Detection method of circulating tumor cells and application thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] A method for detecting circulating tumor cells.
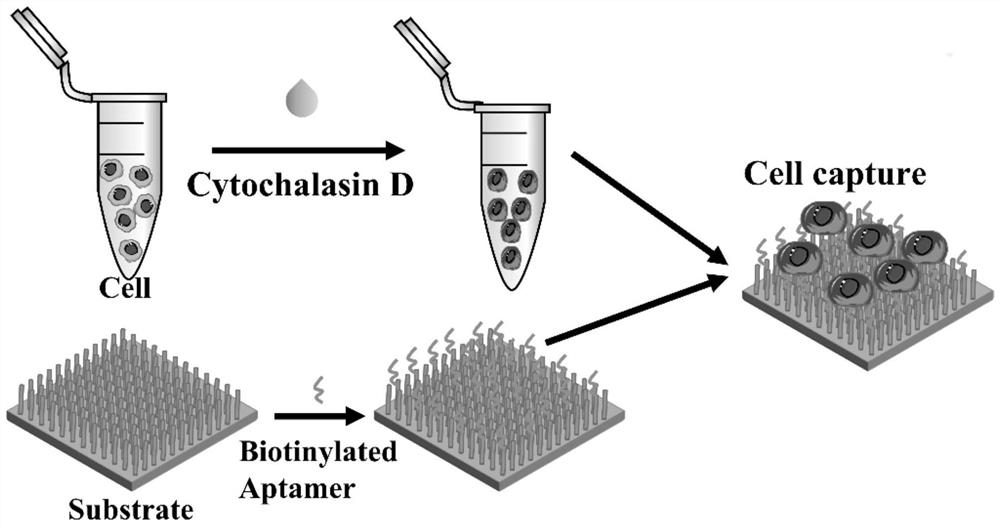
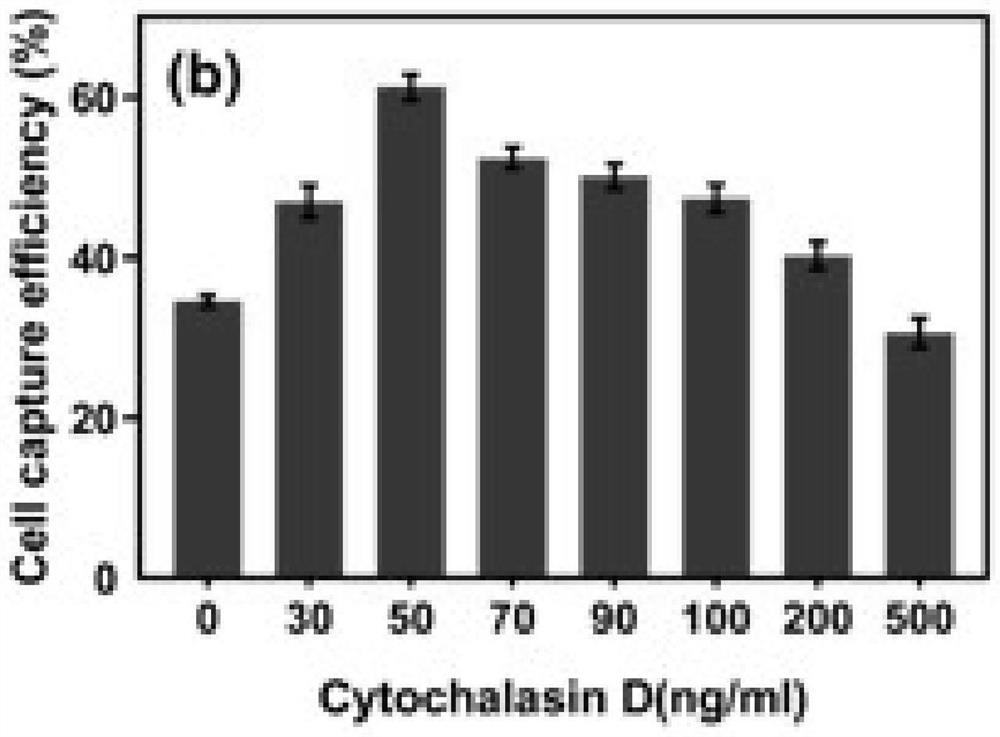
[0064] 1. Softening: Cytochalasin D was used to treat circulating tumor cells, and cytochalasin D was added to the cells at a concentration of 10 5 MCF-7 cells / mL culture medium allows cytochalasin D to enter circulating tumor cells in a subsequent capture step to destroy filamentous actin, thereby softening circulating tumor cells.
[0065] 2. Capture: Synthesis of TiO by hydrothermal method 2 nanowire array, cell culture medium supplemented with cytochalasin D was added to the TiO 2 nanowire arrays in a petri dish, making circulating tumor cells in TiO 2 The nanowire array was cultured on the substrate surface for 40 minutes at a temperature of 37°C. During this process, the filamentous actin of circulating tumor cells was destroyed by cytochalasin D, and the cells were softened, and the softened circulating tumor cells were treated with TiO 2 Nanowire Array Capture.
[0066] The experimental process of embodiment...
Embodiment 2
[0072] A method for detecting circulating tumor cells.
[0073] Existing techniques usually carry out chemical modification on the surface of nanostructured substrates to further improve cell capture efficiency. Those skilled in the art can modify biomolecules, such as antibodies and aptamers, on the substrate of Example 1 according to requirements. In order to investigate whether cytochalasin D treatment is still effective in improving the cell capture efficiency on the surface of the modified substrate, the inventors set up 4 groups for experimental comparison in this example.
[0074] In the control group, the circulating tumor cells were not treated with cytochalasin D, and the substrate surface of the TiO2 nanowire array was not modified;
[0075] Ap group is circulating tumor cells without cytochalasin D treatment, and biotinylated aptamer modified TiO2 nanowire array substrate surface;
[0076] In the CD group, circulating tumor cells were treated with cytochalasin D,...
Embodiment 3
[0081] A study of the effect of cytochalasin D on cell adhesion.
[0082] 1. Characterize the cell morphology of circulating tumor cells after adhesion.
[0083] The ability to capture cells on the substrate surface is closely related to cell adhesion, strong cell adhesion means high cell capture efficiency. In order to study the effect of cytochalasin D treatment on cell adhesion, this example uses a scanning electron microscope (SEM) to characterize the cell morphology after cell adhesion.
[0084] The result is as Figure 7 As shown, the inventors found that when the cells were not treated with cytochalasin D, the cells captured by the surface of the modified or unmodified substrate showed a distinct protrusion shape. However, cytochalasin D-treated cells exhibited flattening on both modified and unmodified substrate surfaces.
[0085] 2. To study the effect of cytochalasin D on the actin of cells.
[0086] In order to further study the adhesion of cells on the substrat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com