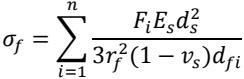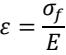Calculation method and control method for coating film strain of ultra-thin lens, and ultra-thin lens
A technology of control methods and calculation methods, applied in computer material science, design optimization/simulation, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as optical focusing and divergence, and performance degradation of optical components, and achieve the effect of solving technical obstacles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1 provides a method for calculating the coating strain of an ultra-thin lens, comprising the following steps:
[0041] Step A1, the first required for ultra-thin lenses For each film layer material, the relationship model between its coating stress and thickness is obtained; , n is the number of film layers required for the ultra-thin lens.
[0042] Among them, the film material required for ultra-thin lenses is determined according to the optical property requirements required by the product, and is responsible for forming specific spectral properties in the product.
[0043] The relationship between the thickness and strain of coating materials in different film systems has a certain degree of nonlinear dependence. Therefore, in this embodiment, for each film layer material, the relationship model between its coating stress and thickness is established as:
[0044]
[0045] In the formula, F and d represent the coating stress and thickness of an...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2 provides a method for controlling the coating strain of an ultra-thin lens, comprising the following steps:
[0058] Step B1, using steps A1 to A3 in the method described in Example 1, to solve the stress of the coating layer of the ultra-thin lens ;
[0059] Step B2, designing a metal oxide film layer, the vector sum of its coating stress and the stress of the coating layer of the ultra-thin lens is less than the preset stress threshold;
[0060] Step B3, during the coating process of the ultra-thin lens, adding the designed metal oxide film layer to the coating layer of the ultra-thin lens.
[0061] In a more optimal solution, when designing the metal oxide film layer in step B2: first preselect a metal oxide material, and calculate the relationship between the coating stress and the thickness of the metal oxide film layer material according to the same method as in step A1 in Example 1. Then input the stress value opposite to the stress of the coating...
Embodiment 3
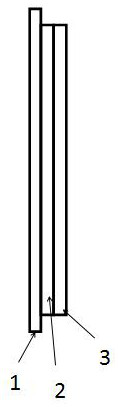
[0064] Embodiment 3 provides an ultra-thin lens, a lens with a thickness not greater than 0.1mm, including a substrate, a metal oxide film layer and several existing film layers, the metal oxide film layer is located between the substrate and the existing film layers, the The vector sum of coating stresses of the metal oxide film layer and all existing film layers is less than a preset stress threshold. Wherein, the metal oxide film layer is designed and obtained by adopting the method for controlling the coating strain of the ultra-thin lens described in Embodiment 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com