Integral microchip laser with frequency modulation function
A microchip laser and frequency modulation technology, applied in lasers, laser parts, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problems of stable and reliable operation of device manufacturing, and achieve the effects of improving stability, reducing costs, and compacting devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
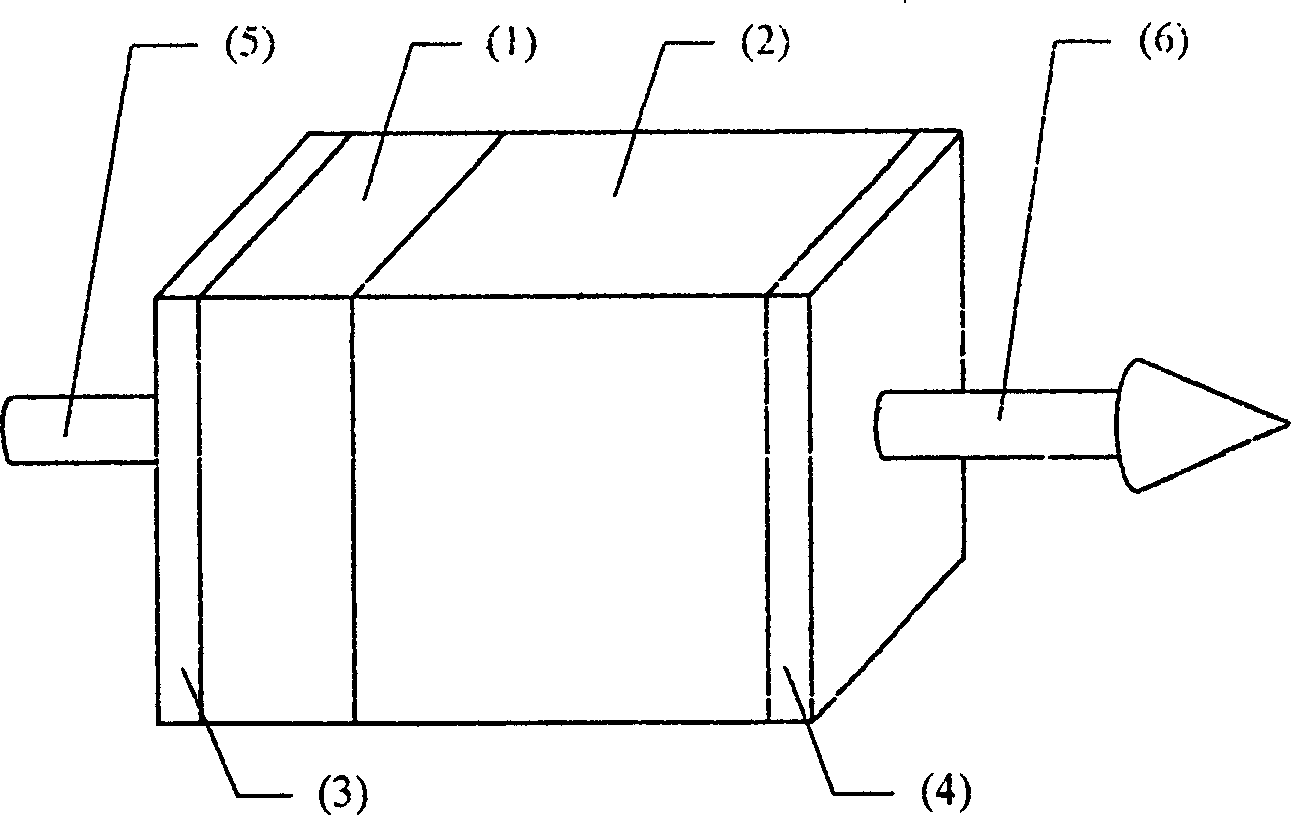
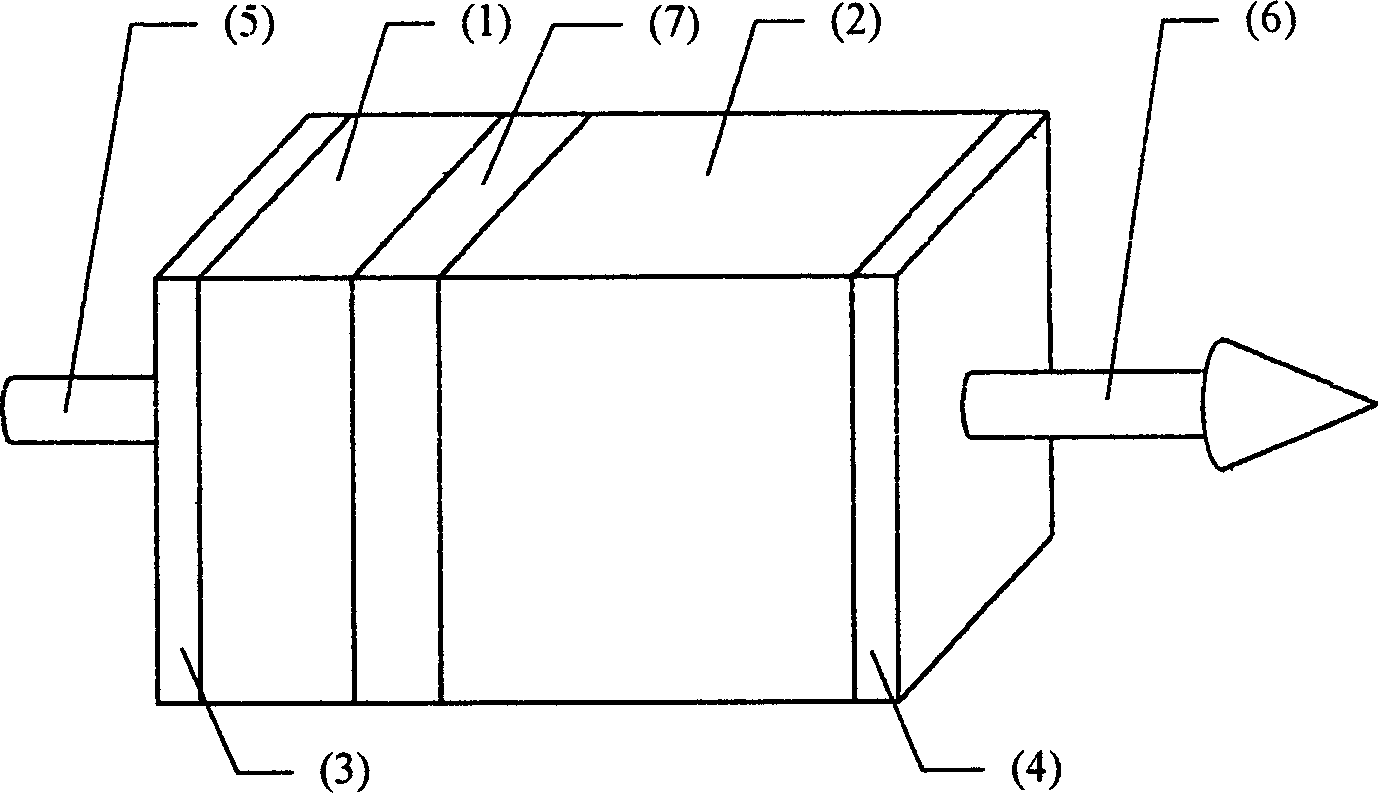
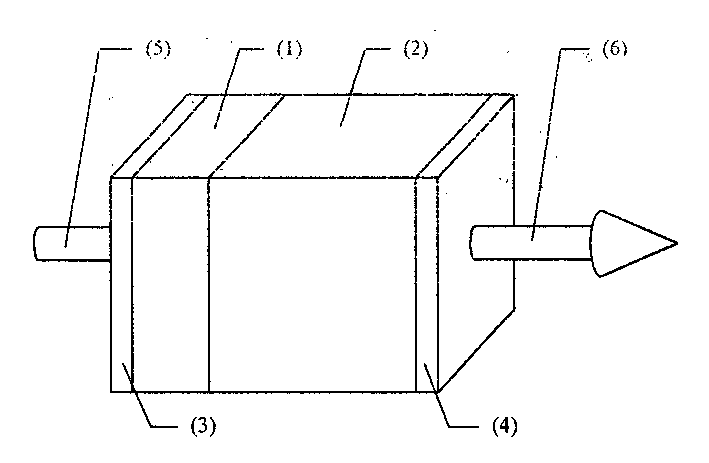
[0021] Example 1: For Nd 3+ ions of 1062 nm ( 4 f 3 / 2 → 4 I 11 / / 2 ) Fundamental wave laser frequency doubling produces 531 nm green laser output. Nonlinear Optical Crystal YAl 3 (BO 3 ) 4 Along the type I phase matching angle θ I =30.7° directional cutting, at the same time determine the size of the crystal (generally a square or cylinder with an end area of mm square and a thickness of several mm), and place the end face in Nd containing flux after polishing x Y 1-x al 3 (BO 3 ) 4 (x is between 0.01 and 1) high temperature flux, using YAl 3 (BO 3 ) 4 As a substrate for liquid phase epitaxy growth, the required thickness of Nd can be obtained on one end face perpendicular to the phase matching direction by controlling the growth time and conditions x Y 1-x al 3 (BO 3 ) 4Crystal microchips. After obtaining the functional crystal in which the above-mentioned laser crystal microchip and the nonlinear optical crystal are integrated, plate the end face 3 as sh...
example 2
[0022] Example 2: For Nd 3+ ion at 1338 nm ( 4 f 3 / 2 → 4 I 13 / 2 ) Fundamental wave laser frequency doubling produces 669 nm red laser output. Nonlinear Optical Crystal YAl 3 (BO 3 ) 4 Along the type I phase matching angle θ I = 27.0° directional cutting, at the same time determine the size of the crystal (generally a square or cylinder with an end area of mm square and a thickness of several mm), and place the end face in Nd containing flux after polishing x Y 1-x al 3 (BO 3 ) 4 (x is between 0.01 and 1) high temperature flux, using YAl 3 (BO 3 ) 4 As a substrate for liquid phase epitaxy growth, the required thickness of Nd can be obtained on one end face perpendicular to the phase matching direction by controlling the growth time and conditions x Y 1-x al 3 (BO 3 ) 4 Crystal microchips. After obtaining the functional crystal in which the above-mentioned laser crystal microchip and nonlinear optical crystal are integrated, plate the end face 3 as shown in...
example 3
[0023] Example 3: Nd 3+ ions of 1062 nm ( 4 f 3 / 2 → 4 I 11 / 2 ) The fundamental wave laser is mixed with the 807 nm semiconductor laser as the pump light to generate a 458 nm blue laser output. Nonlinear Optical Crystal YAl 3 (BO 3 ) 4 Along the type I phase matching angle θ I =35.0° directional cutting, at the same time determine the size of the crystal (generally a square or cylinder with an end area of mm square and a thickness of several mm), and place the end face in Nd containing flux after polishing x Y 1-x al 3 (BO 3 ) 4 (x between 0 and 1) high temperature flux, using YAl 3 (BO 3 ) 4 As a substrate for liquid phase epitaxy growth, the required thickness of Nd can be obtained on one end face perpendicular to the phase matching direction by controlling the growth time and conditions x Y 1-x al 3 (BO 3 ) 4 Crystal microchips. After obtaining the functional crystal in which the above-mentioned laser crystal microchip and the nonlinear optical crystal ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com