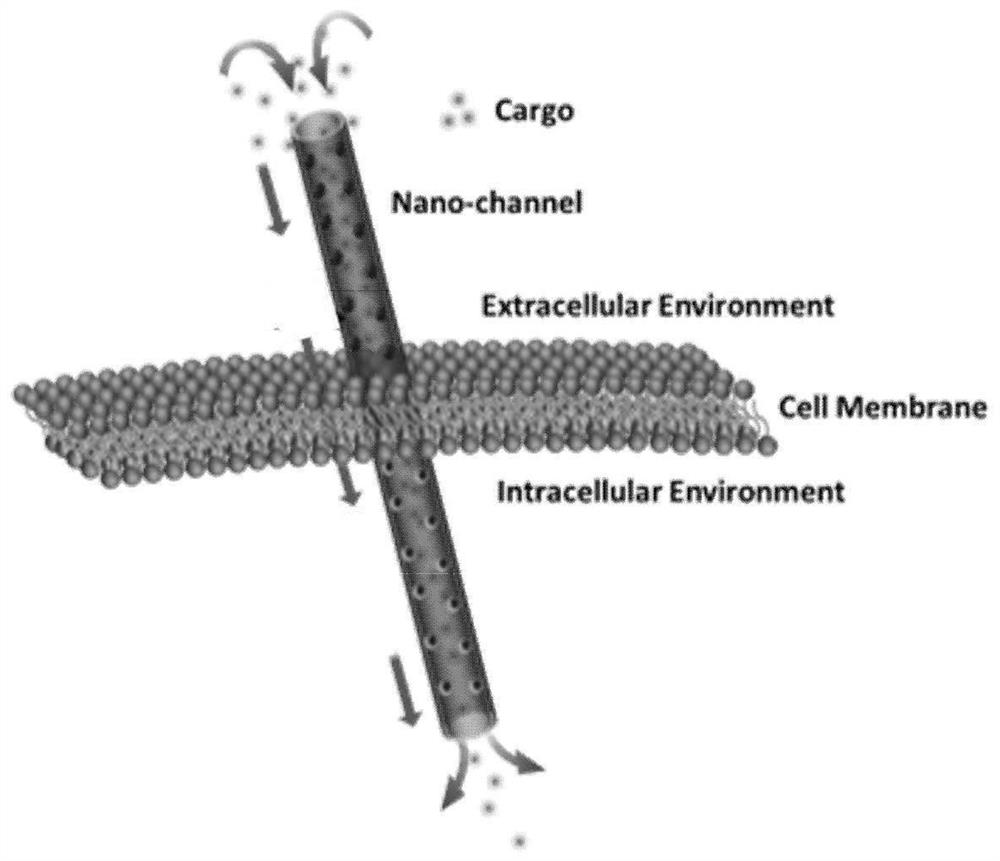
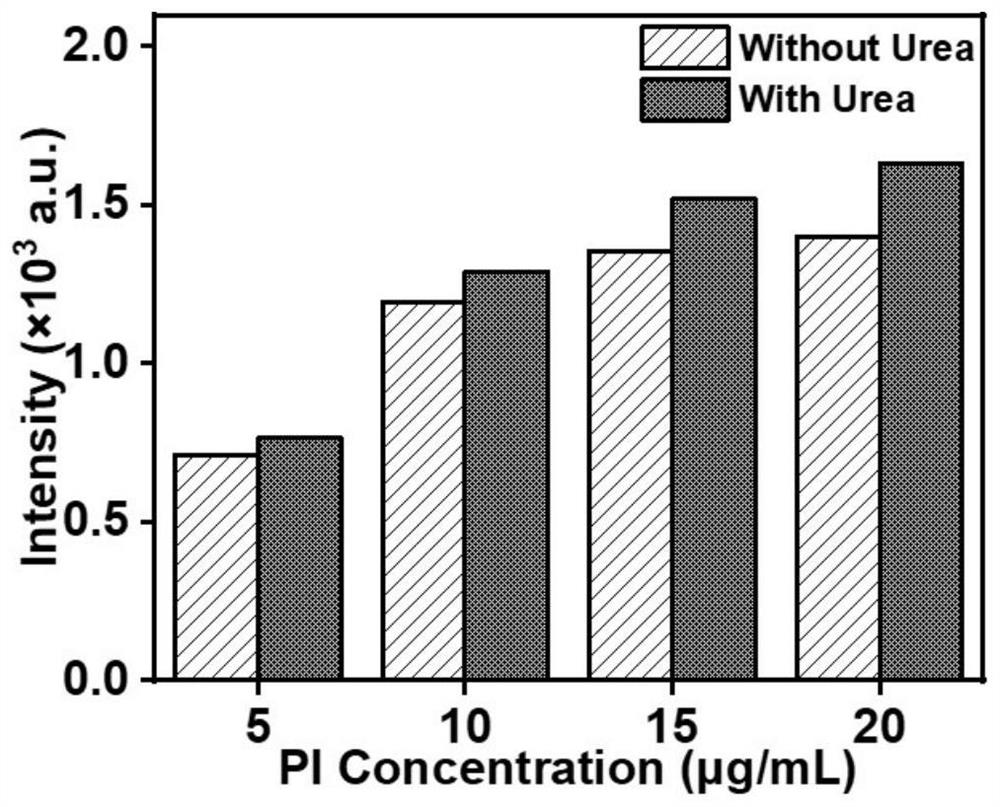
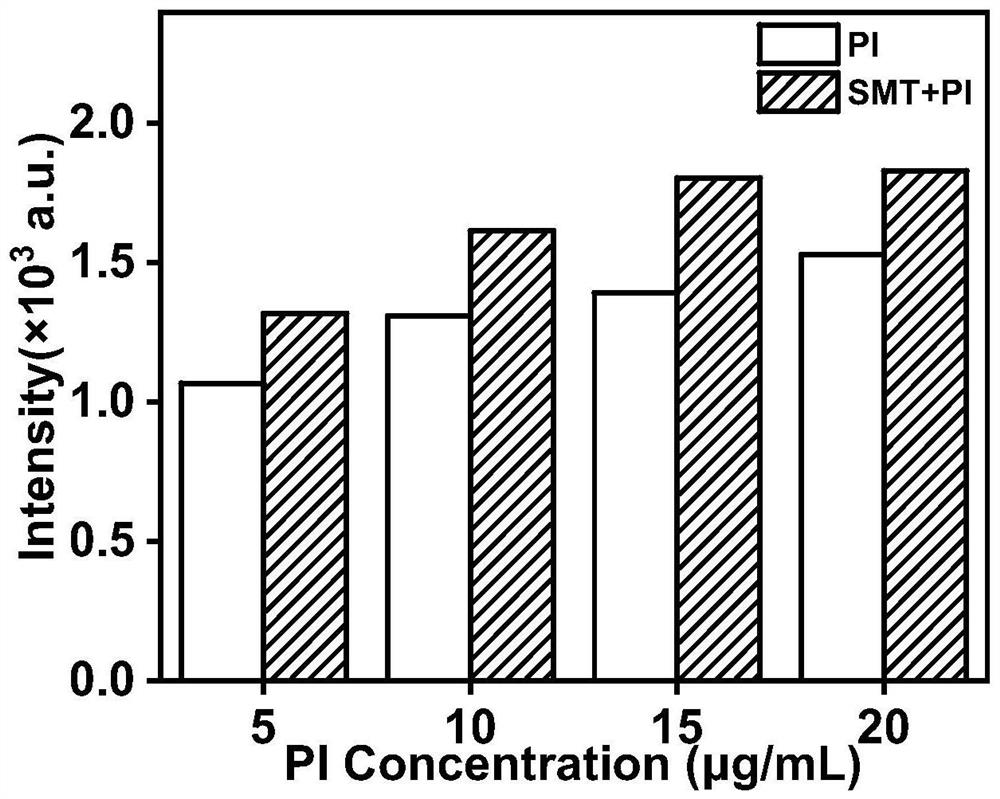
[0036]Using a transmembrane drug delivery method based on a biological enzyme-driven micropump in Example 1, after successfully establishing the artificial transmembrane channel of the biomimetic micropump, by comparing the transmembrane drug propidium iodide (PI) with / without urea Membrane delivery, to verify the auxiliary effect of the micron enzyme pump on drug delivery. Specific as figure 2 As shown, the present invention promotes the efficient entry of extracellular substances into cells with the assistance of the micro-nano flow field generated by the catalyzed decomposition of urea by urease.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com