Vacuum temperature fuse, series battery row, parallel battery row and battery pack
A temperature fuse and vacuum technology, which is applied to battery pack components, batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problem of thermal runaway increase of the monomer, and achieve the effect of small size, relatively small size, and convenient use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] The temperature fuse is an effective slow-fuse protection element. When one of the conductors at both ends of its electrical connection is overheated, it will be conducted to its own heat-sensitive material and thermally blown, thereby disconnecting an electrical appliance that disconnects the circuit. For overheating protection of circuits and electrical equipment. When the thermal runaway of the power battery will generate high heat, the bus bar electrically connected to its pole will be the first to receive heat spread. However, the existing fuses cannot be used in the thermal protection of groups of new energy power batteries, because the molten metal will flow, and the smart terminal is vibrating, which will easily cause the liquid metal to flow to other positions in the battery module. A short circuit between normal working batteries is brought about, which in turn leads to new and greater safety risks.
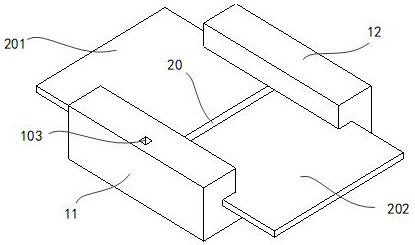
[0065] Embodiment 1 provides a vacuum temperature fuse 1 w...
Embodiment 2
[0119] Embodiment 2 provides a vacuum thermal fuse 1 , which differs from Embodiment 1 mainly in the position of the vacuum suction port 101 .
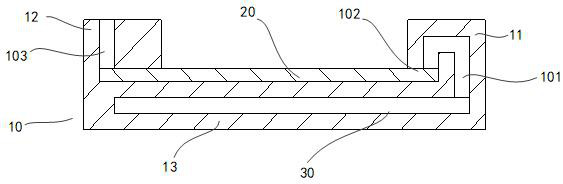
[0120] As a preferred technical solution, the vacuum suction port 101 is located on the lower surface of the first end of the fuse bar 20 .
[0121] according to Figure 7-Figure 8 , the vacuum suction port 101 is located on the lower surface of the fuse bar 20, and makes the vacuum suction channel 102 communicate with the fuse bar 20. The path of the vacuum suction channel 102 is short, and the fuse bar 20 in the molten state only depends on its own weight and vibration. Just can enter in the vacuum cavity 30.
[0122] During the process of changing the fuse strip 20 from a non-fuse state to a fuse state, when the second end of the fuse strip 20 has not entered a completely melted state, the fuse strip 20 at the position of the vacuum suction port 101 first falls directly into the vacuum chamber 30 Inside: due to the viscosity insi...
Embodiment 3
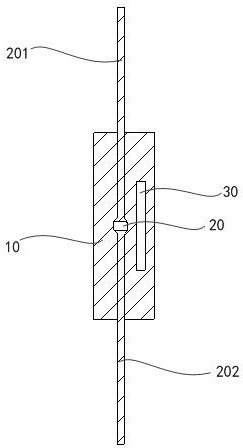
[0127] The vacuum temperature fuse 1 of embodiment 1 is applied to the series battery row, according to Figure 9 , the embodiment provides a series battery row, comprising:
[0128] A plurality of single cells 40, the single cells 40 include a positive pole 401 and a negative pole;
[0129] A plurality of bus bars, each bus bar including a fused bus bar. The fusing busbar includes a first conductor 201 electrically connected to the positive pole 401 of a single battery 40, a second conductor 202 electrically connected to the negative pole of an adjacent single battery 40, and the vacuum temperature of Embodiment 1-2 Fuse 1; preferably, the bus bar electrically connects the positive pole 401 and the negative pole between the adjacent single cells 40 arranged in the previous sequence, and electrically connects the negative pole and the positive pole between the single cells 40 arranged in the subsequent sequence Pole 401; the combination of each first conductor 201, second co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com