Preparation of pyrogallic acid with pyridine as decarboxylation catalyst of 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid
A technology of pyrogallic acid and gallic acid, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of low yield, unreported, poor product quality, etc., achieve high yield, improve Purity, product quality good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
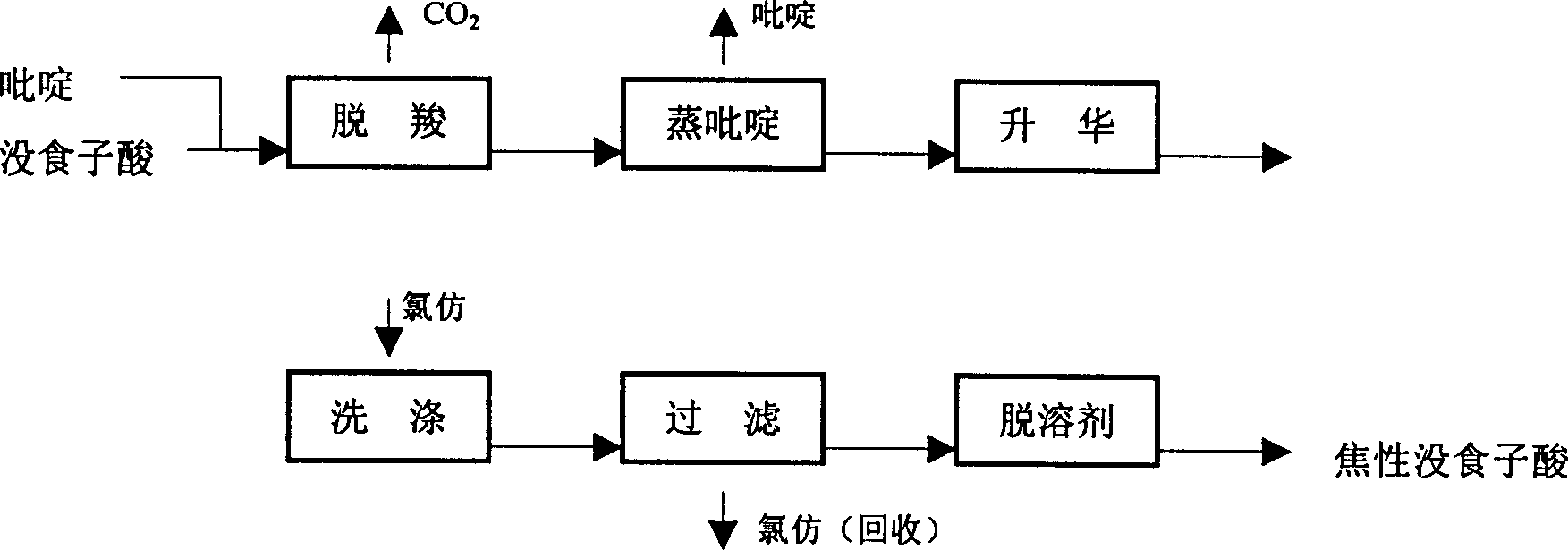
[0029] A method for preparing pyrogallic acid with pyridine as a gallic acid decarboxylation catalyst, comprising the following steps:
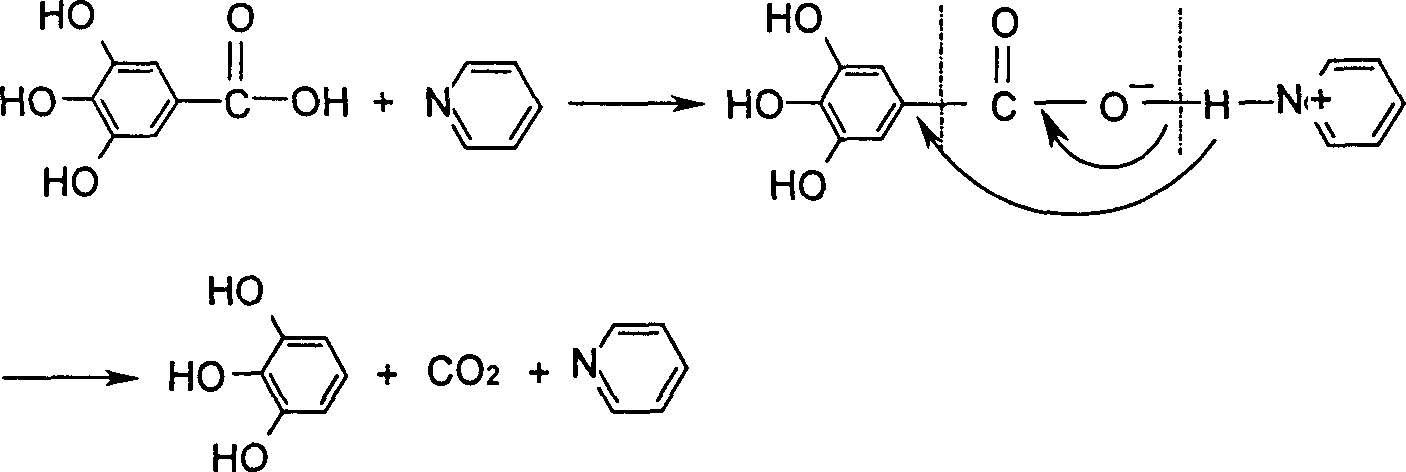
[0030] In the first step, anhydrous gallic acid and pyridine are stirred and mixed at a molar ratio of 1: (0.1-0.4), and reflux reaction is performed at 130-160°C. The material becomes a melt and a large amount of CO 2 Bubbles escape, keep warm until no bubbles are generated in the reaction product,
[0031] Wherein, the ratio of the amount of substances of anhydrous gallic acid and pyridine can be 1: 0.15, 1: 0.18, 1: 0.22, 1: 0.27, 1: 0.33, 1: 0.36, 1: 0.38, and the temperature of the reflux reaction can be 135°C, 146°C, 153°C, 158°C; the holding temperature is the same as the reflux reaction temperature, which is 130-160°C;
[0032] In the second step, keeping the temperature of the reaction product at 130 to 160° C., and gradually reducing the pressure of the atmosphere of the above reaction product to below 2 kPa from 1 standard atmosph...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Weigh 30g of anhydrous gallic acid and place it in a flask with a stirring and condenser tube, add 5ml of pyridine, and heat to 155°C under reflux for reaction under stirring. The material becomes a melt, and there is a large amount of CO at the same time 2 Bubbles escape. Incubate the reaction until no bubbles are formed. At normal pressure first, then depressurized to 2kPa, pyridine was distilled at 155°C. Continue vacuuming until the pressure is below 2kPa, and slowly raise the temperature to 175°C, and the product begins to sublimate. Keep the temperature and vacuum constant until no sublimation products escape. Take out the product and grind it, put it into a washing container, add 70ml of chloroform, stir and wash thoroughly. After filtering, rinse with a small amount of chloroform. After filtering and drying, the residual chloroform was removed in a vacuum oven at 55°C to obtain 18 g of the product. The yield is 81%. The product yield refers to the ratio of...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Weigh 100 g of anhydrous gallic acid and place it in a flask with a stirring and condenser tube, add 10 ml of pyridine, and heat to 135° C. for reflux reaction under stirring. The material becomes a melt, and there is a large amount of CO at the same time 2Bubbles escape. Incubate the reaction until no bubbles are formed. At normal pressure first, then depressurized to 2kPa, pyridine was distilled off at 150°C. Continue vacuuming until the pressure is below 2kPa, and slowly raise the temperature to 160°C, and the product starts to sublimate. Keep the temperature and vacuum constant until no sublimation products escape. Take out the product and grind it, put it into a washing container, add 180ml of chloroform, stir and wash thoroughly. After filtering, rinse with a small amount of chloroform. After filtering and drying, the residual chloroform was removed in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C to obtain 59 g of the product. The yield was 81%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com