Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with broad-spectrum antagonism, microbial agent and application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens
A technology of amylolytic spores and microbial agents, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of few resources of excellent strains, narrow antibacterial spectrum, and limited application range, so as to reduce the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers, increase the biomass of tobacco, and widely The effect of applying the foreground
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1 Identification of antagonistic bacteria F012 strain
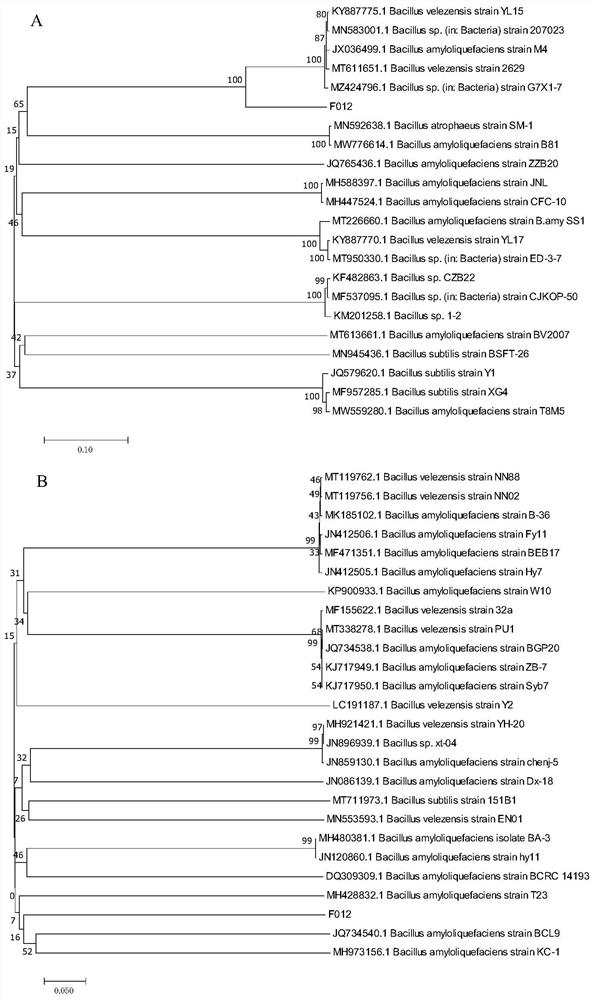
[0047] A broad-spectrum antagonistic strain F012 was isolated from the root soil of healthy plants in the tomato gray mold disease-affected area of Qingdao City, Shandong Province in the early stage of the laboratory, and was kept in the laboratory. The morphological identification, physiological and biochemical identification and molecular biological identification of the antagonistic bacteria F012 were confirmed to be Bacillus amyloliquefaciens.
[0048] 1. Morphological Identification
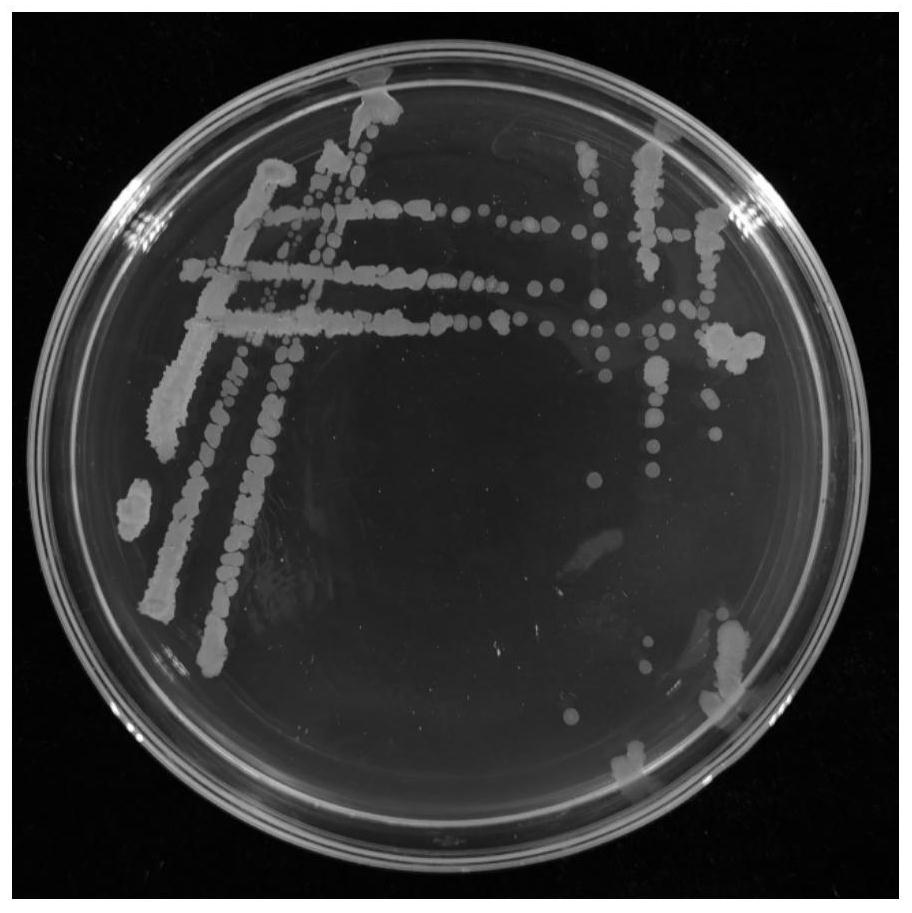
[0049] like figure 1 As shown, the colony of the antagonistic bacteria F012 on the LB solid medium is irregular and circular as a whole; the initial stage is colorless and transparent, the surface is smooth, moist, sticky, and the edges are neat; There are folds on the edge, and the diameter is 2-3mm.
[0050] 2. Physiological and biochemical identification
Embodiment 2
[0066] The functional qualitative identification of embodiment 2 antagonistic bacteria F012
[0067] 1. Experimental method:
[0068] Before the experiment in this example, the antagonistic bacteria F012 was cultured in shake flasks, activated and multiplied, and NA solid medium was prepared, and a plate for sterilized bacteria was prepared. After the culture medium was sterilized, wait until the temperature dropped to about 55 degrees Celsius and add 1ml of activated bacterium. The antagonistic bacteria F012 was poured onto the plate, and after solidification, it was placed in an incubator at 28°C for 24 hours. Ralstia solanacearum is carried out as above-mentioned steps and is poured out plate, after coagulation, to culture medium (the mixture of culture medium and bacterium) that is full of antagonistic bacteria F012 and the non-cultured R. solanacearum with punching device The bacteria-carrying medium of Yeerichia was punched separately. Pick out the bacterium cake (diam...
Embodiment 3
[0074] The antagonism of embodiment 3 antagonistic bacteria F012 to multiple strains of pathogenic fungi
[0075] 1. Experimental method:
[0076] Put the sterilized PDA medium in shift. After solidification, place two Oxford cups on both sides of the plate at a distance of 2 cm from the center of the plate, and then introduce the PDA medium again. After solidification, remove the Oxford cups and inoculate the pathogenic fungi in the center of the plate. Add 2 μL of antagonistic bacteria F012 to the wells on both sides. The control plate was not added with bacterial solution. After culturing at 28 degrees for 7 days, the diameter of the inhibition zone was measured, and the antibacterial rate of the antagonistic bacteria F012 against various pathogenic bacteria was calculated according to the following formula.
[0077] Bacteriostatic rate calculation formula: bacteriostatic rate=[(control colony diameter-bacteria cake diameter)-(treatment colony diameter-bacteria cake diame...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com