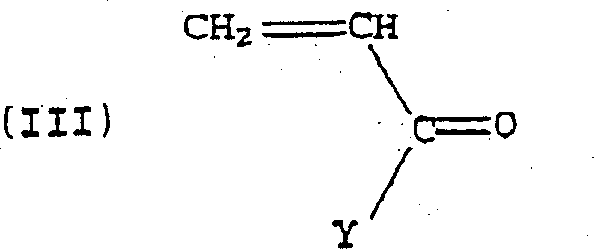
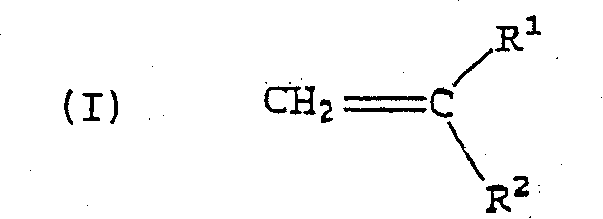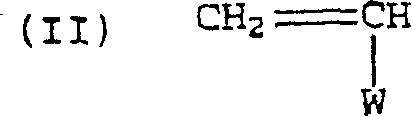Alternating copolymers of isobutylene type monomers
A technology of copolymers and monomers, applied in the direction of coating, etc., can solve problems such as toxicity, poor stability, and discoloration of coatings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-A
[0183] Synthesis of alternating copolymer diisobutylene / methyl methacrylate-alternating-hydroxypropyl acrylate / butyl acrylate. Polymerization was performed using the ingredients in Table 3 below.
[0184] table 3
[0185] Element
[0186] Feedstock 1 was added to a 4 liter stirred stainless steel pressure reactor. The reactor was then pressurized with nitrogen to provide a 5 psig blanket over the reactor. The stirring on the reactor was 500 rpm and the reactor temperature was adjusted to 125°C. Feedstock 2 was added to the reactor at a rate of 9.62 grams / hour over a period of 3.5 hours. Fifteen minutes after starting feed 2, feed 3 was added to the reactor at an addition rate of 262.10 g / hr over a period of 3 hours. During the monomer addition, the temperature was maintained at 125°C, 40 PSI. After the addition of starting material 2 and starting material 3 was complete, the reaction mixture was allowed to stand for 2 hours. The reactor was then cooled to 25...
Embodiment 1-B
[0188] Synthesis of alternating copolymer diisobutylene-alternating-hydroxypropyl acrylate / butyl acrylate. Polymerization was carried out in isopropanol solvent using the ingredients in Table 4 below.
[0189] Element
[0190] Feedstock 1 was added to a 4 liter stirred stainless steel pressure reactor. The reactor was pressurized with nitrogen to provide a 5 psig blanket over the reactor. The stirring on the reactor was set to 500 rpm and the reactor temperature was adjusted to 150°C. Feedstock 2 was added to the reactor at an addition rate of 48 grams / hour over a period of 2.5 hours. After 15 minutes, feedstock 3 was added to the reactor at an addition rate of 250 grams / hour over a period of 2 hours. During the monomer addition, the temperature was maintained at 150°C and 100 PSI. After feedstock 2 and feedstock 3 were added to the reactor, the reaction mixture was left for 2 hours. The reactor was then cooled to 25°C and vented. GC analysis of the reaction...
Embodiment 1-C
[0192] Synthesis of alternating copolymer diisobutylene-alternating-hydroxyethyl acrylate / butyl acrylate. Polymerization was carried out in isopropanol solvent using the ingredients in Table 5 below.
[0193] Element
[0194] Feedstock 1 was added to a 4 liter stirred stainless steel pressure reactor. The reactor was then pressurized with nitrogen to provide a 5 psig blanket over the reactor. The stirring on the reactor was set to 500 rpm and the reactor temperature was adjusted to 150°C. Feedstock 2 was added to the reactor at an addition rate of 48 grams / hour over a period of 2.5 hours. After 15 minutes, feedstock 3 was added to the reactor at an addition rate of 250 grams / hour over a period of 2 hours. During the monomer addition, the temperature was maintained at 150°C and 100 PSI. After feedstock 2 and feedstock 3 were added to the reactor, the reaction mixture was left for 2 hours. The reactor was then cooled to 25°C and vented. GC analysis of the reac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| dispersity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polydispersity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com