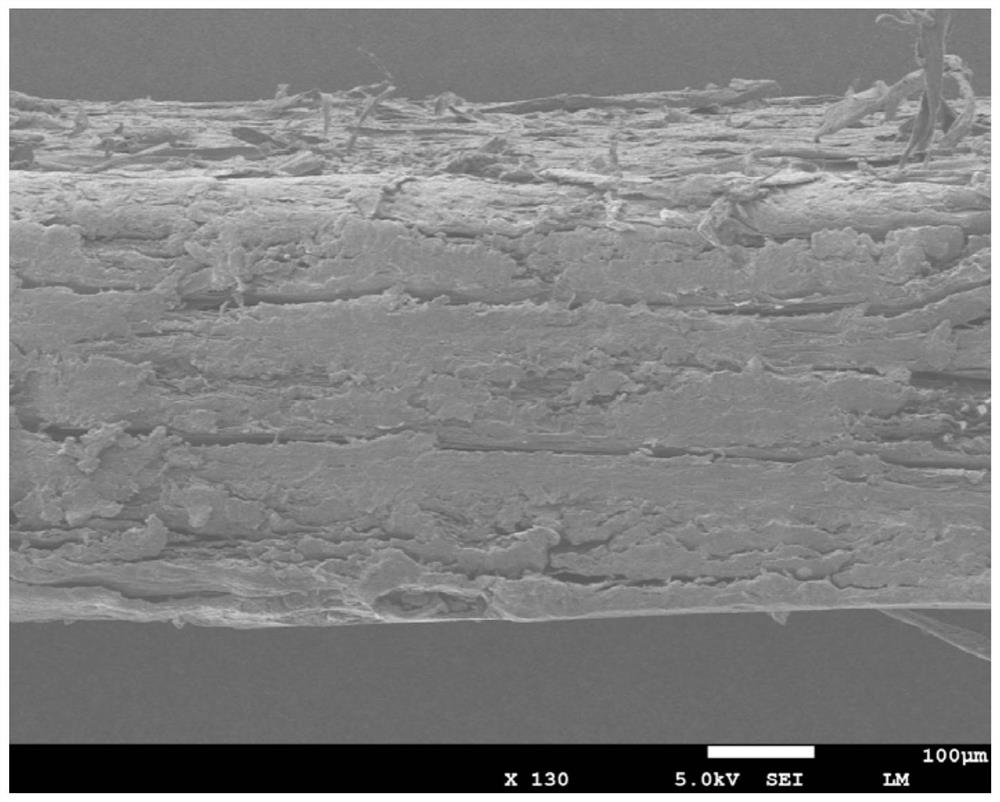
Ultrahigh-content cellulose reinforced polymer composite material with shell-like structure and preparation method thereof
A composite material and polymer technology, used in chemical instruments and methods, wood impregnation, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as uniform dispersion of ultra-high content cellulose, and achieve the effects of improving mechanical strength, reducing usage, and high toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] This example provides a method for preparing a super-high-content cellulose-reinforced polymer composite material imitating a shell structure, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0023] Step 1, delignification treatment:
[0024] Place a balsa wood veneer with a thickness of 1mm in a sodium chlorite solution with a concentration of 1wt.%. The sodium chlorite solution is adjusted to a pH value of 4.6 by glacial acetic acid, soaked at 80°C for 12h, and after taking it out Washing with distilled water to complete the delignification treatment;
[0025] Step 2, TEMPO oxidation treatment:
[0026] Prepare 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer, TEMPO, NaClO according to the volume to mass ratio of 100ml:0.016g:1.13g:10mL 2 and 0.1mol / L NaClO phosphate buffer; TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine oxide) and NaClO 2 Add 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer solution, then add 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer solution, mix well to obtain 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer solution; add the sample obtained in s...
Embodiment 2
[0037] This example provides a method for preparing a super-high-content cellulose-reinforced polymer composite material imitating a shell structure, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0038] Step 1, delignification treatment:
[0039] Place a poplar veneer with a thickness of 0.2mm in a sodium chlorite solution with a concentration of 1wt.%. The sodium chlorite solution is adjusted to a pH value of 4.6 by glacial acetic acid. Washing with distilled water to complete the delignification treatment;
[0040] Step 2, TEMPO oxidation treatment:
[0041] Prepare 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer, TEMPO, NaClO according to the volume to mass ratio of 100ml:0.016g:1.13g:10mL 2 and 0.1mol / L NaClO phosphate buffer; TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine oxide) and NaClO 2 Add 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer solution, then add 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer solution, mix well to obtain 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer solution; add the sample obtained in step 1 into the TEMPO oxidation treatment solution ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] This example provides a method for preparing a super-high-content cellulose-reinforced polymer composite material imitating a shell structure, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0052] Step 1, delignification treatment:
[0053] Place a eucalyptus veneer with a thickness of 0.5mm in a sodium chlorite solution with a concentration of 2wt.%. The sodium chlorite solution is adjusted to a pH value of 4.6 by glacial acetic acid. Washing with distilled water to complete the delignification treatment;
[0054] Step 2, TEMPO oxidation treatment:
[0055] Prepare 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer, TEMPO, NaClO according to the volume to mass ratio of 100ml:0.016g:1.13g:10mL 2 and 0.1mol / L NaClO phosphate buffer; TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine oxide) and NaClO 2 Add 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer solution, then add 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer solution, mix well to obtain 0.1mol / L phosphate buffer solution; add the sample obtained in step 1 into the TEMPO oxidation treatment solut...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com