Application of antisense oligonucleotide ASOYAP1 in inhibition of multiple YAP1 positive cancers
An antisense oligonucleotide and oligonucleotide technology, which is applied in the direction of DNA / RNA fragments, organic active ingredients, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient research and development of inhibitors, and achieve high knockout efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0132] Embodiment 1 Design and detection of YAP1 antisense oligonucleotide
[0133] 1. Biological identification of ASO sequences and comparison of modification schemes and sites
[0134] Use the BLAST biological serial information primary structure online comparison tool in NCBI (https: / / blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / Blast.cgi) to compare and analyze the mRNA structure information of each transcript of YAP1 mRNA, and record it consensus sequence. Use the "soligo" page (http: / / sfold.wadsworth.org / cgi-bin / index.pl) in the sfold RNA secondary structure online prediction tool to input the consensus sequence of each transcript of YAP1, and select the oligo length as 20nt. Submit and record screening results.
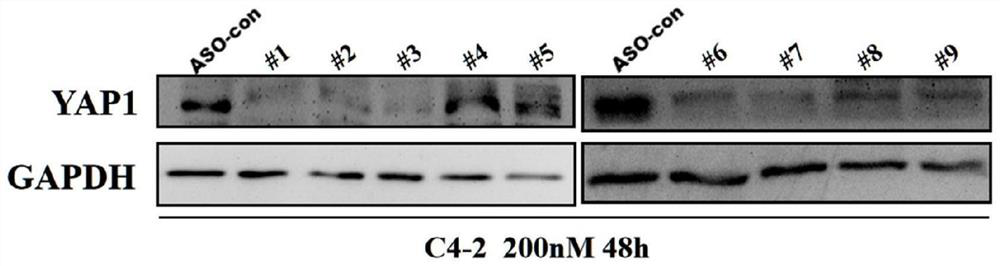
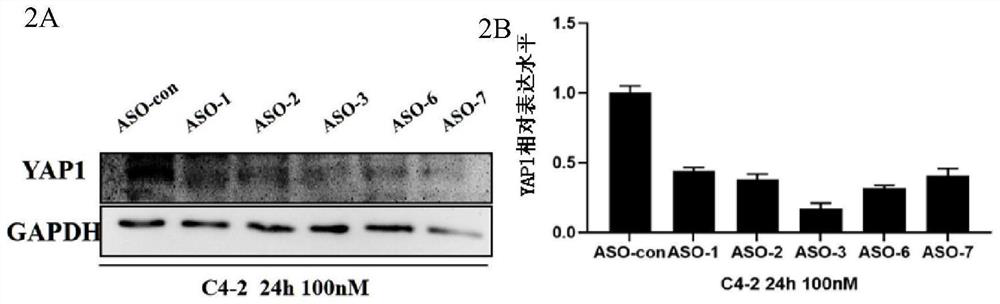
[0135] According to the basic principle of complementary base pairing, we designed 9 (see Table 1) antisense oligonucleotides ASO covering 20 nucleic acids including functional sites Yap1 , and use phosphorothioate full-chain modification as basic modification (Table 2)
[0136...
Embodiment 2
[0164] The antisense oligonucleotide ASO of embodiment 2 methoxyethyl modification YAP1 The mode of action of knocking out YAP1
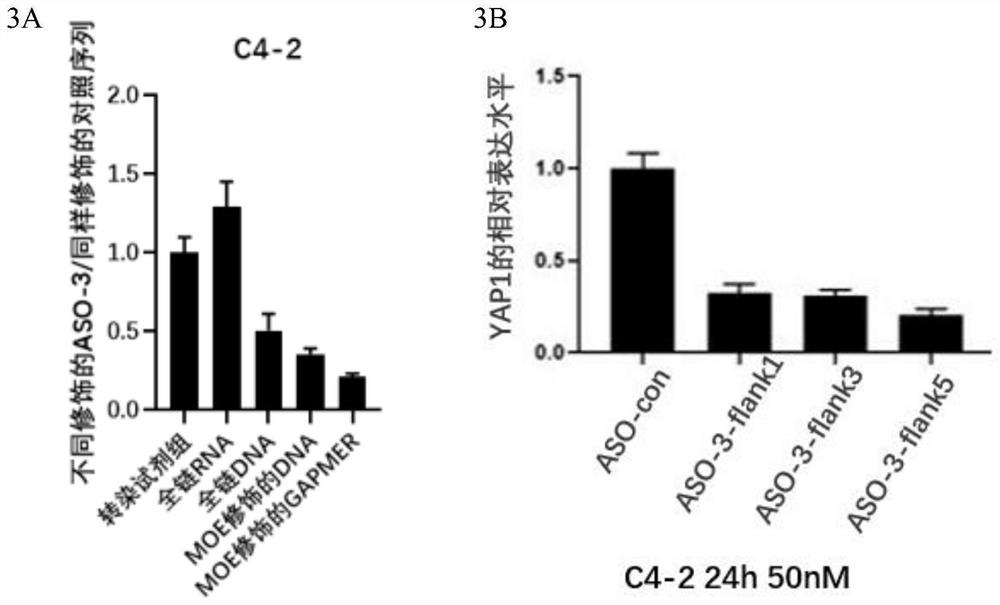
[0165] The C4-2 cells were cultured in a six-well plate in vitro, and the cells were transfected 24 hours after the cells were plated. methoxyethyl-modified antisense oligonucleotide ASO YAP1 Mix ASO-3-flank5 and liposome transfection reagent evenly and incubate at room temperature for 20min, then add the mixture evenly into the culture medium. makes ASO YAP1 The final concentrations in the medium were 0nM, 50nM, 100nM, 200nM, and the cell culture medium was removed after 48h, and Trizol / RIPA reagent was added to extract the total RNA and total protein of the cells. Another plate was spread, and cells were transfected 24 hours later, and ASO was transfected with liposomes at a final concentration of 100 nM. After 0, 12h, 24h and 48h respectively, the same method was used to extract the total RNA and total protein of the cells. The total RNA wa...
Embodiment 3
[0167] Embodiment 3 detects ASO YAP1 Knockout ability of YAP1 protein level in various cancer cells
[0168] Use ASO-3-flank5 and liposome transfection reagent to transfect breast cancer MCF-7 cells, lung cancer cells A549 cells, cervical cancer cells Hela cells, bladder cancer T24 cells, and liver cancer cells HUH-6. Western blot and RT-QPCR were used to detect the expression levels of YAP1 protein and mRNA 48h after transfection with 100nM ASO.
[0169] The result is as Figure 5 As shown, in breast cancer MCF-7 cells, lung cancer cells A549 cells, cervical cancer cells Hela cells, bladder cancer T24 cells, and liver cancer cells HUH-6, the expression levels of YAP1 mRNA and protein in the experimental group were significantly down-regulated.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com