Application of circular RNA CircNFIB in diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma
A technology for inner bile duct and cell carcinoma, applied in the prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, circular RNA CircNFIB in the field of diagnosis, can solve the problem of little research on the role of circular RNA, and achieve inhibition The effect of tumor growth, inhibition of proliferation, and enhancement of anti-tumor activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
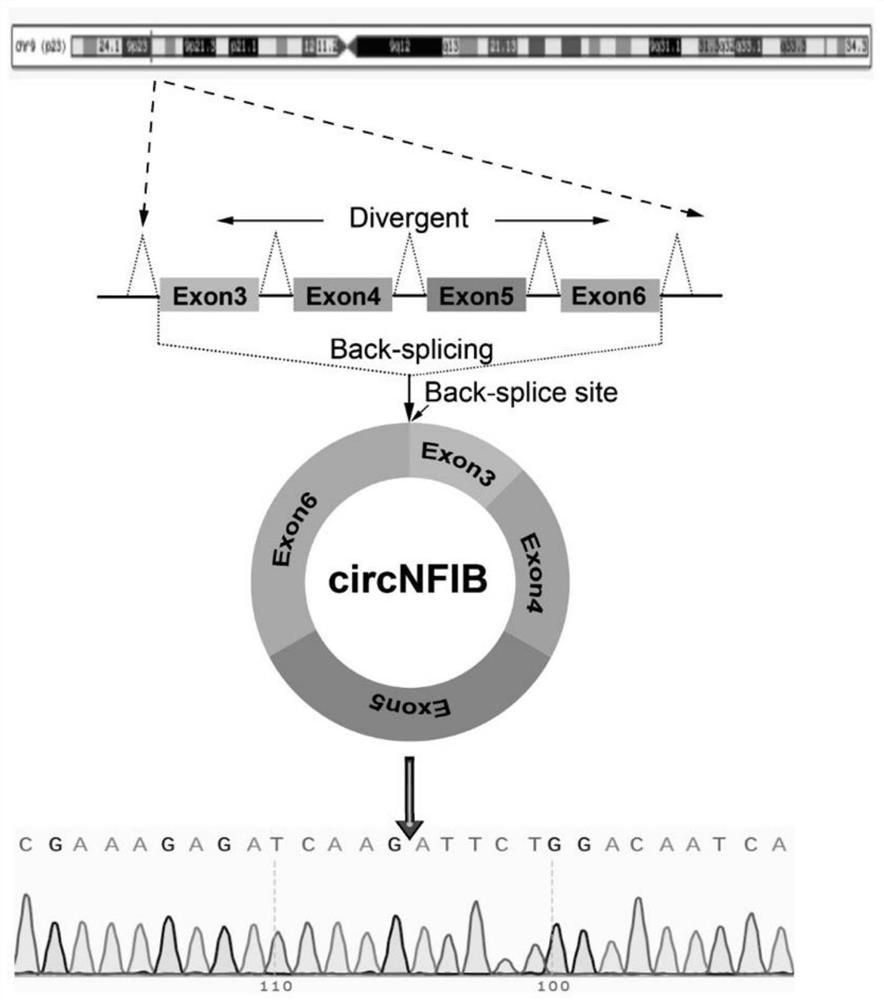
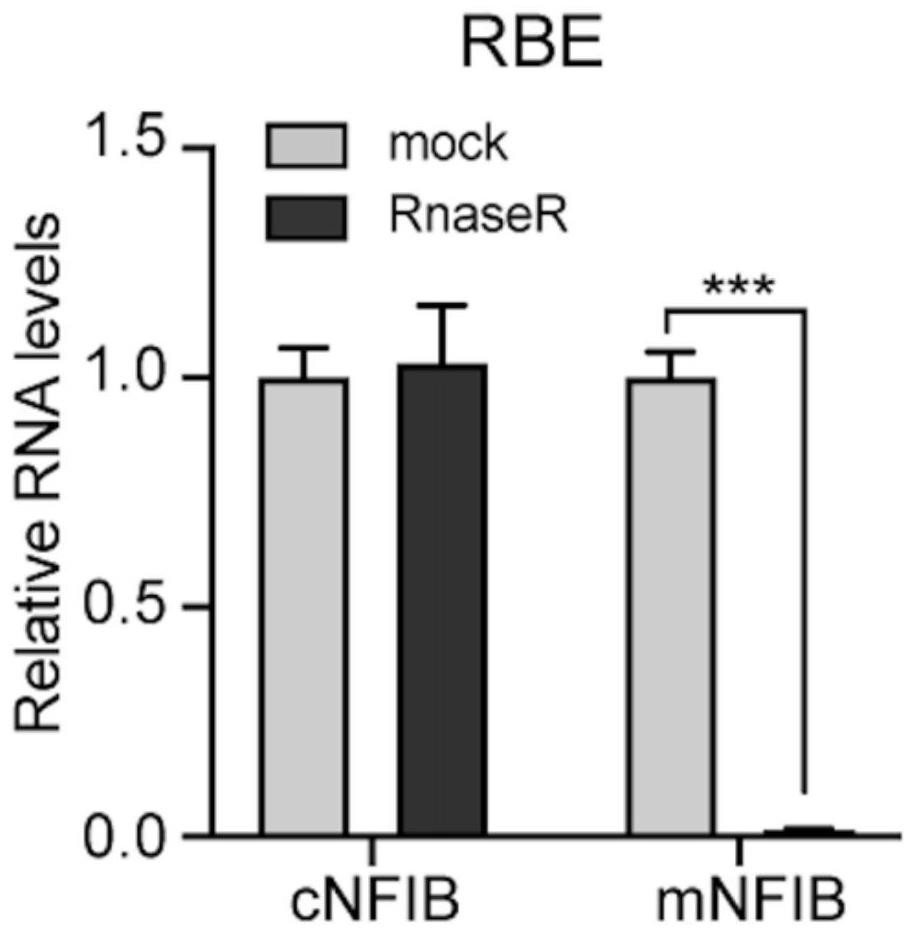
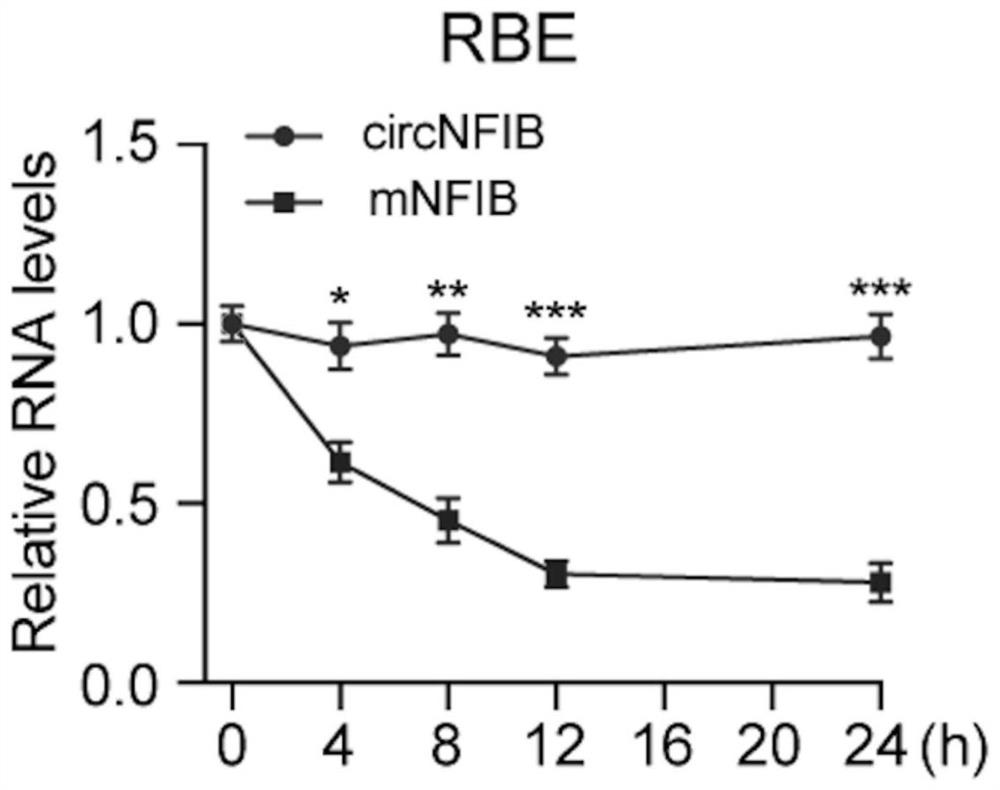
[0051] In this example, the inventors designed a pair of specific primers capable of amplifying the circular RNA cNFIB, and used the primer pair to amplify cNFIB, and confirmed the splicing site (back-splice site) of the circular RNA by the method of generation sequencing. ), and then through the RNase R digestion experiment, it was determined that cNFIB is a circular RNA molecule with a closed circular structure, and the stability of cNFIB was proved by the actinomycin D experiment.
[0052] The experimental scheme of this embodiment is as follows:
[0053] Total RNA was extracted from RBE cells using Trizol reagent, and the purity and concentration of total cellular RNA was detected by an ultra-micro nucleic acid analyzer. Prepare the reverse transcription reaction system on ice. After the preparation is completed, add the prepared total cellular RNA for reverse transcription. The reverse transcription reaction system is:
[0054]
[0055] The reverse transcription react...
Embodiment 2
[0066] In this example, the expression difference of cNFIB in the tumor tissue and the corresponding non-tumor tissue was detected by fluorescent quantitative PCR, and it was found that the expression of cNFIB in the tumor tissue was significantly higher than that in the corresponding non-tumor tissue, indicating that the expression level of cNFIB can be detected by using for the diagnosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
[0067] The experimental scheme of this embodiment is as follows:
[0068] Total RNA was extracted from cells and tumor tissues using the Total RNA Isolation Kit according to the manufacturer's instructions, using ChamQ TM SYBR@qPCR Master Mix for real-time PCR analysis. Relative expression of RNA was normalized by β-actin or U6 and quantified by the 2-ΔΔCt method.
[0069] Specifically, the cDNA reverse transcription reaction in Example 1 was used to perform tissue RNA reverse transcription.
[0070] The PCR reaction system was prepared on ice (take ...
Embodiment 3
[0085] In this example, using the median value of relative cNFIB expression in ICC tissues, 120 ICC patients were divided into cNFIB low expression group (n=60) and cNFIB high expression group (n=60), β-actin Alternatively U6 was used as an endogenous control.
[0086] like Figure 5 As shown, by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, ICC patients with lower cNFIB expression levels had shorter overall survival and recurrence-free survival after curative resection.
[0087] Table 1 shows the prognostic factors for overall survival and recurrence-free survival from the univariate COX proportional hazards regression model. In univariate analysis, serum CA19-9 level, tumor number, tumor volume, tumor differentiation, microvascular invasion, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage, and cNFIB expression level were associated with overall survival and recurrence-free survival.
[0088] Table 1:
[0089]
[0090] In multivariate analysis, low expression of cNFIB was associated with poorer tum...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com