Deoxidation and alloying method for free-cutting steel smelting
A free-cutting steel and alloying technology, applied in the field of free-cutting steel, can solve the problems of reduced alloy yield, low active oxygen, and high active oxygen content, so as to increase alloy yield, reduce smelting costs, and improve Adjusting the effect of efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
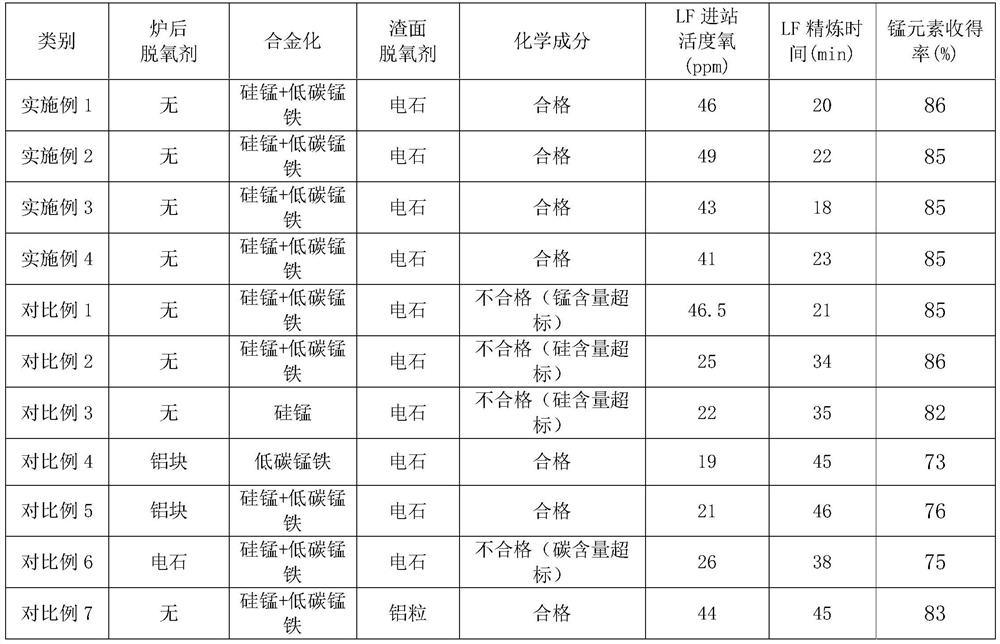
[0035] 1. Chemical composition
[0036] The chemical composition is designed as C: 0.07%, Si: 0.04%, Mn: 1.22%, P: 0.05%, S: 0.39%, Cr: 0.04%, Ni: 0.03%, Cu: 0.05%, [O ]: 37ppm.
[0037] 2. Blast furnace ironmaking
[0038] The blast furnace uses sintered iron ore as the main raw material, which is smelted into molten iron as the main raw material for free-cutting steel smelting.
[0039] 3. Primary refining of converter
[0040] The initial smelting process of the converter uses blast furnace molten iron and scrap steel as the charge, of which molten iron accounts for 90%, scrap accounts for 10%, and the total furnace capacity is 150 tons. The converter first blows oxygen to oxidize and remove elements such as C and Si (remove C to 0.04%~0.06%, and remove Si to ≤0.08%), and then create low-basicity slag (basicity 2.4~2.8) and ensure the slag Sufficient amount. The tapping temperature of the converter is 1618 ° C, and the tapping C is controlled at 0.05%; no deoxidizer is...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Replace "silicon-manganese consumption 600kg / furnace, low-carbon ferromanganese consumption 1500kg / furnace" in step 3 of Example 1 with "silicon-manganese consumption 600kg / furnace, low-carbon ferromanganese consumption 1400kg / furnace", other conditions are the same as in Example 1 .
Embodiment 3
[0048] 1. Chemical composition
[0049] The chemical composition is designed as C: 0.08%, Si: 0.06%, Mn: 1.35%, P: 0.08%, S: 0.36%, Cr: 0.08%, Ni: 0.02%, Cu: 0.09%, [O ]: 35ppm.
[0050] 2. Blast furnace ironmaking
[0051] The blast furnace uses sintered iron ore as the main raw material, which is smelted into molten iron as the main raw material for free-cutting steel smelting.
[0052] 3. Primary refining of converter
[0053]In the primary smelting process of the converter, blast furnace molten iron and scrap steel are used as the charge, of which molten iron accounts for 90%, scrap accounts for 10%, and the total furnace capacity is 145 tons. The converter first blows oxygen to oxidize and remove elements such as C and Si, and then produces low-basicity slag (basicity 2.5-2.8) and ensures that the amount of slag is sufficient. The converter tapping temperature is 1616 ℃, and the tapping C is controlled at 0.06%; no deoxidizer is added during the tapping process, silic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com