Method and device for in-situ remediation of groundwater pollution by electrically driven biological PRB (permeable reactive barrier)
A groundwater pollution and in-situ remediation technology, which is applied in biological water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, electrochemical and biological combined treatment, etc., can solve problems such as limited remediation effect, limited effect of groundwater pollution remediation, and increased cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
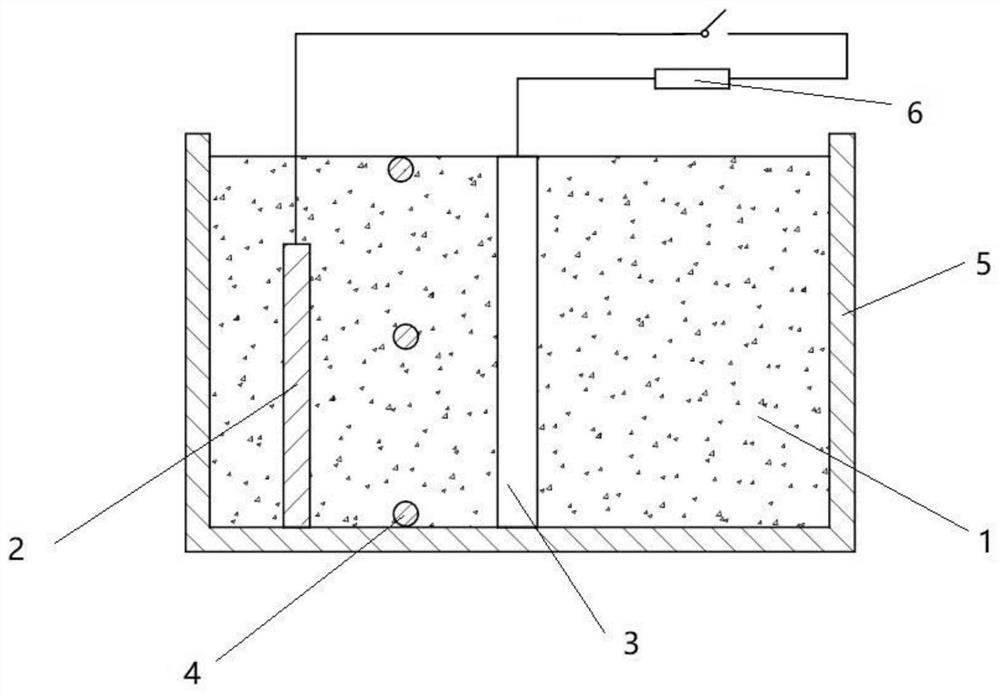
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, the permeable reaction wall 1 is set as a cylinder, and its volume is Φ75 mm × 100 mm. The cylindrical permeable reaction wall 1 is filled with a mixed filler of 140g of conductive carbon material and 28g of zero-valent iron material, wherein the mass ratio of conductive carbon material and zero-valent iron material is 20%. The conductive carbon material uses graphite particles with a particle size of 2-4mm and a density of 2.1-2.3g cm-3; the zero-valent iron material uses zero-valent iron particles with a particle size of 2mm and a density of 3.5-4.0g cm-3 . A carbon rod with a volume of Φ5 mm × 100 mm is inserted into the permeable reaction wall 1 as the anode 2, and the permeable reaction wall 1, anode 2 and microorganisms together constitute the anode area of the biological PRB.
[0044] An air cathode was inserted in the center of the bio-PRB anode area as the cathode 3, the volume of the air cathode was Φ20 mm × 100 mm, and platinum ...
Embodiment 2
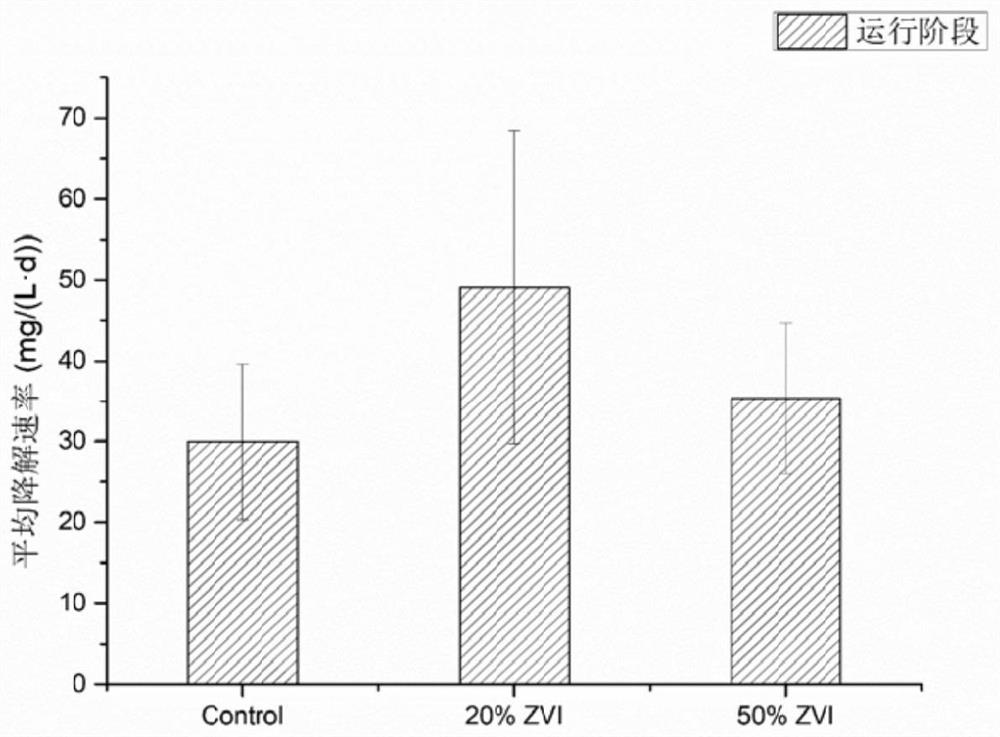
[0048] The filler of the permeable reaction wall 1 is: a mixed filler of 140g of conductive carbon material and 70g of zero-valent iron material, the mass ratio of conductive carbon material and zero-valent iron material is 50%, and the rest of the components are the same as in Example 1.
[0049] In the control group, the filler of the permeable reaction wall 1 is 140g of conductive carbon material without zero-valent iron material, and the rest is the same as that of Example 1.
[0050] The device of the present invention can adjust the shape, structure and position of the permeable reaction wall 1, the anode 2, the cathode 3, the water-conducting wall 4, the external circuit element 6 and the final reactor 5 according to the environment.
Embodiment 3
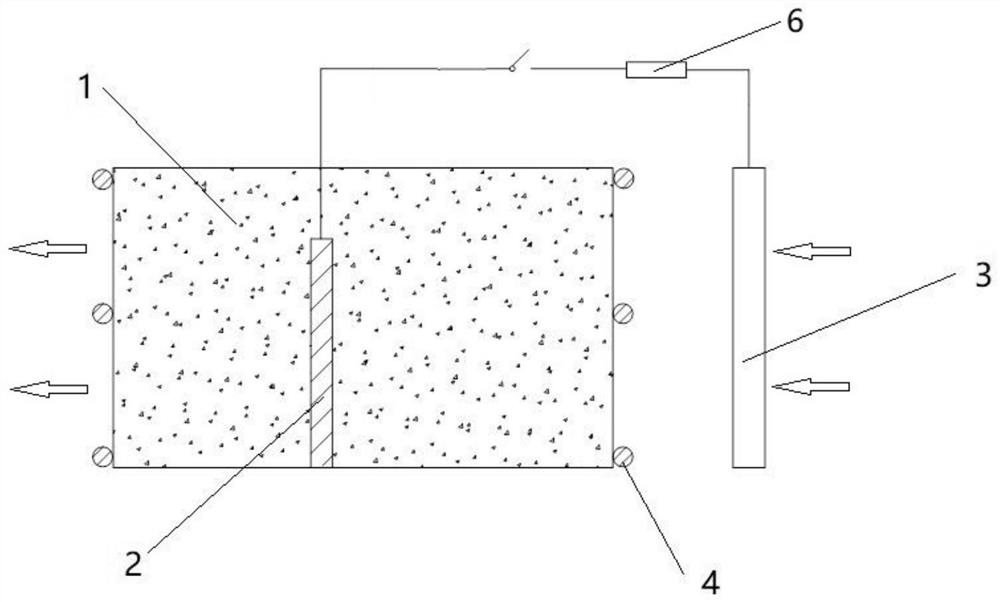
[0052] As an embodiment of the device of the present invention, such as figure 2 As shown, the anode 2 is inserted into the permeable reaction wall 1, and the permeable reaction wall 1, anode 2 and microorganisms together constitute the anode area of the biological PRB. The cathode 3 is installed at the water inlet end of the bio-PRB anode area, and a water-conducting wall 4 is set between the bio-PRB anode area and the cathode 3, and a water-conducting wall 4 is also provided at the water outlet of the bio-PRB anode area. The external circuit element 6 is a power supply; the cathode 3 is connected to the negative electrode of the external circuit element 6 through a copper wire, and the anode area of the biological PRB is connected to the positive electrode of the external circuit element 6 through an anode.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com