Method for separating and measuring content of optical isomers in tartaric acid
A technology for optical isomers and tartaric acid, applied in the field of chemical analysis, can solve problems such as high cost and complicated detection process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] 1. Chromatographic conditions:
[0054] Chromatographic column: CHIRALPAK AD-H 4.6×250mm, 5μm
[0055] Stationary phase: Amylose-tris[3,5-dimethylcarbamate] derivative
[0056] Mobile phase: Measure 850ml of n-hexane, 150ml of isopropanol, 10ml of tert-butanol, 2ml of trifluoroacetic acid, mix well, and elute isocratic
[0057] Column temperature: 25°C
[0058] Mobile phase flow rate: 0.8ml / min
[0059] Detection wavelength: 223nm
[0060] Injection volume: 20μL
[0061] 2. Experimental steps
[0062]1) Take an appropriate amount of tartaric acid sample, dissolve it with ethanol, and prepare a solution containing 10 mg of tartaric acid sample per 1 ml, then dilute with mobile phase to a solution of 5 mg per 1 ml of tartaric acid sample;
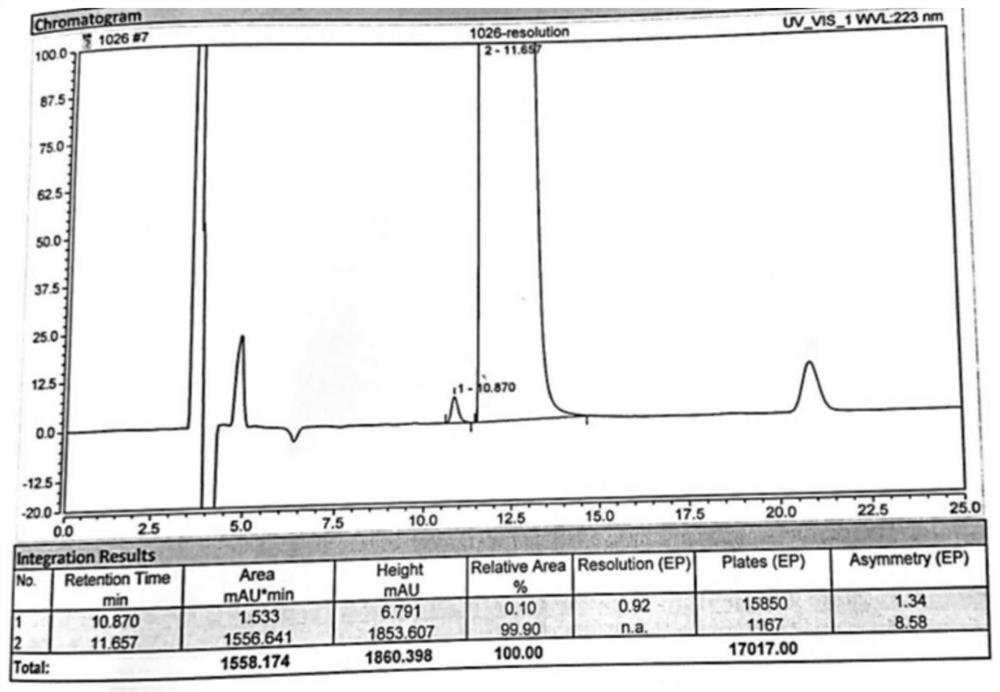
[0063] 2) Take 20 μl of the sample solution obtained in step 1) and inject it into a high-performance liquid chromatograph, and record the chromatogram. attached figure 1 The experimental results show that peak No. 1 is D-tarta...
Embodiment 2
[0065] 1. Chromatographic conditions:
[0066] Chromatographic column: CHIRALPAK AD-H 4.6×250mm, 5μm
[0067] Stationary phase: Amylose-tris[3,5-dimethylcarbamate] derivative
[0068] Mobile phase: Measure 830ml of n-hexane, 170ml of isopropanol, 10ml of tert-butanol, 2ml of trifluoroacetic acid, mix well, and elute isocratic
[0069] Column temperature: 25°C
[0070] Mobile phase flow rate: 0.8ml / min
[0071] Detection wavelength: 223nm
[0072] Injection volume: 20μL
[0073] 2. Experimental steps
[0074] 1) Take an appropriate amount of tartaric acid sample, dissolve it with ethanol, and prepare a solution containing 10 mg of tartaric acid sample per 1 ml, then dilute with mobile phase to a solution of 5 mg per 1 ml of tartaric acid sample;
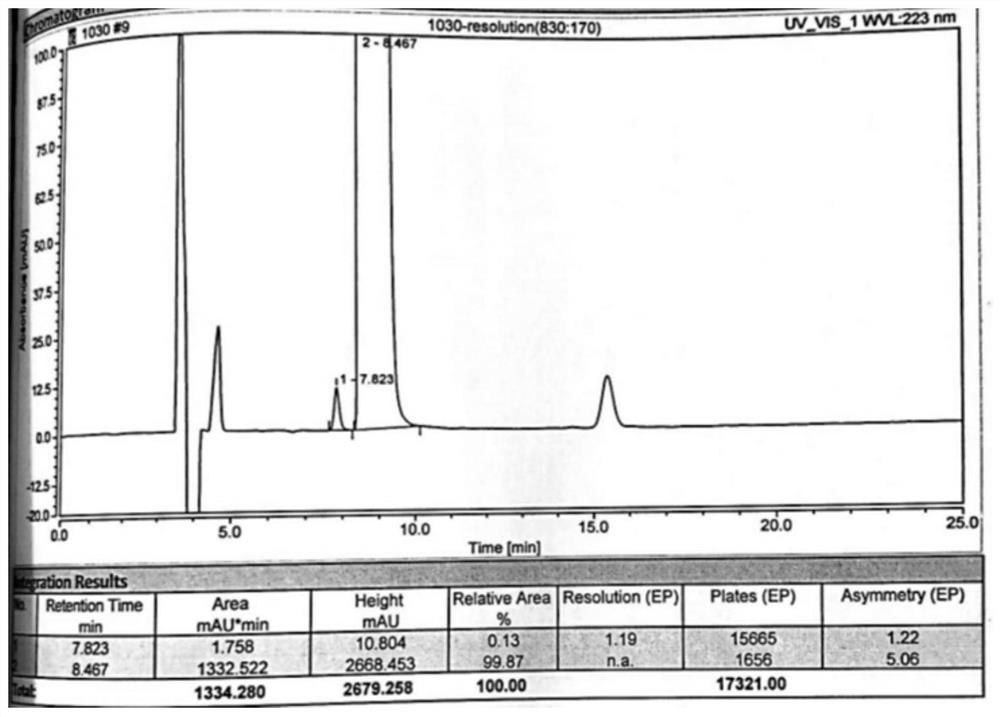
[0075] 2) Take 20 μl of the sample solution obtained in step 1) and inject it into a high-performance liquid chromatograph, and record the chromatogram. attached figure 2 The experimental results show that peak No. 1 is D-tar...
Embodiment 3
[0077] 1. Chromatographic conditions:
[0078] Chromatographic column: CHIRALPAK AD-H 4.6×250mm, 5μm
[0079] Stationary phase: Amylose-tris[3,5-dimethylcarbamate] derivative
[0080] Mobile phase: Measure 880ml of n-hexane, 120ml of isopropanol, 10ml of tert-butanol, 2ml of trifluoroacetic acid, mix well, and elute isocratic
[0081] Column temperature: 25°C
[0082] Mobile phase flow rate: 0.8ml / min
[0083] Detection wavelength: 223nm
[0084] Injection volume: 20μL
[0085] 2. Experimental steps
[0086] 1) Take an appropriate amount of tartaric acid sample, dissolve it with ethanol, and prepare a solution containing 10 mg of tartaric acid sample per 1 ml, then dilute with mobile phase to a solution of 5 mg per 1 ml of tartaric acid sample;
[0087] 2) Take 20 μl of the sample solution obtained in step 1) and inject it into a high-performance liquid chromatograph, and record the chromatogram. attached image 3 The experimental results show that peak No. 1 is D-tart...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com