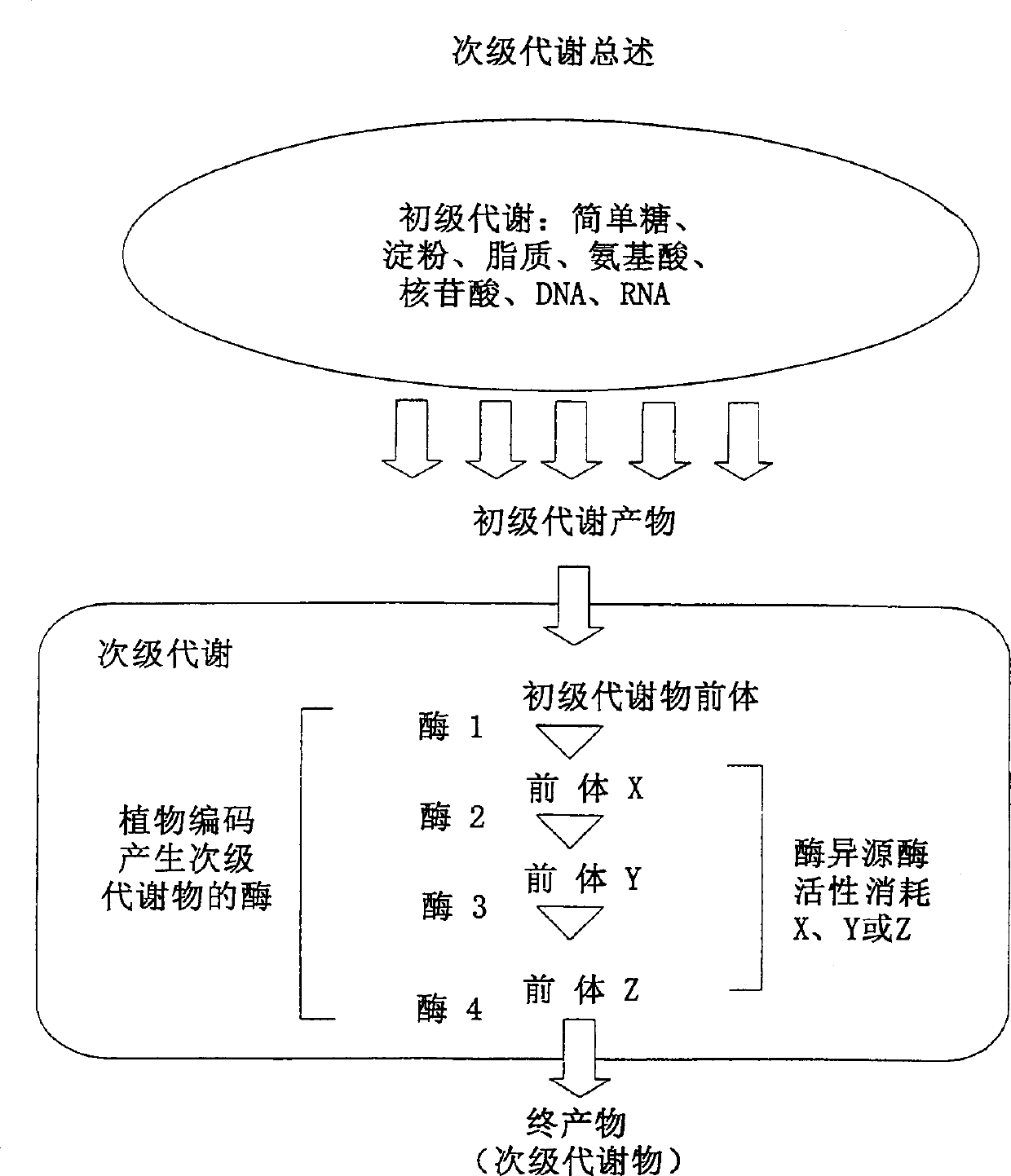
Method for compositions for modifying levels of secondary metabolic compounds in plants
A technology for plants and plant cells, applied in the field of genetic constructs and vectors, modified seed powder, seed powder with reduced or changed secondary metabolite content, and plant seeds, which can solve the problem of affecting the expression of related genes, without providing secondary Metabolites, harmful effects, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
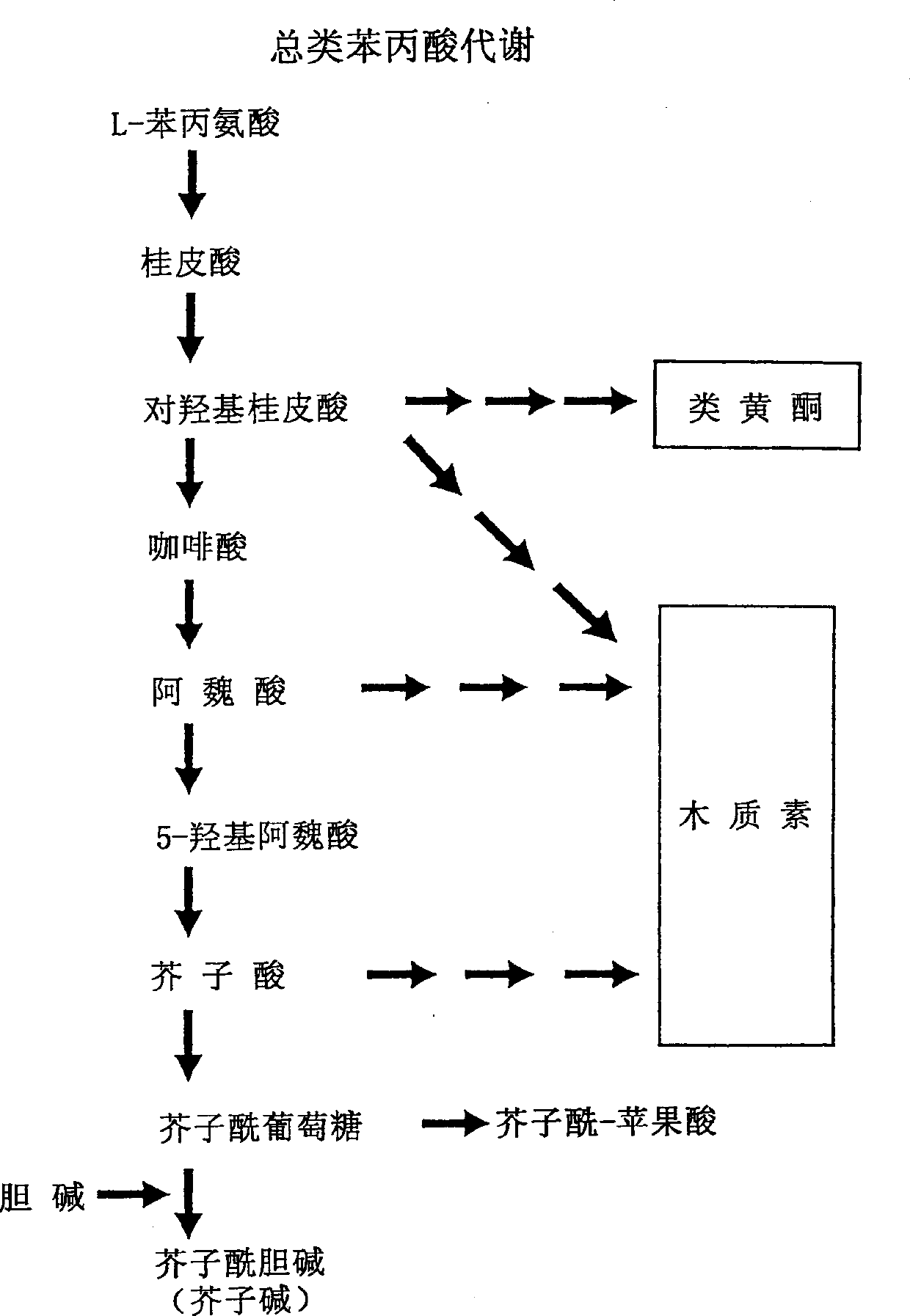
[0207] The following examples serve to illustrate this method, but in no way limit the scope of the invention. Example 1: General method used to identify products of the phenylpropanoid pathway: Determination of the content of sinapine, the end product of the phenylpropanoid pathway, in the seeds of cruciferous plants
[0208] It will be apparent that all of the exemplified methods can be adapted by the skilled artisan for the determination of products in the phenylalanoid pathway with reference to numerous publications in analytical chemistry. In the first method as an example, a simple assay for the identification of sinapine in plant tissue, namely the seed tissue of cruciferous plants, was adapted from a published method (Chapple C.C.S., T. Vogt, B. E. Eills and C. R. Somerville, 1992, The Plant Cell 4: 1413-1424). Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) protocols were standardized for the assessment of the product sinapine in the phenylalanine pathway. This method uses the isol...
Embodiment 2
[0215] Plant material can also be extracted with a chloroform:methanol:formic acid (CMF) mixture in a ratio of 5:12:3, respectively. Typically, 2 μl of CMF is added to 1 mg of sample, the sample is crushed, left overnight (16 hours) at room temperature (21-23° C.), and then centrifuged at approximately 12,000×g for 5 minutes. The supernatant was collected, and the pellet was thoroughly mixed with another volume of CMF added as before, left for 20 minutes, and centrifuged as above. The supernatants were pooled and extracted with chloroform-water (CW) as previously described, and the aqueous fraction was analyzed as above. Example 2: Identification of the localization of product synthesis of the phenylpropanoid pathway in specific plant tissues.
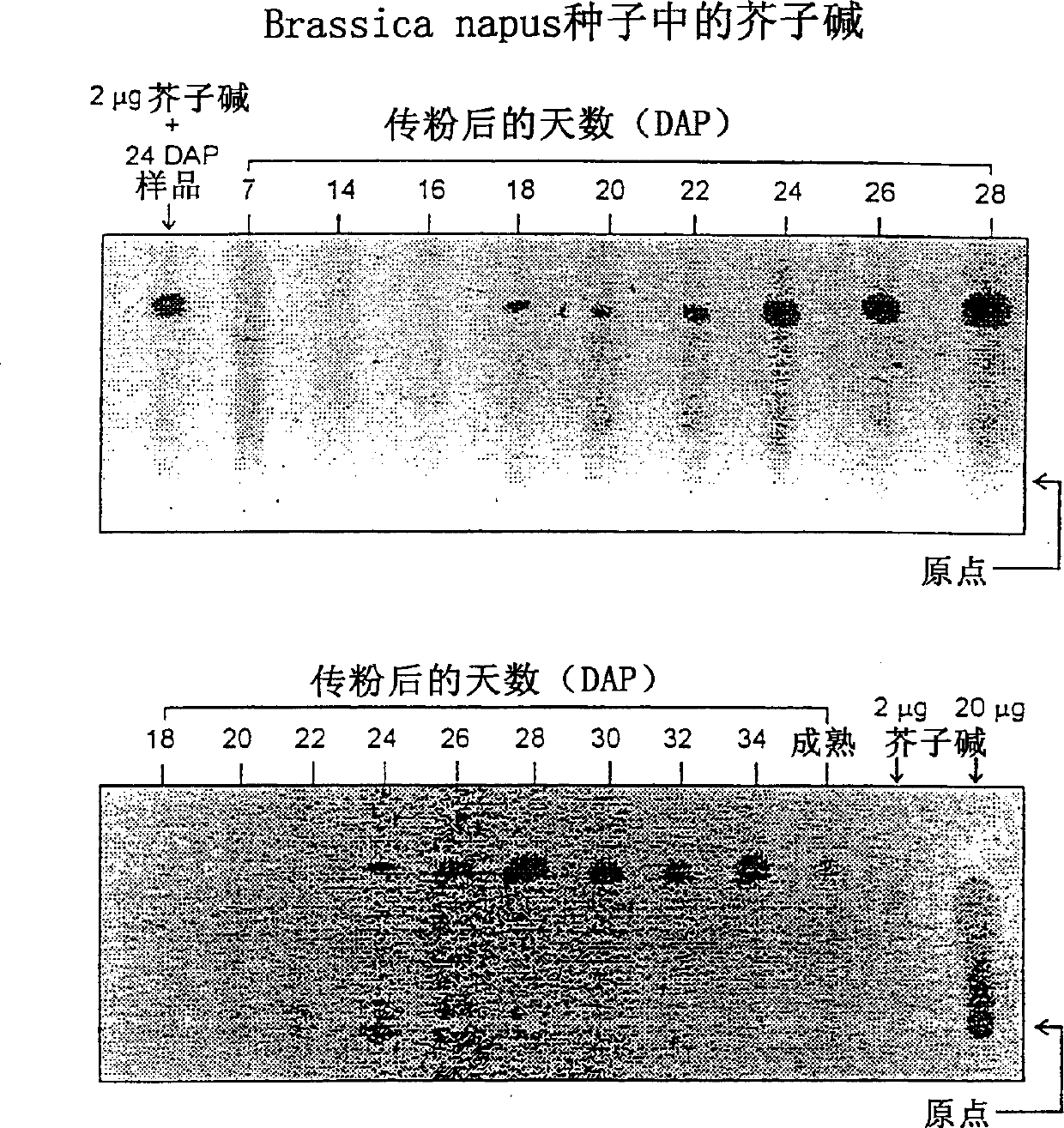
[0216] In this example, the developmental timing of product synthesis of the phenylalanoid pathway was determined. This particular example exemplifies sinapine synthesis and accumulation in cruciferous plant seed tissues. In this ex...
Embodiment 3
[0217] The portion of the pod wall from which the seeds were detached contained no sinapine, as did the younger seeds on the samples from 7-, 14-, and 16-DAP. This analysis indicated the onset of sinapine accumulation at approximately 18 DAP, however, because this method uses UV fluorescence detection, even small amounts present in younger seeds were not detectable. Figure 3 shows an example of TLC analysis of samples up to 28 DAP, the second panel shows an example up to seed maturity. Since, the above results are not quantitative, extracts of whole seeds obtained with methanol solution were analyzed by HPLC as described in Example 1. The results presented in Figure 4 demonstrate a rapid sequential growth from 20DAP sinapine synthesis to maturity. The amount of sinapine in mature seeds is about 0.8% dry weight of seeds, since oil will make up about 45% of seeds, which will convert to about 1.5% of defatted seed meal. Example 3: Determination of Temporal and Spatial Aspects o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com