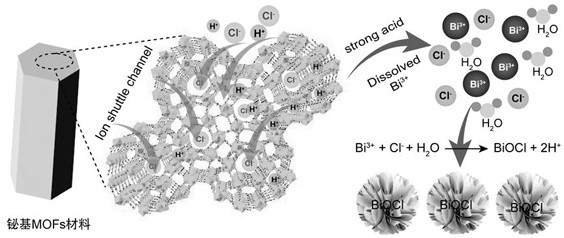
Method for rapidly removing chloride ions in wastewater by using bismuth-based metal organic framework material
An organic framework and metal-based technology, applied in the field of wastewater treatment in environmental protection, can solve the problems of long time consumption, low chlorine removal efficiency, consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of fast reaction rate, high chlorine removal efficiency, and large specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Removal of chloride ions by bismuth-based MOFs in simulated wastewater at pH=1
[0033] (1) According to the molar ratio of material to chloride ion, Bi 3+ / Cl - =1.5:1, weighing 0.6421 g of bismuth-based MOFs material sample;
[0034] (2) Take 10 mL of simulated waste liquid with an initial chloride ion concentration of 3500 mg / L and pH=1, put it into a 20 mL small glass bottle, add magnetons, and weigh the bismuth-based MOFs material sample. Add to the simulated waste liquid and stir at 500 rpm;
[0035] (3) Sampling according to different times, namely 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 20 minutes, 2 hours and 4 hours;
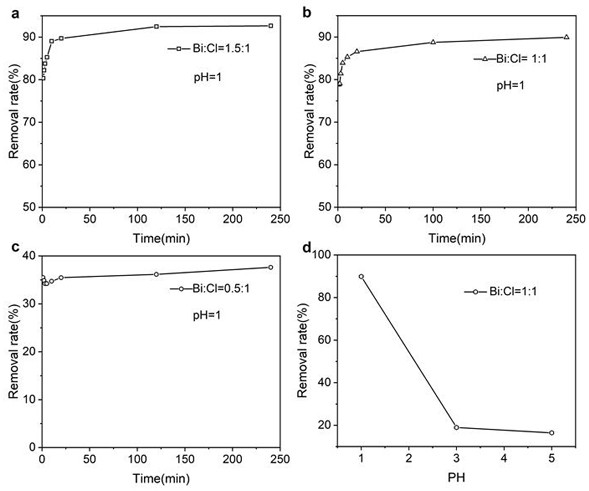
[0036] (4) Centrifuge the dechlorinated sample at a centrifugal speed (5000 rpm, 5 min), aspirate the supernatant, and use 0.01mol / L AgNO 3 The solution is titrated, as shown in the figure 2 As shown in a, the removal efficiencies of para-chloride ions were 80.3%, 82.2%, 83.8%, 85.3%, 89.1%, 89.7%, 92.5%, and 92.7% at the abov...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Removal of chloride ions by bismuth-based MOFs in simulated wastewater at pH=1
[0039] (1) According to the molar ratio of material to chloride ion, Bi 3+ / Cl - =1:1, weigh 0.4281 g of bismuth-based MOFs material sample;
[0040] (2) Take 10 mL of simulated waste liquid with an initial chloride ion concentration of 3500 mg / L and pH=1, put it into a 20 mL small glass bottle, add magnetron, and weigh the bismuth-based MOFs material sample. Add to the simulated waste liquid and stir at 500 rpm;
[0041] (3) Sampling according to different times, namely 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 20 minutes, 2 hours and 4 hours;
[0042] (4) Centrifuge the dechlorinated sample at a centrifugal speed (5000 rpm, 5 min), aspirate the supernatant, and use 0.01mol / L AgNO 3 The solution is titrated, as shown in the figure 2 As shown in b, the removal efficiencies of para-chloride ions were 78.8%, 79.1%, 81.4%, 83.9%, 85.3%, 86.6%, 88.7%, and 89.9% at the above t...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Removal of chloride ions by bismuth-based MOFs in simulated wastewater at pH=1
[0045] (1) According to the molar ratio of material to chloride ion, Bi 3+ / Cl - =0.5:1, weighing 0.2141 g of bismuth-based MOFs material sample;
[0046] (2) Take 10 mL of simulated waste liquid with an initial chloride ion concentration of 3500 mg / L and pH=1, put it into a 20 mL small glass bottle, add magnetron, and weigh the bismuth-based MOFs material sample. Add to the simulated waste liquid, and stir at a speed of 500 rpm;
[0047] (3) Sampling according to different times, namely 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 20 minutes, 2 hours and 4 hours;
[0048] (4) Centrifuge the dechlorinated sample at a centrifugal speed (5000 rpm, 5 min), aspirate the supernatant, and use 0.01mol / L AgNO 3 The solution is titrated, as shown in the figure 2 As shown in c, the final removal efficiency for chloride ions is 36.2%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com