Intravascular stent
A vascular stent and blood flow technology, applied in the field of vascular stents, can solve problems such as the inability to provide vascular stents, reduce extrusion resistance, increase vascular stents, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing flexibility, ensuring strength, and ensuring flexibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
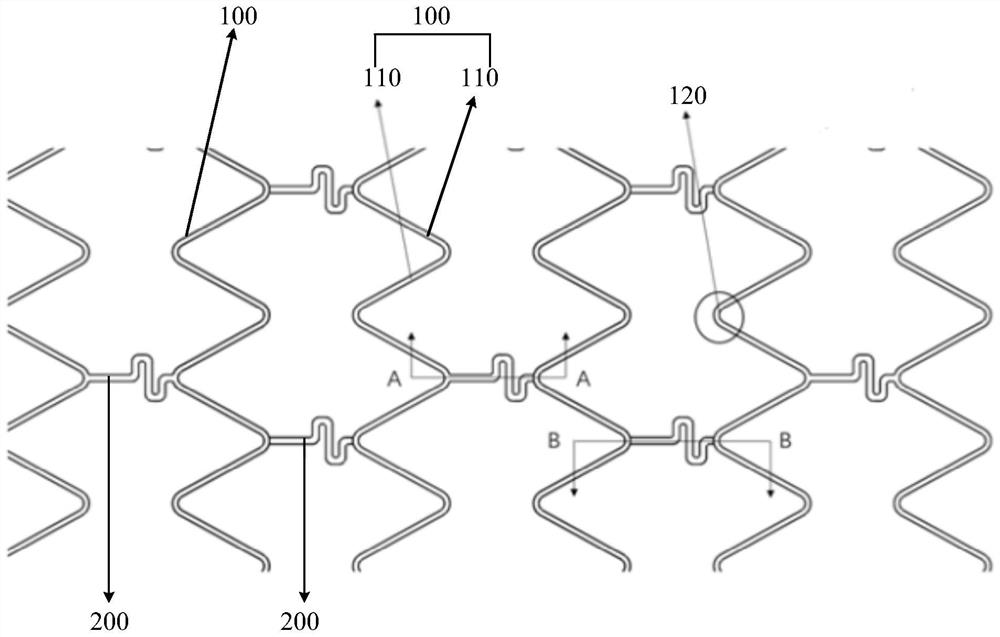
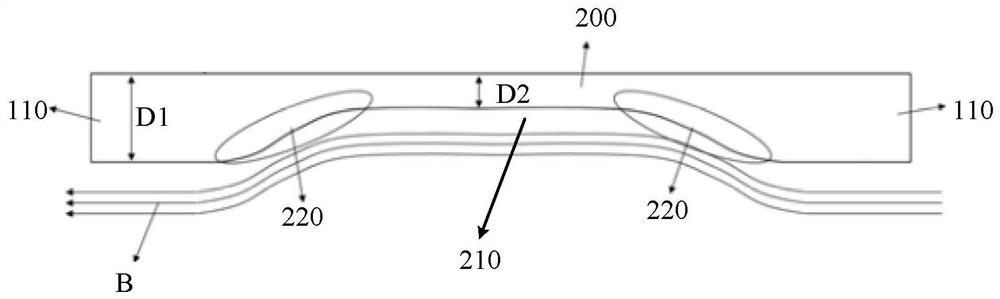
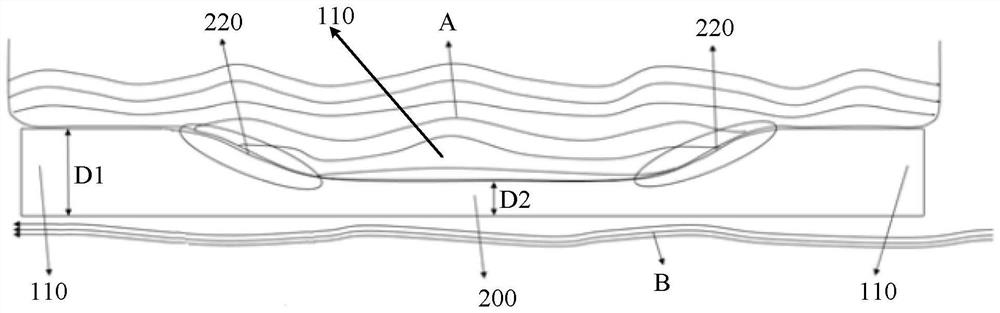
[0059] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, the present embodiment provides a medium vascular stent, the vascular stent includes a plurality of support rings 100 and a plurality of connecting rods 200; The adjoining regions 120 of two adjacent support rods 110 are connected. Wherein, the supporting ring 100 is formed by connecting a plurality of supporting rods 110 connected end to end, and the wall thickness D1 of the supporting rods 110 is 0.1 mm. A part of the connecting rod 200 has a groove 210 on the side wall near the central axis of the vascular stent, and the distance D2 between the bottom of the groove 210 and the side wall of the connecting rod 200 away from the central axis of the vascular stent (that is, the wall of the connecting rod 200 Thickness) is 0.05m, the groove 210 does not exceed any side surface of the connecting rod 200 range, the groove wall of the groove 210 forms a smooth transition zone 220 corresponding to the blood flow direction, the notch of...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Such as Figure 4 , Figure 5 As shown, the present embodiment provides a vascular stent, which includes a plurality of support rings 100 and a plurality of connecting rods 200; the support rings 100 are distributed at intervals along the central axis of the vascular stent. Wherein, the supporting ring 100 is formed by connecting a plurality of supporting rods 110 connected end to end, and the wall thickness D1 of the supporting rods 110 is 0.1 mm. One end of the connecting rod 200 is connected to the adjoining regions 120 of two adjacent support rods 110, and the other end of the connecting rod 200 is connected to the adjoining regions 120 of two adjacent supporting rods 110 through a reinforcing part 300, and the reinforcing part 300 The shape is an "S" placed horizontally. There is a groove 210 on the side wall of the connecting rod 200 away from the central axis of the vascular stent, and the distance D2 between the bottom of the groove 210 and the side wall of th...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the present embodiment provides a vascular stent, which includes a plurality of support rings 100 and a plurality of connecting rods 200; the support rings 100 are distributed at intervals along the central axis of the vascular stent. Wherein, the support ring 100 is formed by connecting a plurality of support rods 110 connected end to end, and the wall thickness D1 of the support rods 110 is 0.1mm; . A groove 210 is provided on the two side walls of the connecting rod 200 away from and close to the central axis of the vascular stent, and the two grooves 210 are aligned and distributed, and the distance D2 between the groove bottoms (ie, the wall thickness of the connecting rod 200) is 0.05mm The groove 210 does not exceed any side surface of the entire connecting rod 200 to form a concave area, and the groove wall of the groove 210 forms a smooth transition zone 220 corresponding to the direction of blood flow. The notch of the groove 210 i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com