Method for catalytically depolymerizing polylactic acid and analogues thereof by magnesium catalytic system
A catalytic system and catalytic depolymerization technology, which is applied in the field of polyester depolymerization, can solve problems such as increased production costs and metal tin toxicity, and achieve the effects of economical production costs, fewer synthesis steps, and good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Depolymerization of PLA
[0030]
[0031] The experimental process includes the following steps:
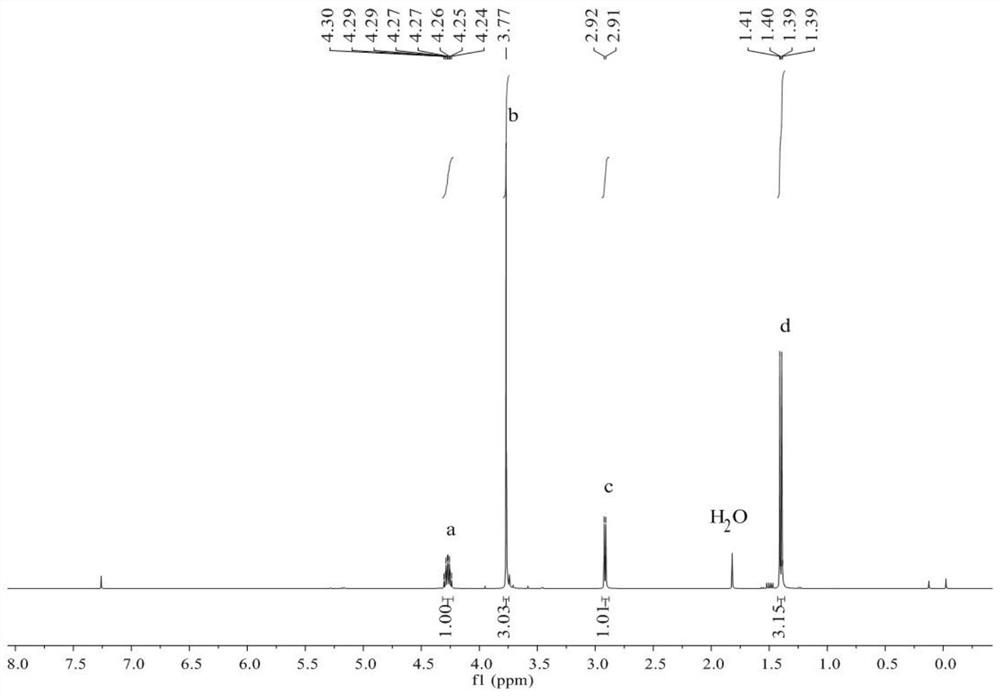
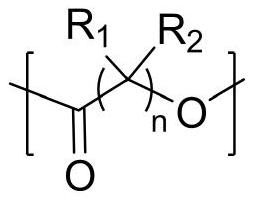
[0032] Take a 5mL Schlenk bottle, roast it and replace the argon, then add 288mg polylactic acid (M n =26000g / mol, PDI=1.09), then add 3.8mg of Mg[N(SiMe 3 ) 2 ] 2 Catalyst, outside the glove box, add 2mL of methanol and 2mL of dichloromethane, and stir at room temperature for reaction. After reacting for 1.5 hours, the reaction system was detected by NMR, and the conversion rate of the polymer was 99%, and the obtained alcoholysis product was methyl lactate.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Depolymerization of PLA
[0035]
[0036] The experimental process includes the following steps:
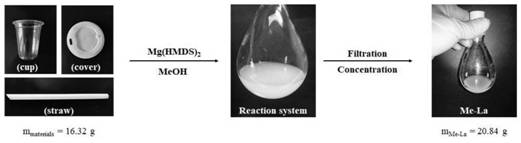
[0037] Take a 500mL three-neck flask, roast it and replace the argon gas, add 16.32g of commercial polylactic acid product (manufacturer: Yiwu Shuangtong Commodity Co., Ltd.; diameter: 12mm) into the glove box, and then add 1.15g of polylactic acid Mg[N(SiMe 3 ) 2 ] 2 Catalyst, outside the glove box, add 113mL of methanol and 113mL of dichloromethane, stir and react at room temperature. After reacting for 2 hours, the NMR detection of the reaction system showed that the conversion rate of the polymer was 99%, and the obtained alcoholysis product was methyl lactate. Remaining methanol was removed by distillation to obtain 20.84 g of methyl lactate with a yield of 80%.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Depolymerization of PLA
[0040]
[0041] The experimental process includes the following steps:
[0042] Take a 5mL Schlenk bottle, roast it and replace the argon, then add 144mg polylactic acid (M n =11300g / mol, PDI=1.17), then add 7.0mg of Mg[N(SiMe 3 ) 2 ] 2 Catalyst, outside the glove box, add 1mL of methanol, and stir at room temperature for reaction. After reacting for 2 hours, the NMR detection of the reaction system showed that the conversion rate of the polymer was 99%, and the obtained alcoholysis product was methyl lactate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com