Inhibition of membrane-associated viral replication
A technology of viruses and inhibitors, applied in antiviral agents, metabolic diseases, and resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., can solve problems such as HCV infection has no effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
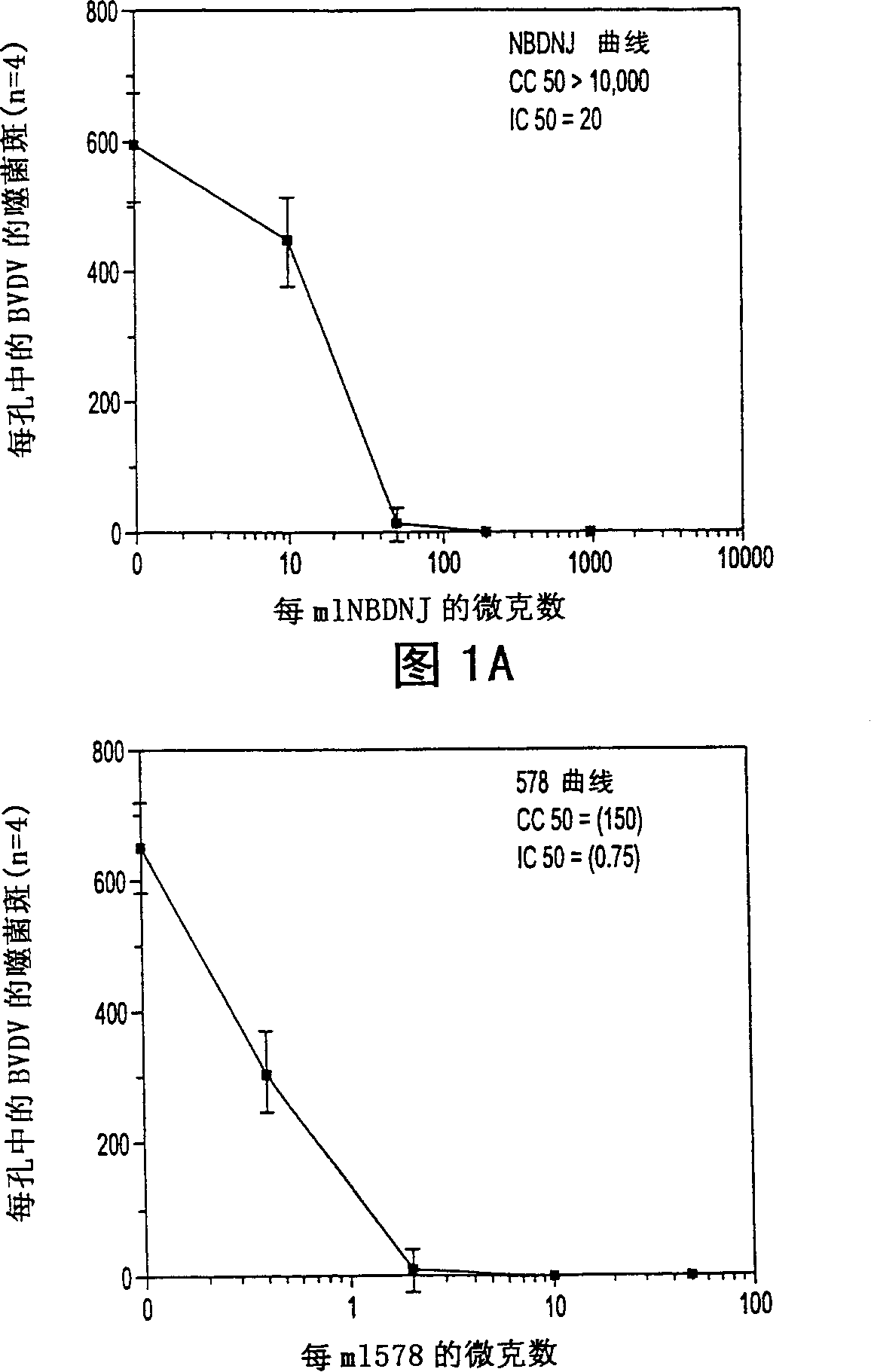
[0125] Presence of antiviral antiglucosidase on MDBK monolayers exposed to BVDV
[0126] Effects on plaque formation
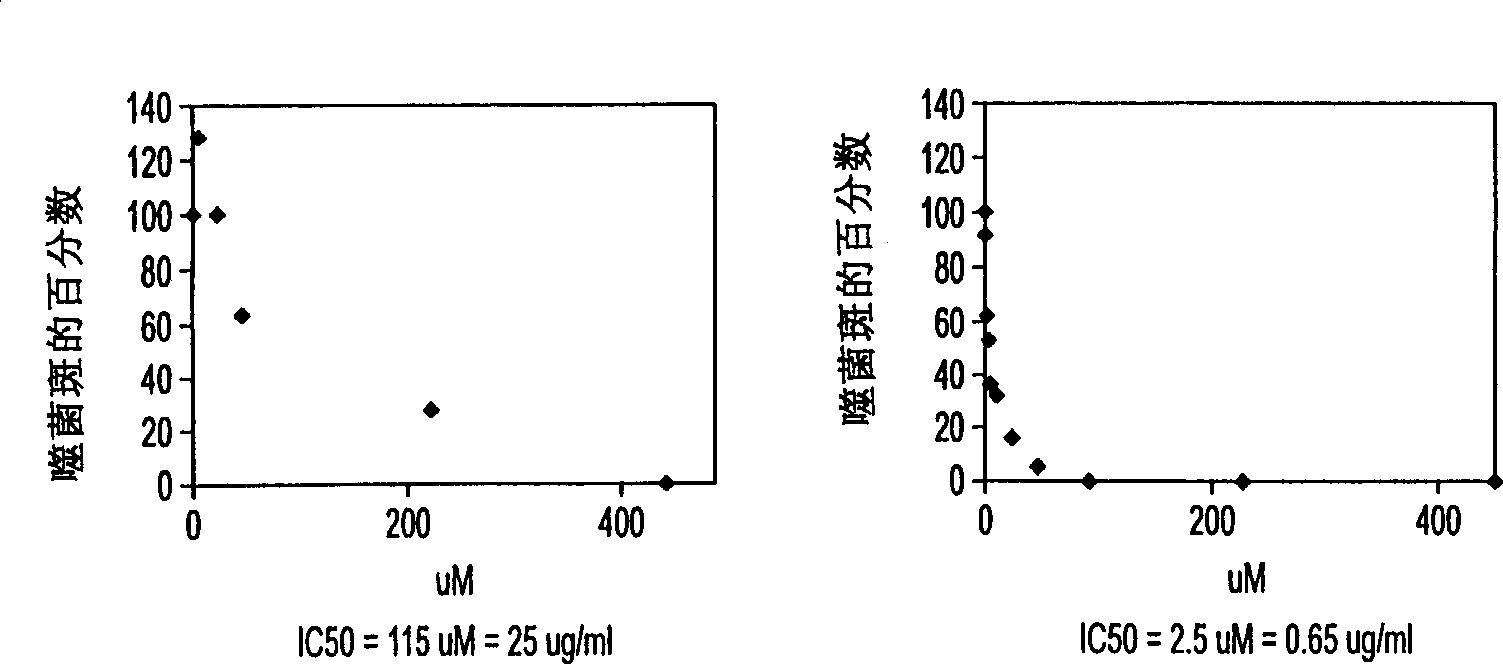
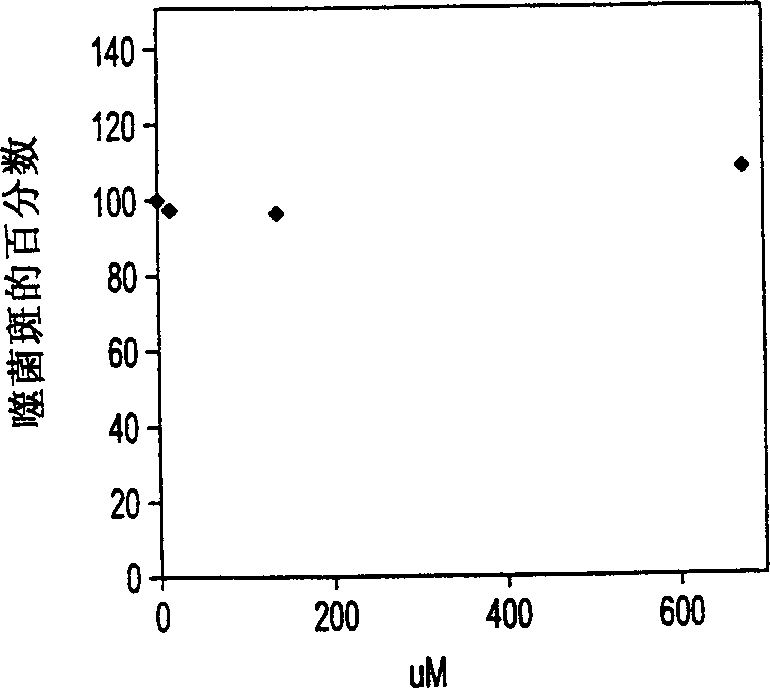
[0127] MDBK cells (ATCC Accession No. 22 CCL F11859, BVDV free) were grown to a semi-confluent state in each well of a 24-well plate and formed a monolayer of cells. The medium used was Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing 10% (v / v) horse serum. A stock solution of the NADL strain of BVDV (ATCC Accession No. NADL 534VR) was diluted to approximately 500 to 1000 plaque-forming units (pfu) per milliliter, suspended in growth medium, and cells were incubated for one hour in the presence of virus to A multiplicity of infection (moi) (plaque formation condition) of less than 1 infects approximately 10 5 cells. growth medium alone or with Figure 5 The growth medium replaces the inoculum with the amount of drug indicated on the axis (up to 1000 micrograms NBDNJ per milliliter). Three days after infection, before and after the monolayer cells were staine...
Embodiment 2
[0133] Secretion of infectious BVDV in the presence of N-butyl-DNJ and N-nonyl-DNJ
[0134] MDBK cells were grown to a semi-confluent state in each well of a 24-well plate. Cells were then infected with BVDV by incubating them at 37°C for 1 hour in the presence of approximately 500 pfu of BVDV's NADL strain suspended in growth medium. The inoculum was replaced with growth medium or growth medium containing NBDNJ and NNDNJ at the concentrations shown in Tables 2 and 3, respectively. The supernatant was taken three days later and used to infect fresh MDBK monolayers in six-well plates. Three days later, the monolayer cells were stained with 0.2% (W / V) crystal violet in ethanol before and after staining with a microscope to detect the presence of phage plaques. Stain to check viability, detect and count virus-induced plaques. Results are expressed as percentage of plaques (=100%) formed when infection was performed with plaque detection supernatant without inhibitor. In Table...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Control detection of NB-DGJ inhibition of ceramide-specific glucosyltransferase
[0144] MDBK cells in 14 C-palmitate N-butyl-deoxygalactojirimycin in the presence of growth to confluence. Cells were washed three times with PBS, scraped from culture flasks, and extracted with chloroform:methanol (2:1, v / v) overnight at 4°C. Save the initial extract and add 0.5 ml of chloroform:methanol (2:1, V / V) for extraction at room temperature for three hours. Extracts were pooled and aliquoted for scintillation counting. The sample was adjusted to 200,000 cpm, dried under nitrogen, then suspended in 10 μl of chloroform:methanol (2:1, V / V), and separated by TLC (chloroform:methanol (2:1, V / V). Radiolabeled Lipids were detected by fluorophore and the observed dose-dependent decrease in Glc-ceramide and gangliosides (data unpublished) indicated inhibition of ceramide-specific glutransferase at concentrations that had no antiviral effect .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com