Pantoea ananatis promoting dissolution of ground phosphate rock and applications thereof
A technology of Pantoea pineapple and phosphate rock powder, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of low grade of phosphate rock powder, weakened pollution control effect, and poor solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: Isolation and purification of phosphate-dissolving bacteria
[0024] First carry out surface disinfection (95% alcohol (1min) → 30% hydrogen peroxide + 3% sodium hypochlorite (20min) → 95% alcohol (1min) → rinse with sterile water three times) to the root of Sedum sedum, and put the root tissue after disinfection. In a sterilized mortar, grind it into juice, add an appropriate amount of phosphate buffer solution, stir evenly, let it stand for 10 minutes, stir again, and dilute Sedum sedum and tissue grinding liquid with sterilized water. Pipette 200 μL from the stock solution and the diluted solution into LB solid medium for culture. After one week of plate culture, count and record the morphology of the colonies. At the same time, according to the characteristics of the colonies, different colonies were selected for new culture, purified once, and stored at -80°C.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: the screening of phosphate-dissolving bacteria
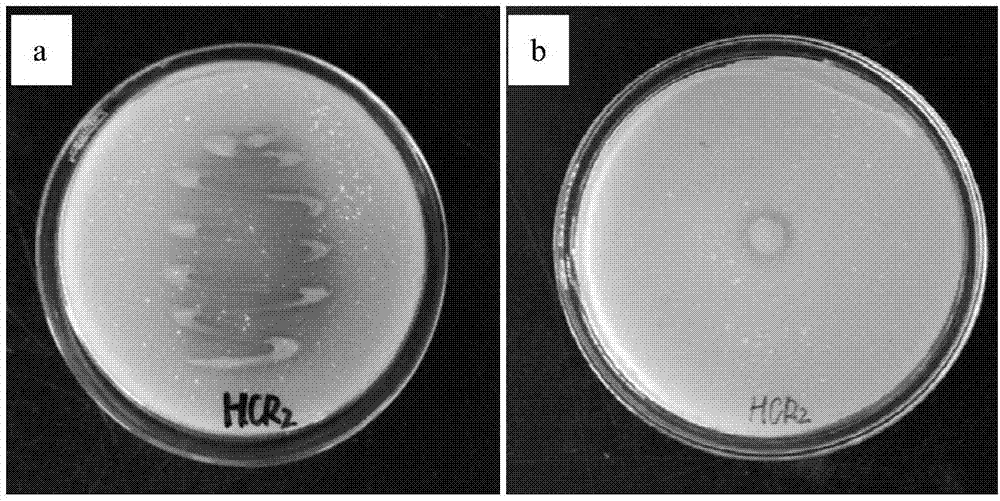
[0026] Qualitative experiment: After activating the strain preserved in Example 1 on LB liquid medium, take 10 μL of the bacterial liquid and spot it in NBRIP (National Botanical Research Institute's phosphate growth medium) solid medium, and place it at 30°C with constant temperature and humidity Cultivate in the incubator for 7 days, if there is an obvious bright circle around the colony, it means that the strain is a phosphate lysing bacteria.
[0027] Quantitative experiment: After the bacterial strain preserved in Example 1 is activated on the LB liquid medium, inoculate 0.5mL of the bacterial liquid of the bacterial strain in the logarithmic growth phase into the 50mL NBRIP liquid medium, and repeat 3 times for each treatment, while adding sterile Ultrapure water was used instead of bacterial solution as blank control, (28°C, 180r·min -1 ) Shaker for 7 days, centrifuged (5 000r·min -1 ) for 10 min, t...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Screening and identification of phosphate-dissolving bacteria
[0033]Species identification, individual morphological observation and physiological and biochemical characteristics were carried out on the screened phosphate-dissolving bacteria. The identification and morphological observation of the bacteria in this study were completed by the Guangdong Provincial Microbiological Analysis and Testing Center. The base sequence of the strain was obtained through the Internet in GenBank, etc. Perform a homologous sequence search (blast search) in the international nucleic acid sequence database to find the type strain with the highest homology between the strain and the database or strains preserved in international culture collection centers such as ATCC or DSM.
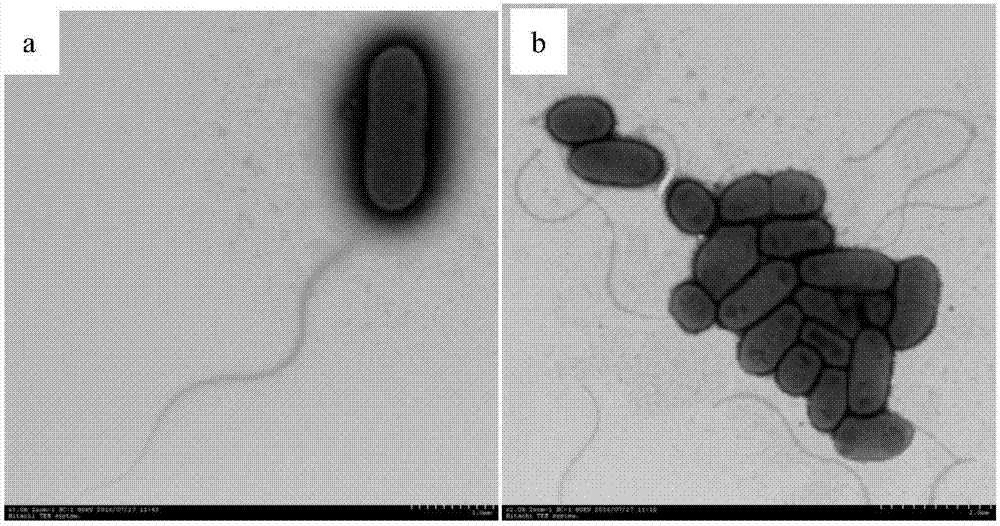
[0034] (1) Morphological characteristics of bacteria
[0035] Gram-negative bacteria. The bacteria are rod-shaped and transformed to anaerobic. The transmission electron microscope characteristic ma...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com