In-situ online characterization method for structural characteristics of micro-fine particle iron mineral aggregate
A technology for structural characteristics and iron minerals, applied in the field of in-situ online characterization of the structural characteristics of fine-grained iron mineral aggregates, can solve the problems that the structural characteristics of iron mineral aggregates cannot be observed and controlled in situ in real time, and achieve the acquisition speed Fast, high-accuracy results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
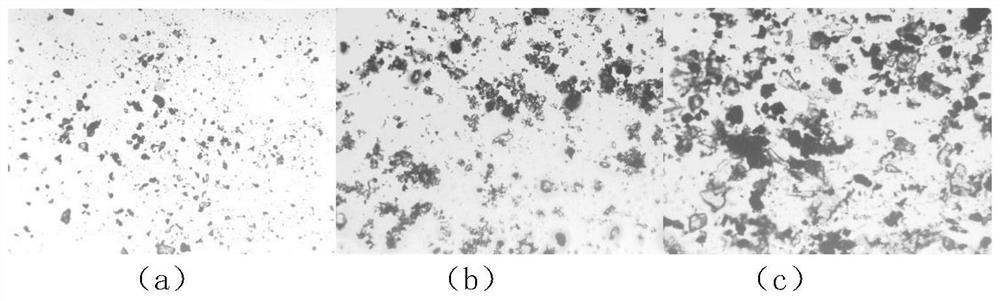
[0019] The fine-grained specularite samples in Gansu area were taken for stirring and slurry mixing. The particle size of the ore samples was -0.038mm, accounting for 87.68%, the average particle size was 12.38μm, and the TFe grade in the ore samples was 30.54%. SiO 2 The content is 58.61%, and the content of other elements is 10.85%, which is separated by agglomeration magnetic separation process. The specific implementation method of the in-situ online characterization method for the structural characteristics of fine-grained iron mineral aggregates is as follows:
[0020] (1) Add the ore sample into the stirring tank to adjust the pH value of the ore pulp to 9.0, and the stirring speed is 750r / min. Add 150g / t of modified tapioca starch according to the mass of the ore sample to agglomerate and adjust the pulp. After stirring for 3 minutes, a small part of the ore pulp Use a centrifugal pump to pour into a transparent mixing tank made of resin material for stirring to preven...
Embodiment 2
[0025] According to the detection result of the structure characteristics of the fine-grained iron mineral aggregates in Example 1, further adjust the process parameters: increase the dosage of 100g / t of medicament, improve the stirring speed to 800r / min, the image collected by the high-speed camera under this parameter is as follows figure 1 (c) shown. The particle size composition of the mineral particles is as follows: the content of -0.038mm is reduced to 40.23%, and the average particle size of the particles is 25.26μm. According to the image analysis results, the average projected area of iron mineral aggregates is 623.56 μm 2 , the fractal dimension is 1.95, and the degree of compactness is higher than that of Example 1. It can be speculated that better sorting indicators can be obtained under such process parameters.
[0026] The iron grade of the finally obtained magnetic separation concentrate is 46.53%, and the iron recovery rate is 80.56%.
Embodiment 4
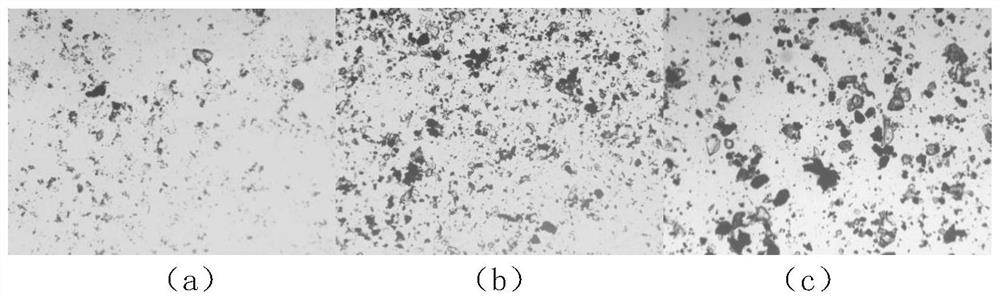
[0031] The fine-grained carbonate-containing magnetic red iron ore sample in Liaoning area was taken for stirring and slurry mixing. The particle size of the ore sample was -0.038mm, accounting for 89.63%, the average particle size was 15.34μm, and the TFe grade in the ore sample was 32.14%. , the content of SiO2 is 63.78%, and the content of other elements is 4.08%, which is selected by agglomeration magnetic separation process. The specific implementation method of the in-situ online characterization method for the structural characteristics of fine-grained iron mineral aggregates is as follows:
[0032] (1) Add the ore sample into the stirring tank to adjust the pH value of the ore pulp to 10.0, and the stirring speed is 900r / min. Add 200g / t of modified tapioca starch according to the mass of the ore sample to agglomerate and adjust the pulp. After stirring for 3 minutes, a small part of the ore pulp Use a centrifugal pump to pump into a transparent mixing tank made of resi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com