Electrode and secondary battery comprising same
An electrode and electrode active material technology, applied in secondary batteries, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, positive electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of electrolyte mobility limitation, battery efficiency reduction, incompatibility, etc., to achieve excellent electrical conductivity, improve lifespan characteristics, the effect of suppressing the decrease in conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0072] The preparation method of the electrode of the present invention may comprise the steps of: preparing a graphene dispersion and a carbon nanotube structure dispersion (S1); and forming an electrode slurry comprising a graphene dispersion, a carbon nanotube structure dispersion and an electrode active material (S2).
[0073] (1) Preparation of graphene dispersion and carbon nanotube structure dispersion (S1)
[0074] 1) Preparation of graphene dispersion
[0075] After preparing the mixed solution comprising the graphene of the above-mentioned embodiment, dispersion medium and dispersant, it can be obtained by using homogenizer, bead mill, ball mill, basket mill, attritor, universal mixer, transparent mixer, Nail mill, TK mixer or ultrasonic treatment method to prepare graphene dispersion. Since the dispersion medium and the dispersant may be the same as those used in the preparation of the carbon nanotube structure dispersion described later, the dispersion medium and...
preparation example 1
[0108] Preparation Example 1: Preparation of Graphene Dispersion
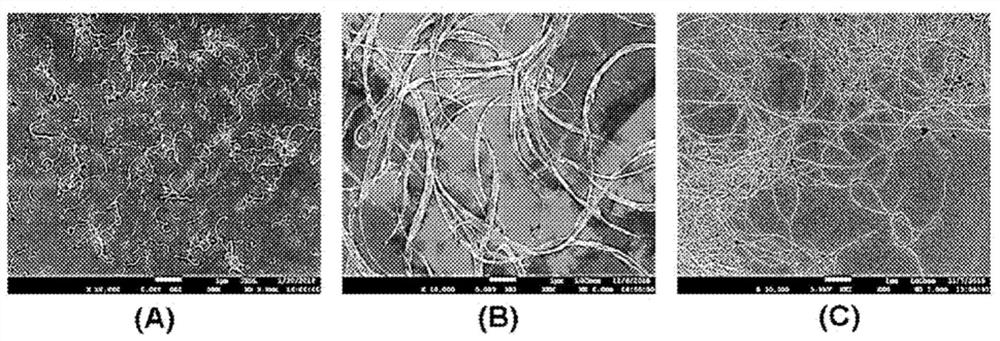
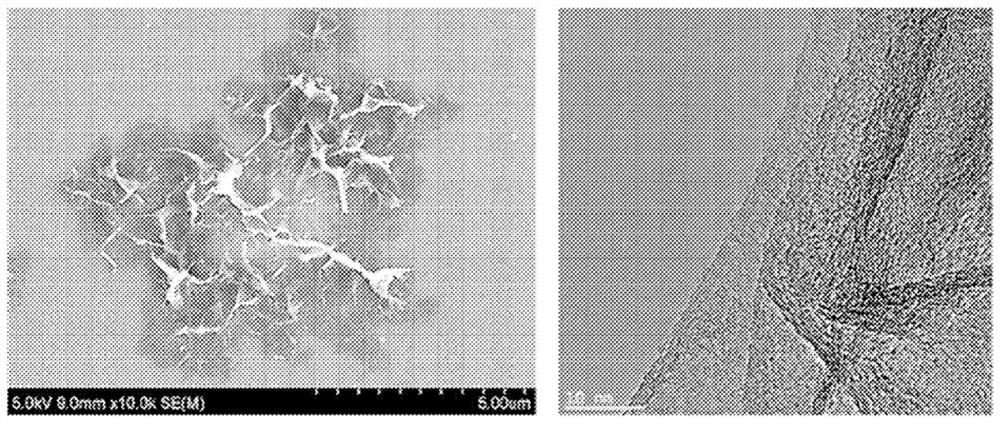
[0109] Chemically expanded graphene (powder form), hydrogenated nitrile rubber (H-NBR) as a dispersant, and N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP, N-methylpyrrolidone) as a dispersion medium in a weight ratio of 3.6:1.2:95.2 Mix to form a mixture. This mixture was fed into a pin mill in which 80% was filled with beads having a diameter of 0.65 mm, dispersed and discharged at a discharge rate of 2 kg / min. By performing this procedure twice, the chemically expanded graphene is completely dispersed to prepare a graphene dispersion (see image 3 ).
preparation example 2
[0110] Preparation Example 2: Preparation of Carbon Nanotube Structure Dispersion
[0111] Bundle-type single-walled carbon nanotubes (specific surface area 650m 2 / g) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVdF, KF9700, weight average molecular weight: 880,000 g / mol) were mixed in N-methylpyrrolidone (N-Methylpyrrolidone: NMP) as a solvent to prepare a solid content of 2.4% by weight mixture.
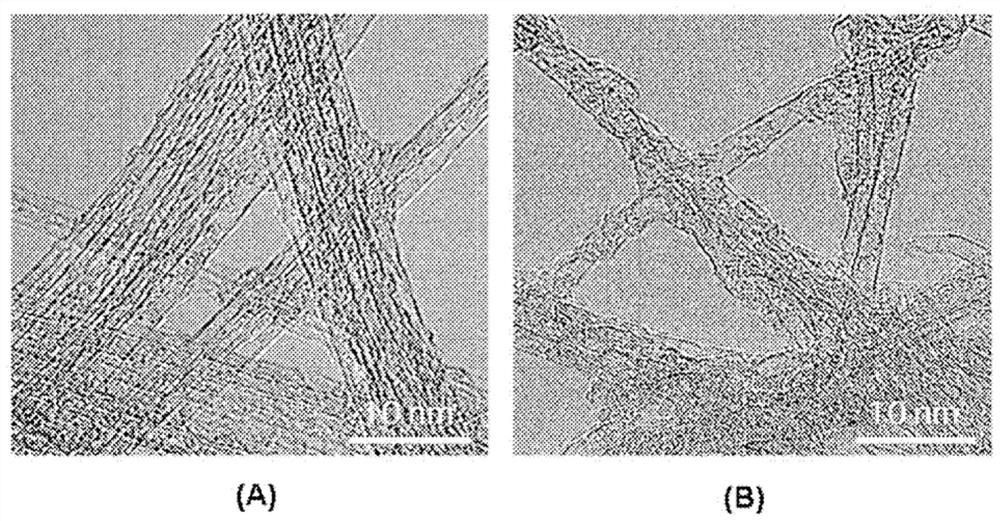
[0112] By stirring the mixture by a bead-mill method, bundle-type single-walled carbon nanotubes were dispersed in a solvent, and thus a carbon nanotube structure dispersion was prepared. In this case, the diameter of the beads was 1 mm, the rotation speed of the stirring vessel containing the beads was 3,000 RPM, and stirring was performed for 60 minutes. Dispersions of carbon nanotube structures include carbon nanotube structures in a form in which 2 to 5,000 single-walled carbon nanotube units are connected side by side (see figure 2 A).
[0113] In the carbon nanotube structure dispersi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com