Heat treatment process for ultra-fine grain structure of annealed hot work die steel
A technology of hot work die steel and hot work die, which is applied in heat treatment equipment, heat treatment process control, manufacturing tools, etc., and can solve the problems affecting the toughness of steel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
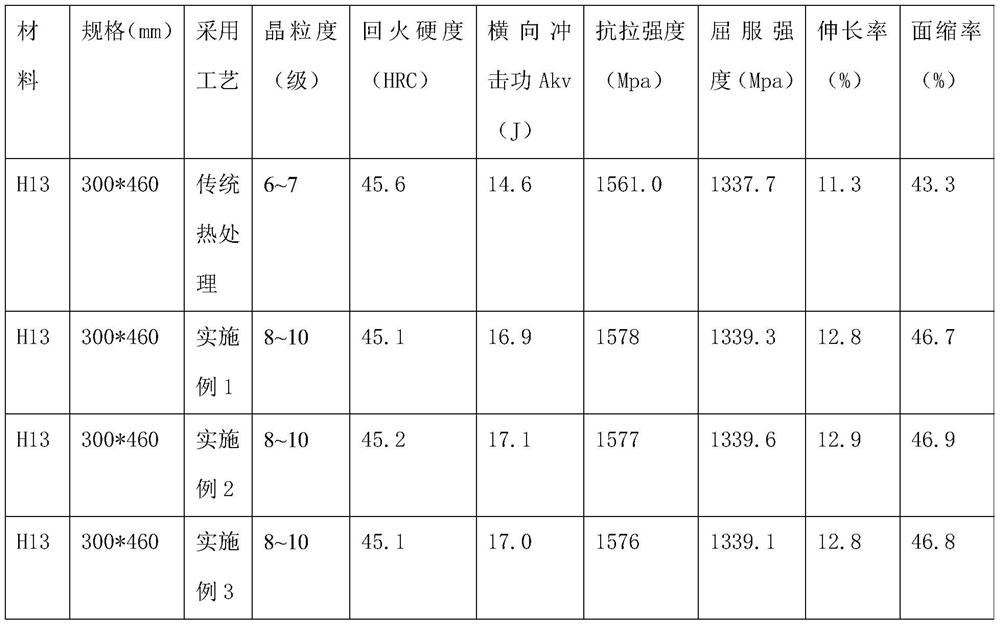
[0019] This example provides a heat treatment process for ultra-fine grained structure of annealed hot work die steel. The heat treatment material is annealed H13 (4Cr5MoSiV1) hot work die steel (meeting the requirements of GB / T 1299-2014 standard), processed according to requirements Form the mold blank, depending on the size of the mold, leave a machining allowance of 1.5mm to 2mm, and install multiple thermocouples for temperature detection on different areas such as the center and surface of the mold; including the following steps:
[0020] (1) The first high-temperature homogenization: This process includes two-stage preheating, heating the mold to be heat-treated to 500°C at a heating rate of 80°C / h for 1 hour, and raising the temperature to 800°C at a heating rate of 80°C / h ℃ heat preservation for 1h; heat up to 1050°C at a heating rate of 80°C / h, and when the core temperature is 5°C lower than the set austenitization temperature, heat preservation for 1h; round steel or...
Embodiment 2
[0027] This example provides a heat treatment process for ultra-fine grained structure of annealed hot work die steel. The heat treatment material is annealed H13 (4Cr5MoSiV1) hot work die steel (meeting the requirements of GB / T 1299-2014 standard), processed according to requirements Form the mold blank, depending on the size of the mold, leave a machining allowance of 1.5mm to 2mm, and install multiple thermocouples for temperature detection on different areas such as the center and surface of the mold; including the following steps:
[0028] (1) The first high-temperature homogenization: This process includes two-stage preheating, heating the mold to be heat-treated to 550°C at a heating rate of 70°C / h for 1 hour, and raising the temperature to 830°C at a heating rate of 70°C / h ℃ heat preservation for 1h; heat up to 1080°C at a heating rate of 70°C / h, and when the core temperature is 8°C lower than the set austenitization temperature, heat preservation for 1h; round steel or...
Embodiment 3
[0035] This example provides a heat treatment process for ultra-fine grained structure of annealed hot work die steel. The heat treatment material is annealed H13 (4Cr5MoSiV1) hot work die steel (meeting the requirements of GB / T 1299-2014 standard), processed according to requirements Form the mold blank, depending on the size of the mold, leave a machining allowance of 1.5mm to 2mm, and install multiple thermocouples for temperature detection on different areas such as the center and surface of the mold; including the following steps:
[0036] (1) The first high-temperature homogenization: This process includes two-stage preheating, heating the mold to be heat-treated to 600°C at a heating rate of 50°C / h for 1 hour, and raising the temperature to 850°C at a heating rate of 50°C / h ℃ heat preservation for 1 hour; heat up to 1100 ℃ at a heating rate of 50 ℃ / h, and when the core temperature is 10 ℃ lower than the set austenitization temperature, heat preservation for 1 hour; round...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com