Ion-sensitive water-dispersible polymers, method of making same and product using same
A technology of ions and compositions, applied in the direction of anionic surface-active compounds, surface-active detergent compositions, detergent compositions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0180] Preparation of Acrylic Acid Terpolymer Modified by Sulfonate Anion
[0181] Acrylic acid (43.3g, 0.60 mole), AMPS (10.7g, 0.052 mole), butyl acrylate (35.2g, 0.27 mole), and 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (20g, 0.11 mole) were dissolved in 55g of acetone / in water (70 / 30) mixture. The initiator, 2,2-azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) (0.51g), 3.1×10 -3 mol), dissolved in 20ml of acetone. By adding N 2 The monomer solution was deoxygenated by bubbling through it for 20 minutes. To a 1000 ml three necked round bottom flask equipped with a condenser, two addition funnels and a magnetic stirrer was added 120 g of an acetone / water (70 / 30) mixture. The solvent was heated to reflux under nitrogen atmosphere. Monomer and initiator were added simultaneously from the addition funnel over 2 hours. The polymerization was allowed to proceed for an additional two hours, at the end of which time the addition funnel and condenser were replaced with a distillation head and mechanical stir bar t...
Embodiment 3
[0188] Preparation of ion-sensitive polymer formulations
[0189] The polymers prepared in Table 5, Sample 9 and Example 2 above were mixed with Dur-O-Set RB to form ion-sensitive polymer formulations of the present invention. The polymer formulations were prepared as shown in Table 6 below.
[0190]
[0191] Solubility of ion-sensitive polymer formulations
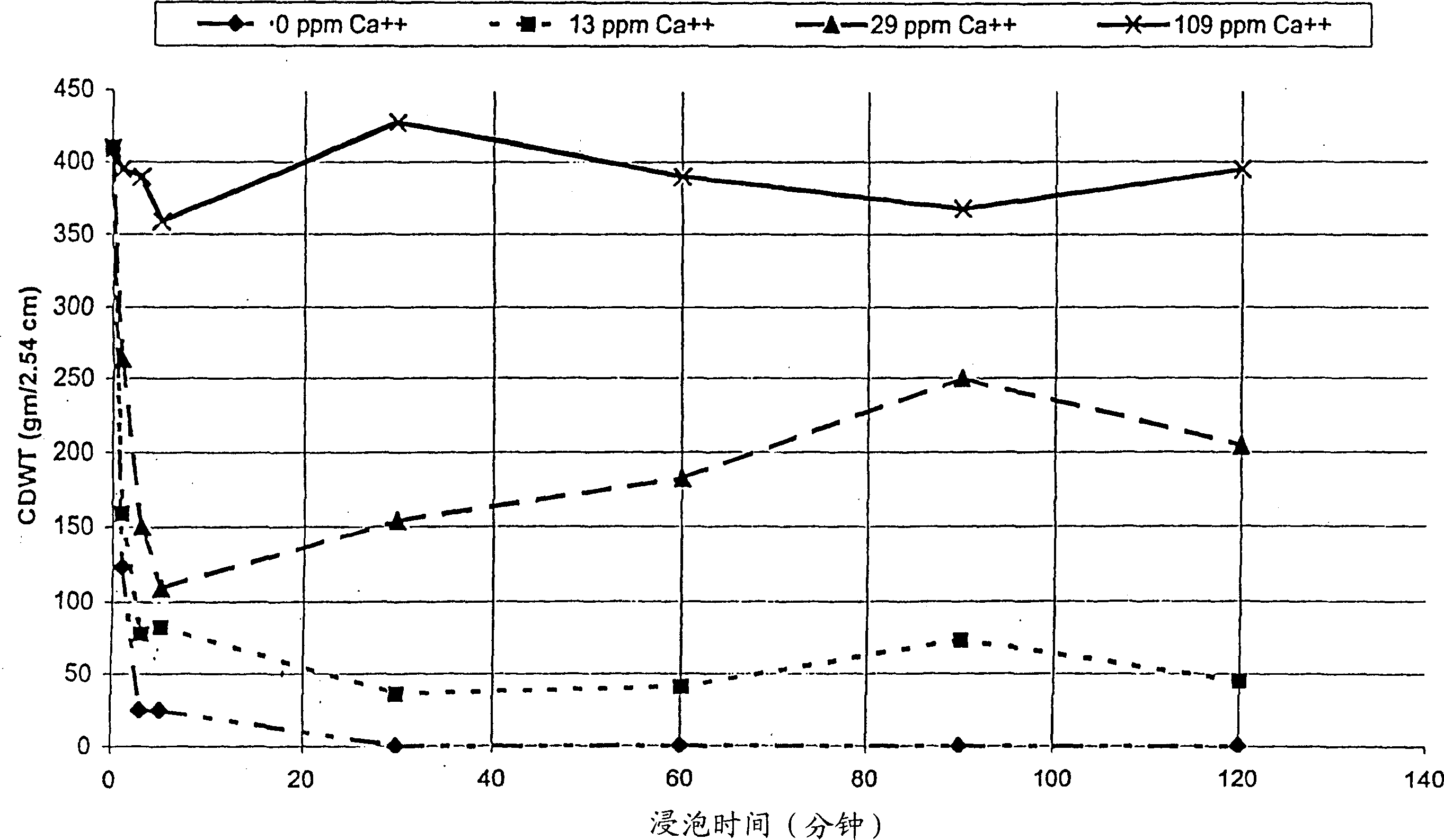
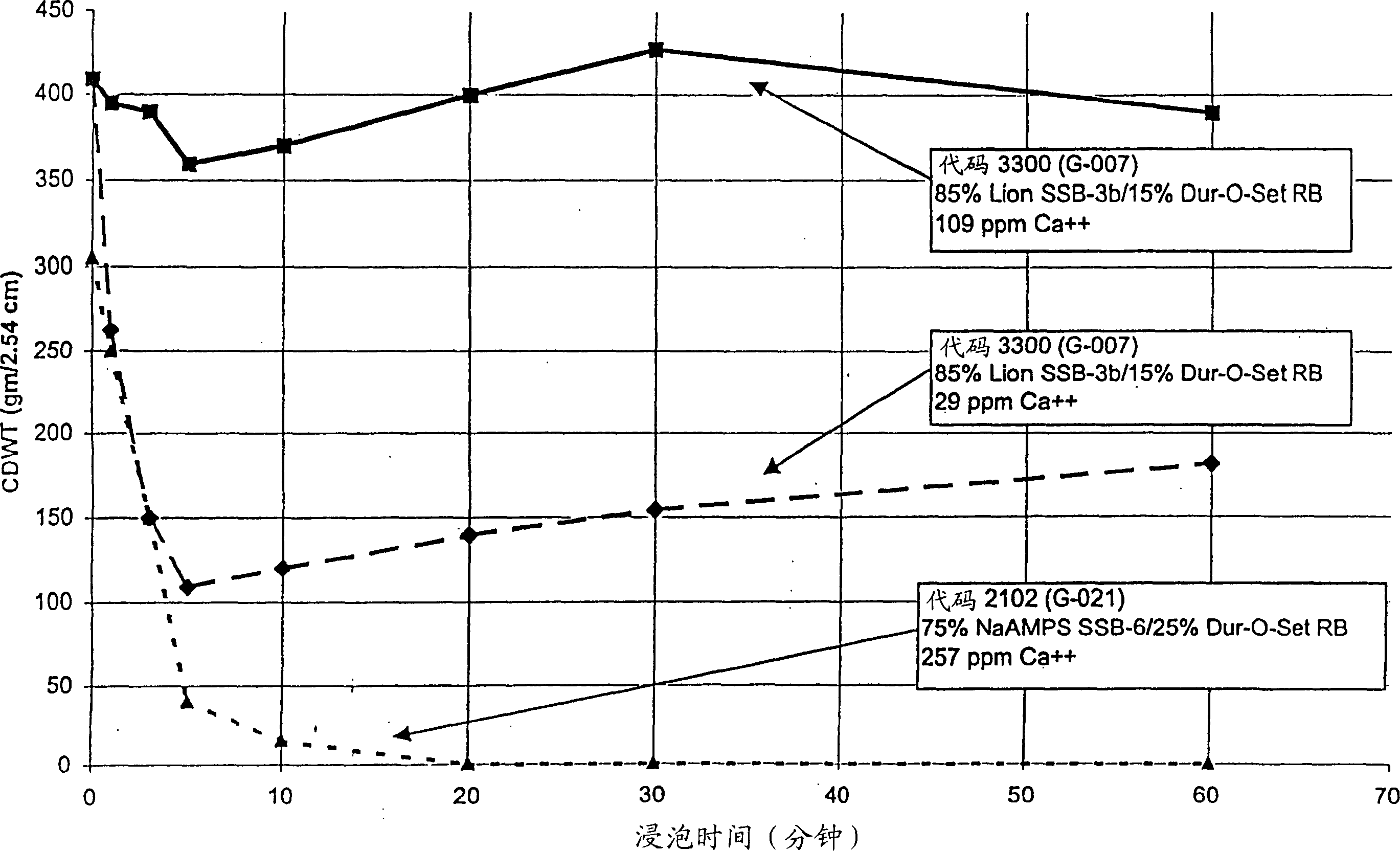
[0192] The sensitivity of the polymer formulation of Example 3 to the presence of divalent cations in hard water was measured. Samples 1-10 of Example 3 were placed with Ca varying from 2+ Several concentrations of CaCl 2 in solution. After soaking for 1 hour, the solubility of each polymer was noted. Solubility results are given in Table 7 below.
[0193] sample
[0194] In each case, films cast from blends containing NaAMPS were more soluble than films containing acrylic acid terpolymer, especially with increasing calcium ion concentration.
Embodiment 5
[0196] Test of cohesive strength of polymer formulations with and without crosslinking
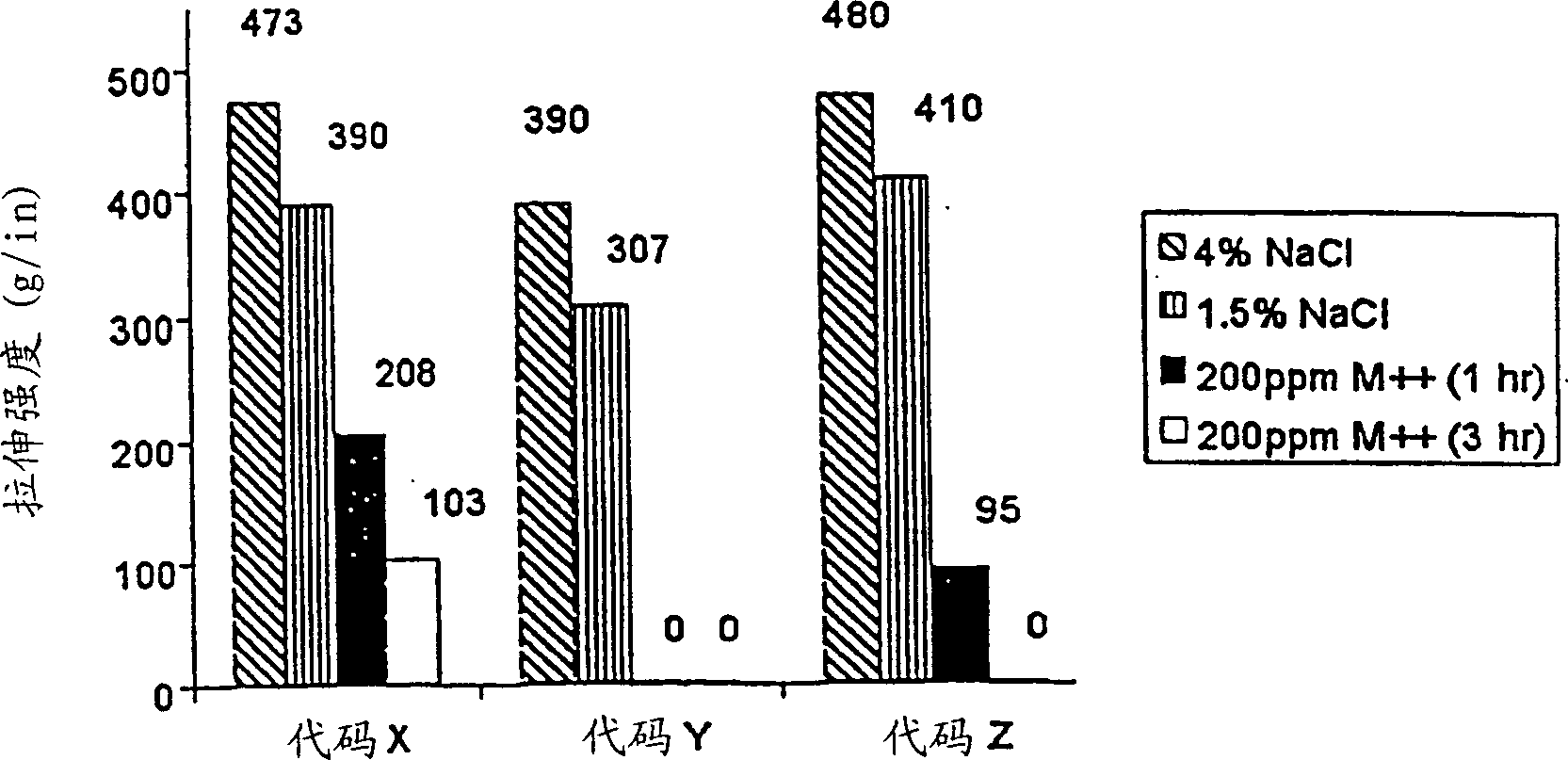
[0197] For pilot scale experiments we used airlaid substrates of the pulp type (CF405 or NB416 pulp form Weyerhaeuser) bonded together with 2-5% bico fibers. The bico fibers were Type-255 with activated polyethylene sheath and polyester core (obtained from KoSa Fibers of Salisbury, NC) or Danaklon fibers with polyethylene sheath and polypropylene core (obtained from FiberVisions of Vbarde, Denmark). Both types of bico fibers are 2-3 denier and cut to 6mm lengths. The adhesive formulation was applied by spraying a 12-15% by weight solution onto both sides of the aforementioned substrate. The strength of the substrate under various conditions is reported after subtracting the basic strength of the sheet due to the bico fibers. Table 8 reports the strength of substrates with different formulations in 0.4% by weight NaCl (CDWT) and after soaking in deionized water for 1 hour (S-CDWT):
[01...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com