Hybrid matrices and hybrid matrix mixtures
A technology of mixtures and compositions, which is applied in the directions of non-active components of polymer compounds, drug combinations, drug delivery, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
[0087] Heparin-Sepharose Hybrid Collagen Matrix (HSHCM) Overview
[0088] HSHCM is produced by mixing together the following components: concentrated Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM), collagen (e.g., rat tail type I or a suitable alternative, e.g., human placental type I or type III collagen), Microcarriers (e.g. collagen macroporous microcarriers or porous gelatin microcarriers as described above), uncoated or treated with angiogenic factors, cytokines or growth factors (e.g. basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) or platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)) coated Heparin-Sepharose(R) beads, and cells expressing the therapeutic protein. In an alternative embodiment, multiple cell lines are mixed into the matrix, one expressing a therapeutic protein of interest and another expressing an angiogenic factor, cytokine or growth factor. A cell line expressing both a therapeutic protein and an angiogenic or growth factor can also be ...
Embodiment II
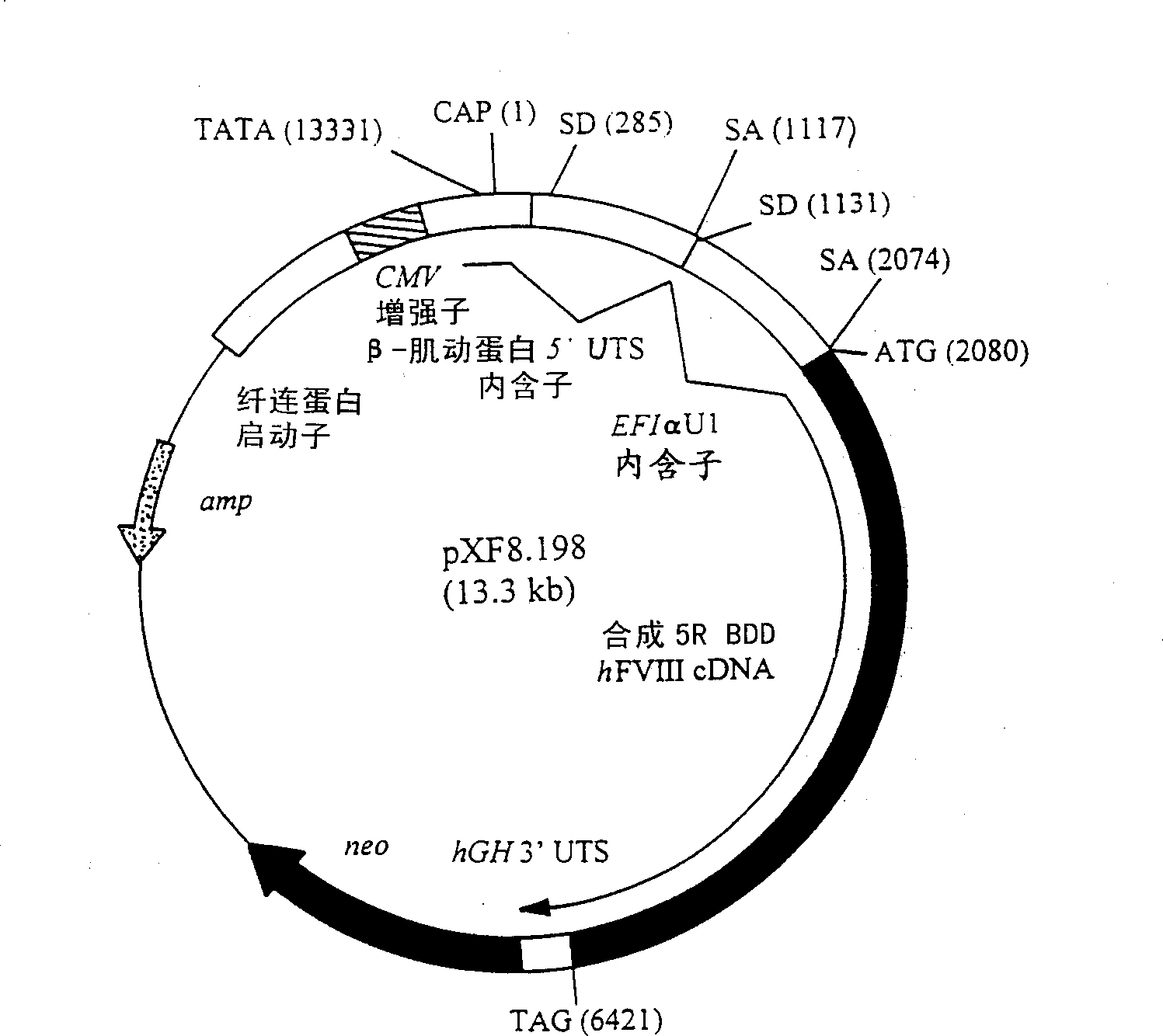
[0121] This example describes the in vivo implantation of HSHCM prepared as described in Example 1. HSHCM containing uncoated Heparin-Sepharose(R) beads or bFGF-coated Heparin-Sepharose(R) beads (50 [mu]g / ml packed beads; 10 [mu]g total bFGF / matrix) was prepared as described in Table 1. Use 5×10 per 4ml matrix 6 HF743 B1-35 cells formed, which is a plasmid containing pXF8.198 ( figure 1 ) and at 20 000-30 000mU / 24h / 10 6 Cellular levels of human foreskin fibroblast clones expressing hFVIII. More detailed procedures for preparing and transfecting cells suitable for the matrices and mixtures of the present invention are provided in WO93 / 09222 (PCT / US92 / 09627), incorporated herein by reference. HSHCM were kept in culture for 2 days prior to implantation. For subcutaneous infusion of matrix, Rag-2 mice (129S6 / SvEvTac-[KO]Rag2, Taconic Farms) were anesthetized and prepared as follows. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with Avertin at a dose of 0.0175ml / g body weight TM (2% ...
Embodiment III
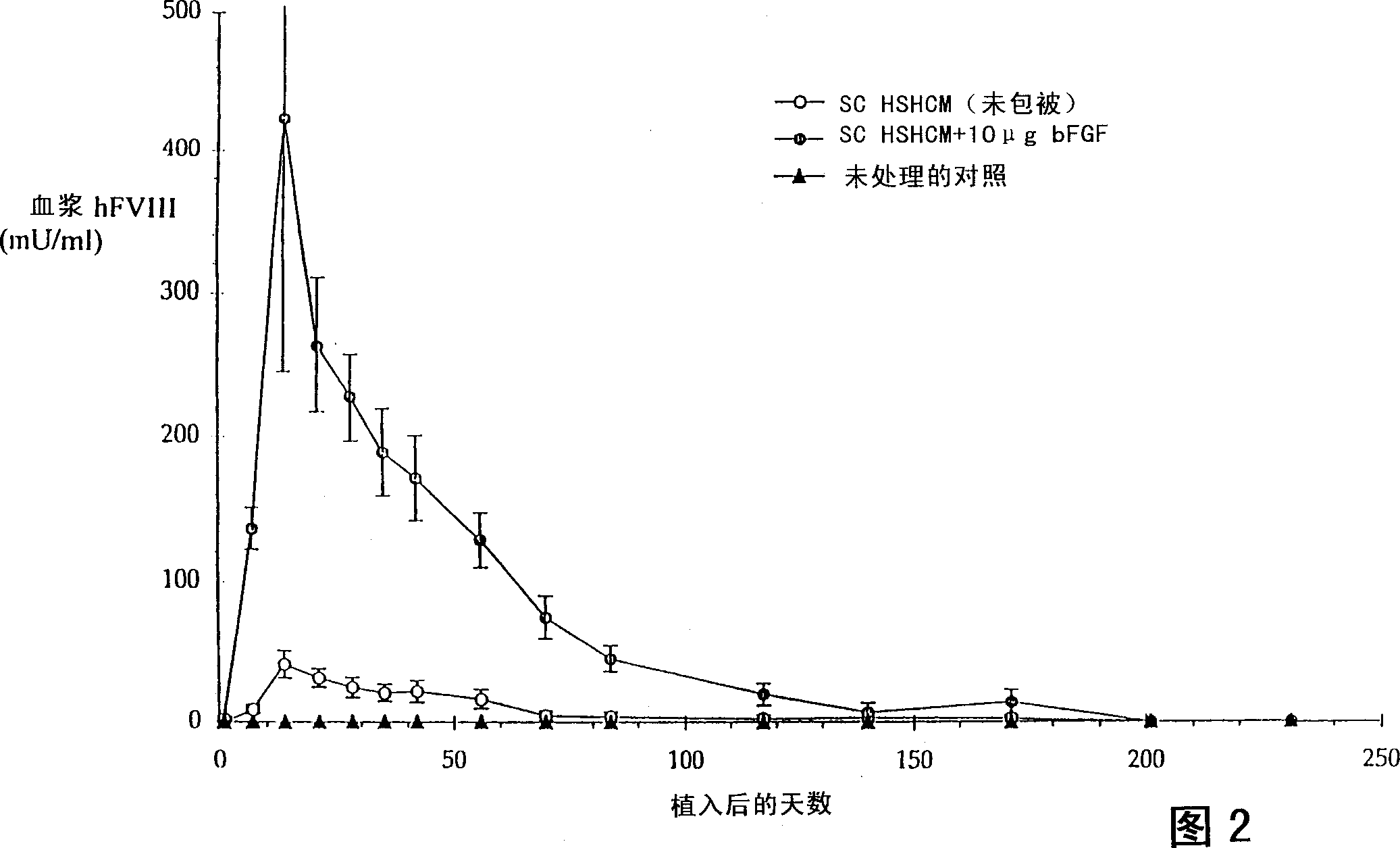
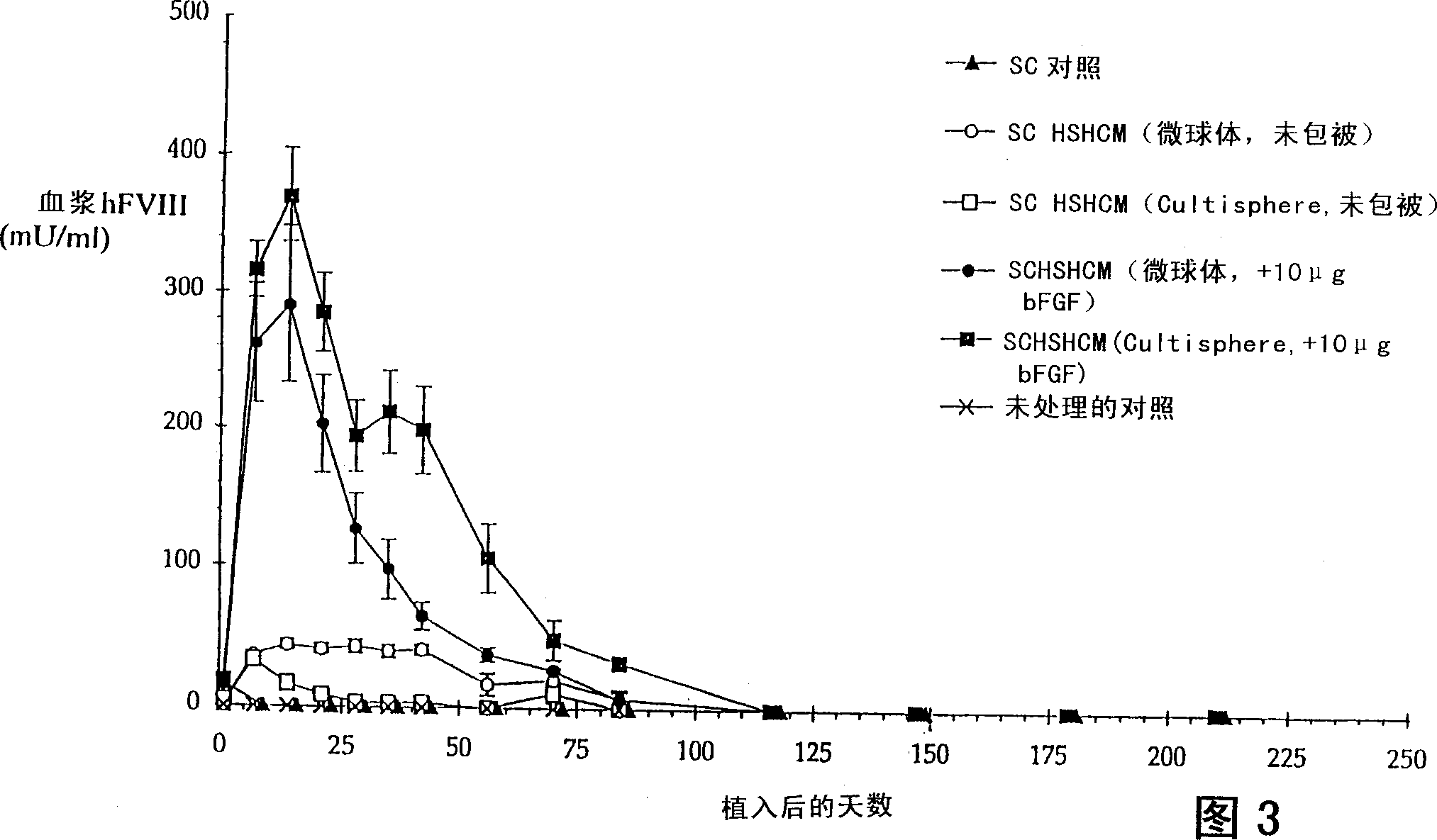
[0125] HSHCM containing uncoated heparin-Sepharose beads or bFGF-coated heparin-Sepharose beads (50 μg / ml packed beads, 10 μg total bFGF / matrix), and collagen microcarriers or gelatin microcarriers, as shown in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively The preparation. The average cell number per matrix and the hFVIII production per matrix (n=3 matrixes per condition) on the day of implantation are listed in Table 3.
[0126] condition
Cell number (×10 6 )
hFVIII (mU / 24h /
HSHCM)
Collagen microcarriers and uncoated heparin
- Sepharose® beads
4.2
84 989
Gelatin microcarriers and uncoated heparin
- Sepharose® beads
3.9
94 407
Collagen microcarriers and bFGF-coated
Heparin-Sepharose® beads
4.3
138 612
Gelatin microcarriers and bFGF-coated
Heparin-Sepharose® beads
3.5
107 683
[0127] A subcutaneous (SC) cell control was included in the experiment and was ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap