Multi-GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) parallel finite-difference time domain electromagnetic simulation method, equipment and medium
A finite difference in time domain and electromagnetic simulation technology, which is applied in design optimization/simulation, resource allocation, multi-programming devices, etc., can solve problems such as long computing time, large memory consumption, and low computing efficiency, and achieve computing performance improvement, The effect of saving calculation time and improving simulation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
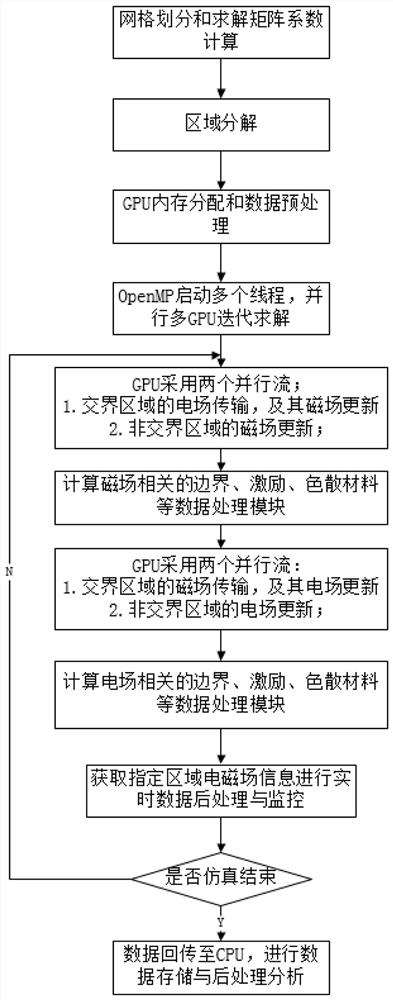
[0045]This embodiment provides a multi-GPU parallel finite difference time-domain electromagnetic simulation method, which can effectively solve the problems of large memory consumption, low calculation efficiency, and long calculation time in the process of solving electromagnetic FDTD algorithms for large-scale simulation cases; at the same time , in the calculation process of a variety of boundary conditions, excitations, dispersive media and other cases, it can effectively solve the problems of the traditional FDTD algorithm in the multi-GPU calculation of poor versatility or low parallel performance.
[0046] refer to figure 1 As shown, the simulation method of this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0047] Step S1: Solution area grid division and coefficient calculation
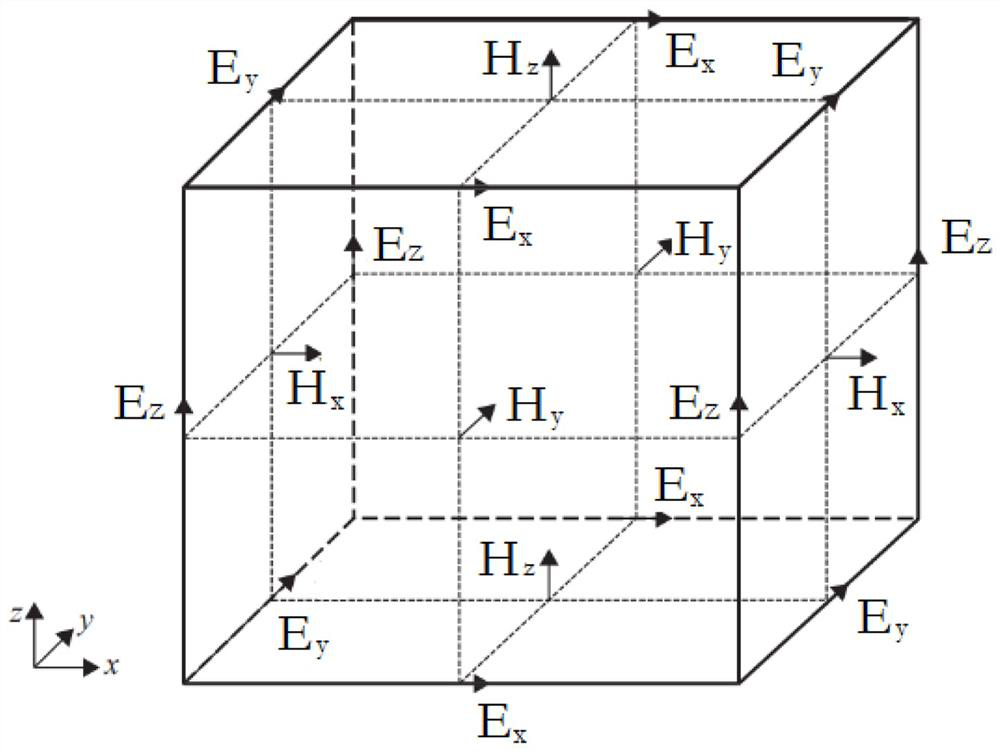
[0048] This embodiment performs Yee grid division for the input three-dimensional electromagnetic model, such as figure 2 As shown, the number of grids corresponding to the three...
Embodiment 2
[0104] This embodiment provides a multi-GPU parallel finite-difference time-domain electromagnetic simulation system, which executes the multi-GPU parallel finite-difference time-domain electromagnetic simulation method as described in Embodiment 1, including:
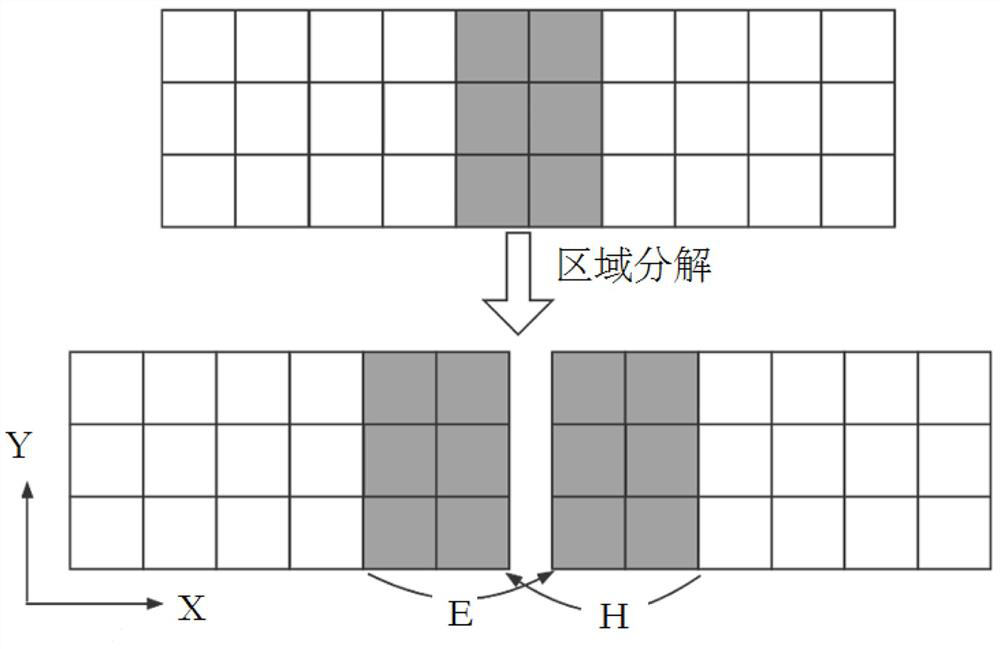
[0105] The regional decomposition module is used to decompose the spatial grid according to the preset GPU parallel number, so that adjacent sub-domains after decomposition contain the same overlapping grid; Divided to obtain;
[0106] The data update module is used to match the regional parameters of its corresponding sub-domain for each GPU, and control each GPU to combine the regional parameters to perform electromagnetic field data update on the overlapping grid corresponding to its sub-domain and the area other than the overlapping grid. iterative operation;
[0107] The result storage module is used for data storage of the iterative calculation results of the electromagnetic field data.
[0108] In addition, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com