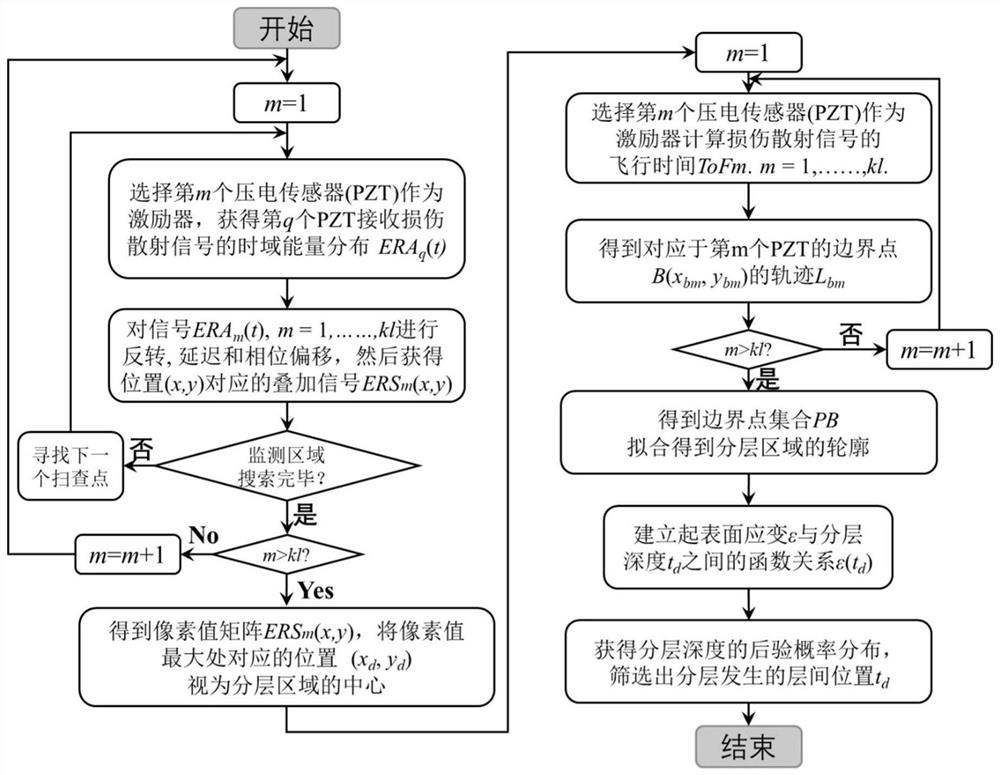
Composite material layered damage identification method based on contour and depth sequence identification
A composite material and identification method technology, which is applied in the field of quantitative identification of multiple types of damage to composite material structures, can solve problems such as sensor sparsity and identification precision, to ensure accuracy and practicability, reduce resource consumption, and ensure The effect of recognition accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
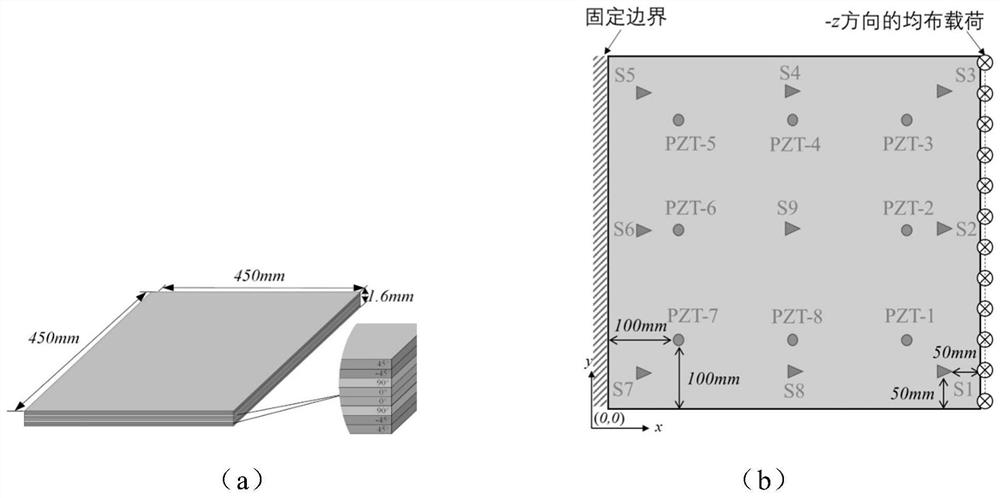
[0059] In order to understand more fully the characteristics of the invention and its applicability to engineering practice, the present invention aims at such as figure 2 Composite laminates containing delamination are shown to validate the method.
[0060] The geometric information of the structure such as figure 2 (a) shown. figure 2 (b) The sensor layout, loading and boundary setup are given. Among these sensors, 8 piezoelectric transducers (PZT) are used to excite and receive Lamb waves in the plate, and 9 strain measuring points S1-S9 are arranged on the lower surface of the composite laminate to measure the structural Strain in the x-direction when subjected to a load opposite to the z-direction. The material properties are listed in Table 1.
[0061] Table 1
[0062]
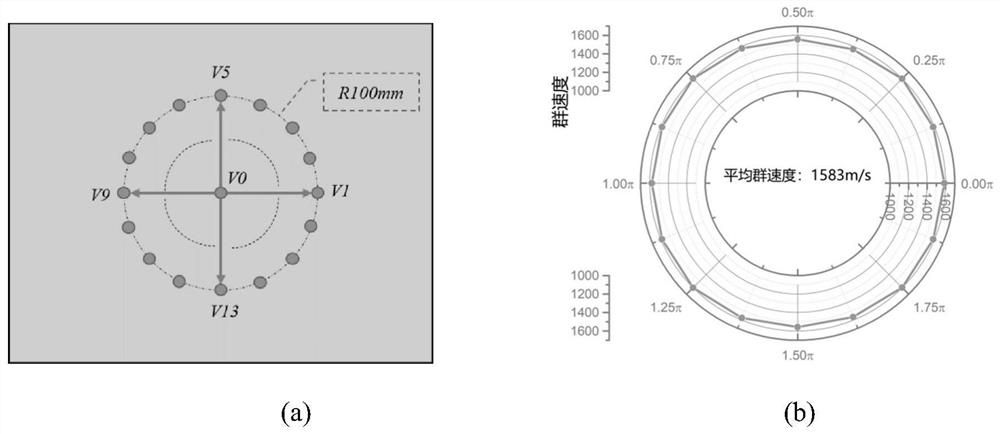
[0063] In order to fully consider the anisotropy of the composite material, an array consisting of 17 PZT image 3(a) The circular PZT array shown. Among them, V0 is used to excite Lamb wave...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com