Intestinal biomarkers for gut health in domesticated birds
A technology for intestinal health and intestinal tract, applied in biological testing, biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0055] Example 1: Determination
[0056]In the following examples, the various assays described below were used for ease of reading. Any deviations from the protocol provided below are indicated in the relevant sections. In these experiments, a spectrophotometer is used to measure the absorbance of the product formed after the reaction is complete.
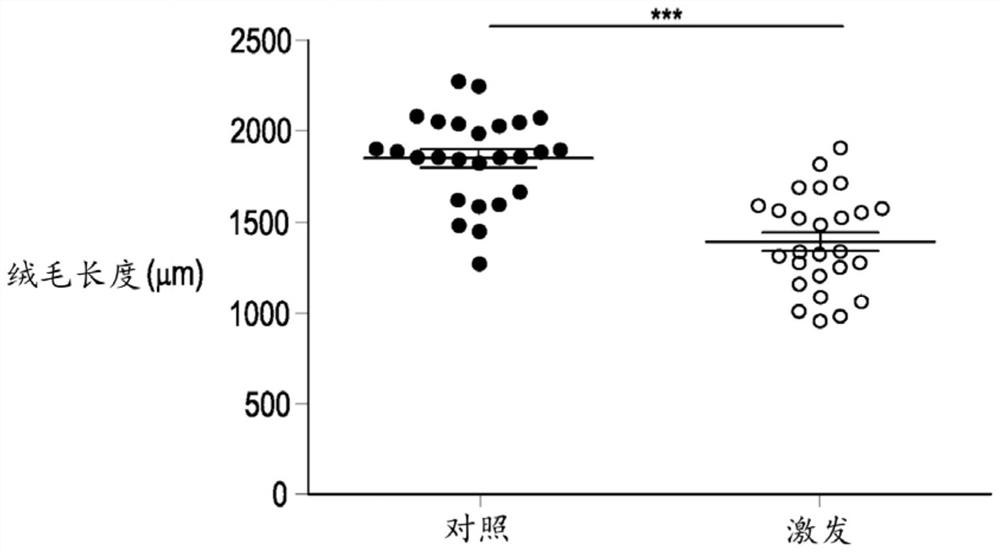
[0057] Histology: Duodenal rings were fixed in 4% formaldehyde for 24 h, dehydrated in xylene and embedded in paraffin. Sections of 4 μm were cut using a microtome (Microme HM360, Thermo Scientific) and processed as described by De Maesschalck et al. (2015). The villus length and occult length in the duodenum were determined by randomly measuring twelve villi / gut segments using a standard light microscope (Leica DM LB2Digita) and the computer-based image analysis program LAS V4.1 (Leica Application Suite V4, Germany). nest depth. The ratio of villi to crypts was then calculated. Antigen retrieval was performed on 4 μm duode...
example 2
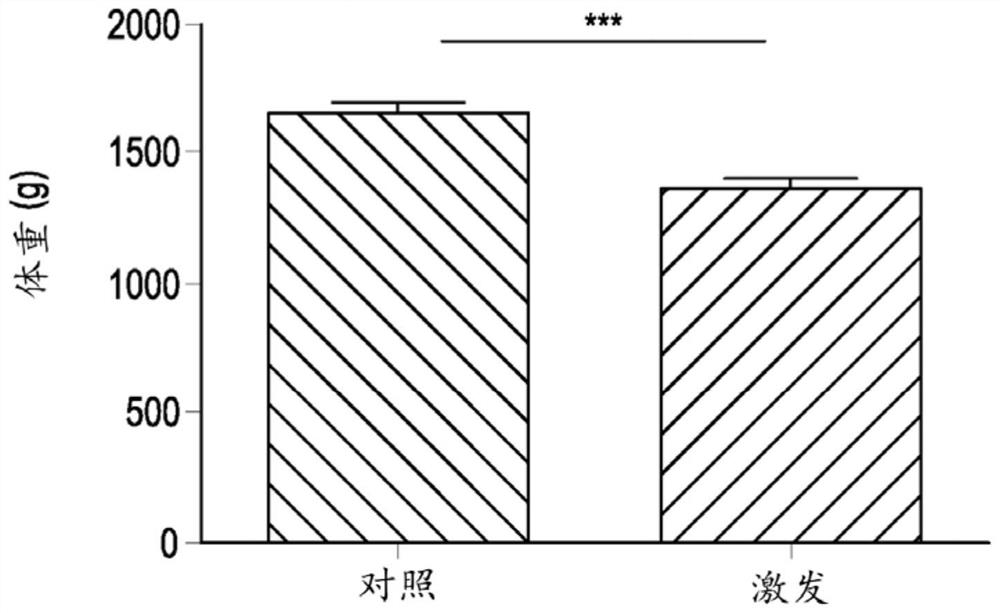
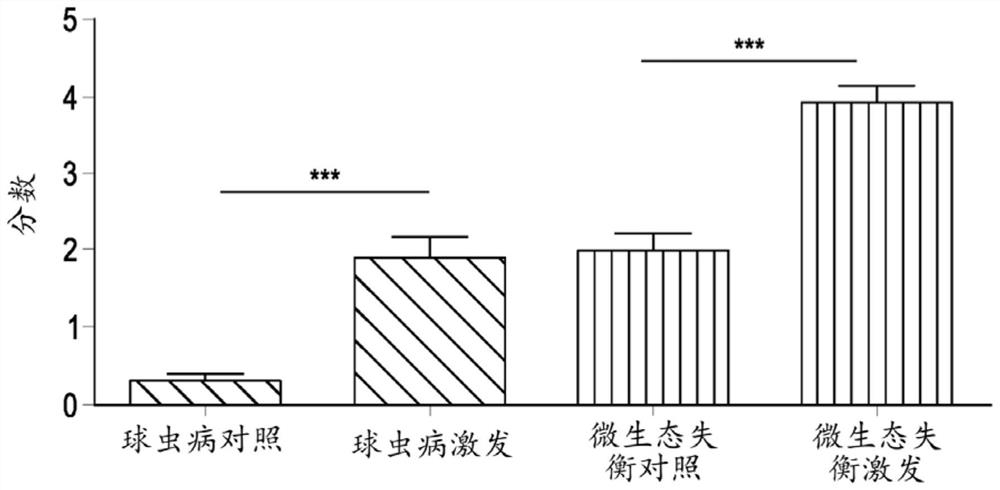
[0069] Example 2: Inducing microecological imbalance in chickens with provocative model tests
[0070] A total of 360-day-old broiler chickens (Ross 308) were obtained from a local hatchery and housed in floor pens on wood shavings. Feed and drinking water were provided ad libitum throughout the study. Broilers were randomly assigned to two treatment groups, a control group and a challenge group (9 pens / treatment, 20 broilers / pen). All animals were fed commercial feed until day 12, and feed was switched to a wheat-based (57.5%) diet supplemented with 5% rye. From day 12 to day 18, all animals from the challenge group received 10 mg florfenicol / kg body weight and 10 mg enrofloxacin / kg body weight daily via drinking water to induce substantial changes in the gut microflora. After antibiotic treatment, give 1 ml daily by oral gavage from day 19 to 21 from 10 9 cfu Escherichia coli (G.78.71), 10 10 cfu Enterococcus species (G.78.62), 10 9 cfu Lactobacillus salivarius (LMG22...
example 3
[0074] Example 3: Identification of metabolic biomarkers associated with gut health
[0075] Metabolomic analysis was performed on colon and cecum samples from control and challenged animals of Example 2. Such as Figure 6A and Figure 6B As shown in the stimulated chicken colon ( Figure 6A ) and cecum ( Figure 6B ) were observed at significantly higher levels compared to their corresponding levels in control chickens. Apart from Figure 6A and Figure 6B In addition to the metabolites shown in , the following additional compounds were found in the gut of challenged chickens at significantly higher levels than those found in unchallenged controls: linoleoylcarnitine, linalool, 3 -[(9Z)-9-octadecenoyloxy]-4-(trimethylammonium)butyrate, (-)-trans-methyldihydrojasmonate, icomerin, 1,3 -Dicaprylylglycerol and ethyl 2-nonanoate. Thus, the presence of one or more of these compounds at levels significantly higher than in healthy control animals is associated with poor gut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com