Method and Application of Recovering Copper and Zinc from Brass Melting and Casting Soot
A brass and soot technology, applied in the field of resource utilization of solid waste in the metallurgical process, can solve the problems of multiple waste residues or waste water, long process flow, and difficulty in impurity removal, and achieve cost reduction, simple process flow, and controllability strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
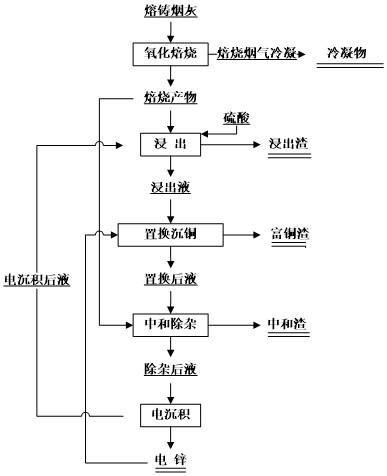
[0097] This embodiment provides a method for reclaiming copper and zinc from yellow miscellaneous copper melting and casting soot, and the process roadmap is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0098] (1) Take 20kg of mixed soot and roast it with air at 900°C for 1 hour to obtain a roasted product, and at the same time condense the roasted flue gas to obtain a condensate.
[0099] (2) The roasted product is leached with dilute sulfuric acid according to the liquid-solid ratio of 5:1, and the final pH value is 2. The leaching solution is filtered to obtain leaching residue and leaching liquid.
[0100] (3) The leaching solution is replaced with a zinc plate, the anode is a zinc plate, the cathode is a titanium plate, and the voltage between the cathode and the anode is 0.2V. After the reaction is completed, copper-rich slag and replaced liquid are obtained.
[0101] (4) Add the roasted product of step (1) to the liquid after replacement to adjust the p...
Embodiment 2
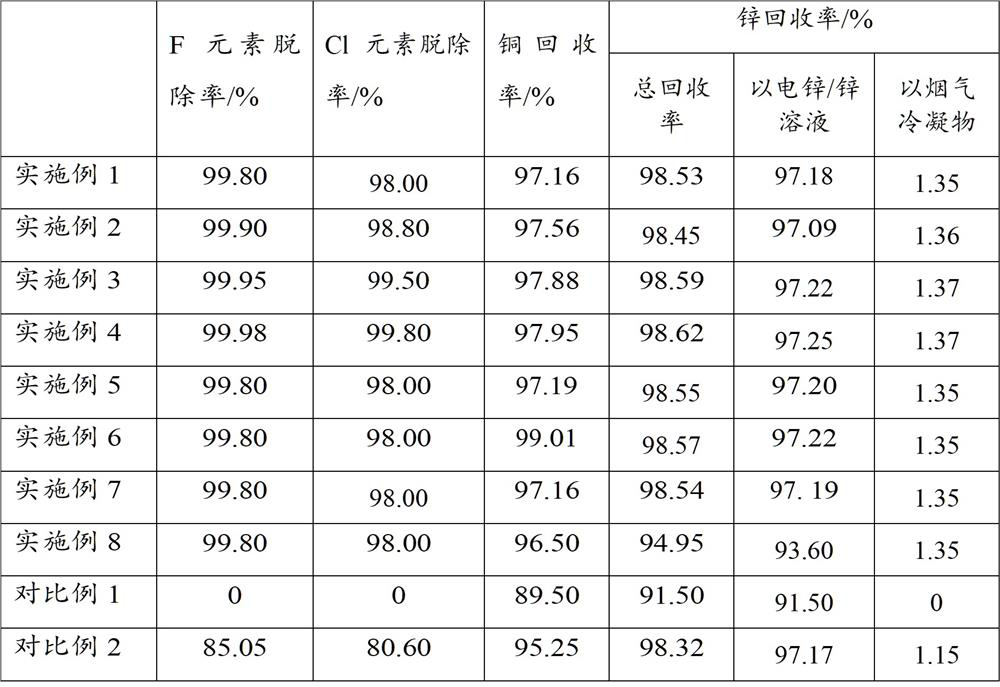
[0104] This example provides a method for recovering copper and zinc from yellow miscellaneous copper melting and casting soot. The difference from Example 1 is that in step (1), air is roasted at 1000°C for 2 hours, and the rest of the steps and conditions are the same as those in Example 1. 1 are the same and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0106] This example provides a method for recovering copper and zinc from yellow miscellaneous copper melting and casting soot. The difference from Example 1 is that in step (1), oxygen is roasted at 1100°C for 1 hour, and the volume concentration of oxygen at this time is 40 %, all the other steps and conditions are the same as in Example 1, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com