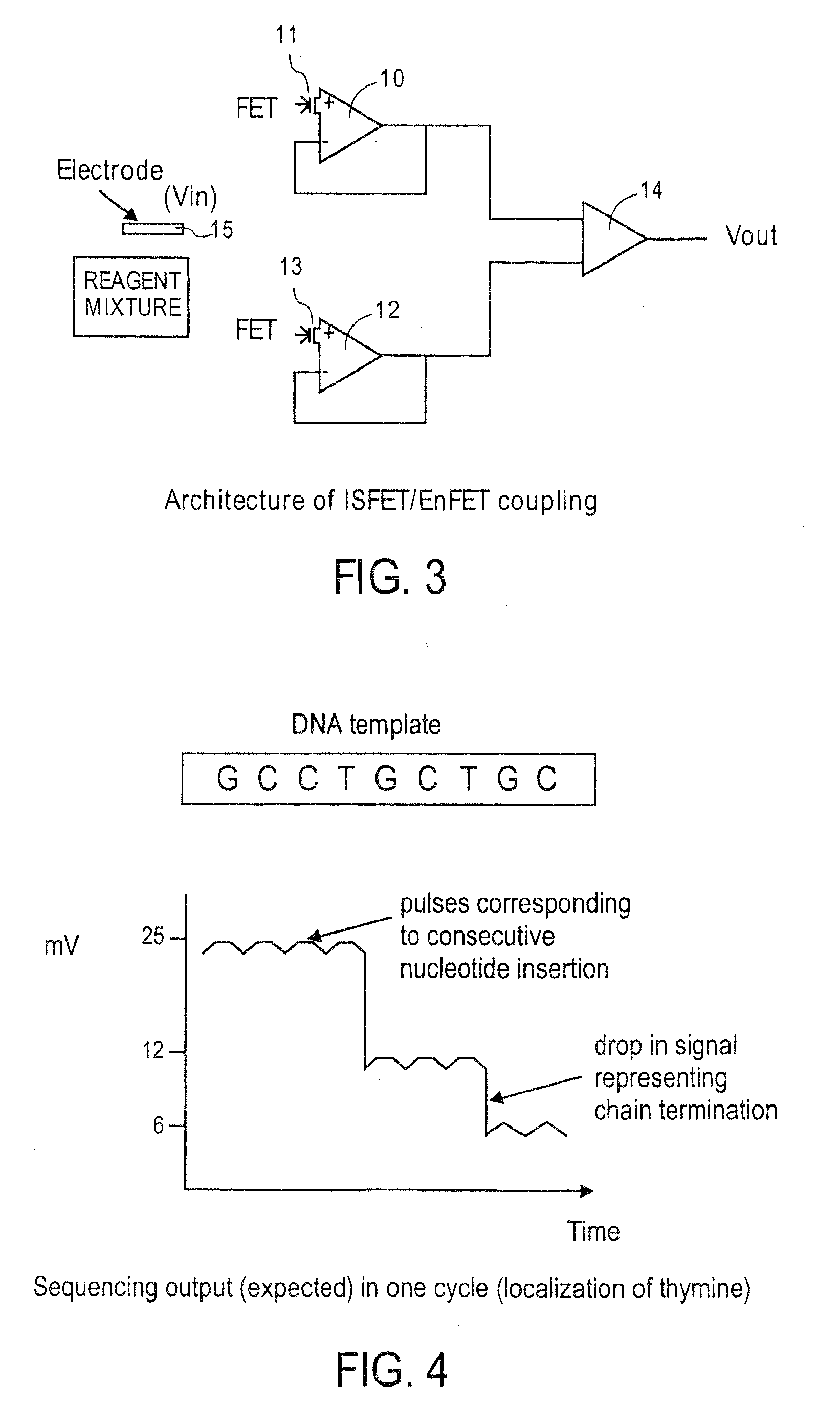
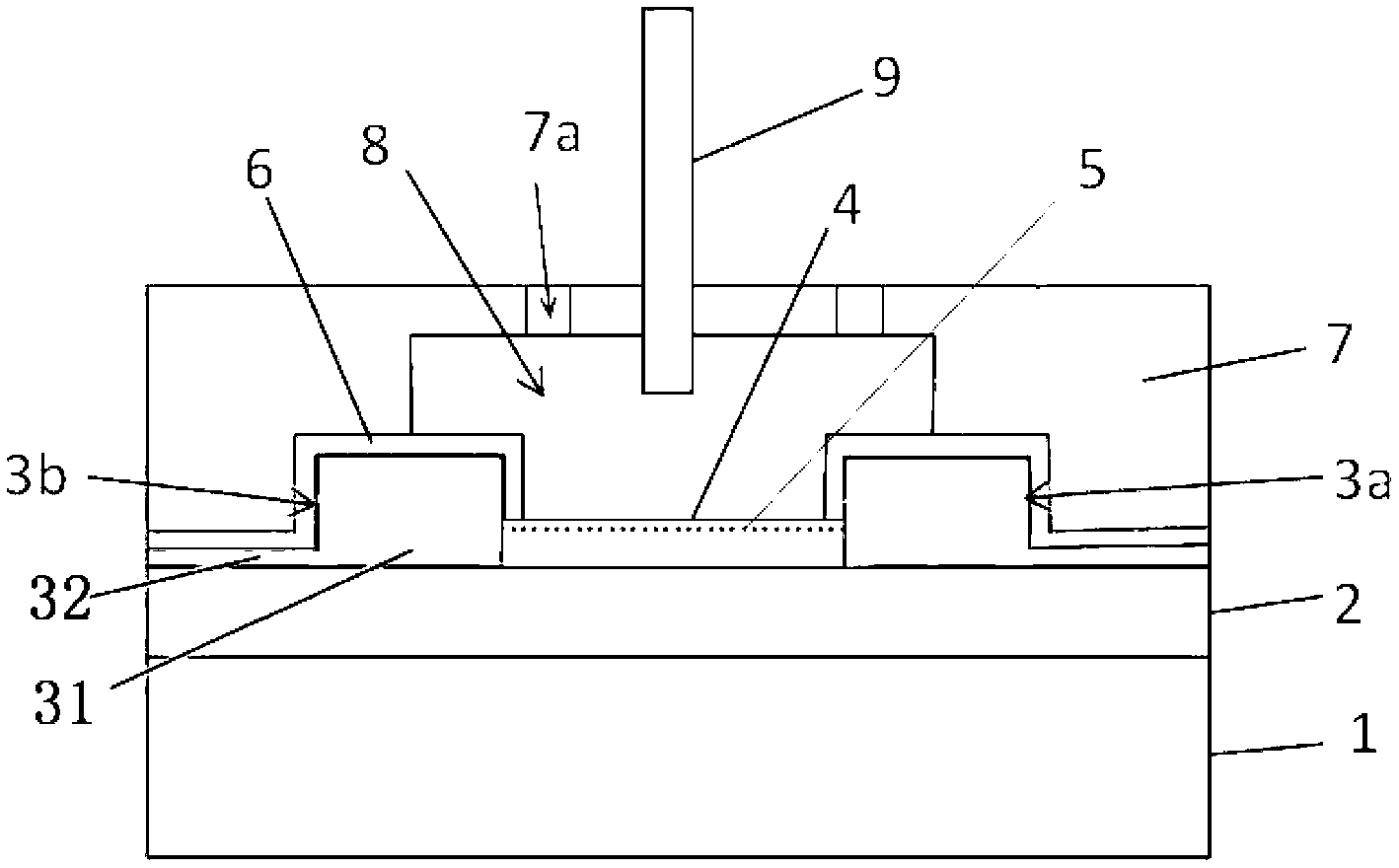
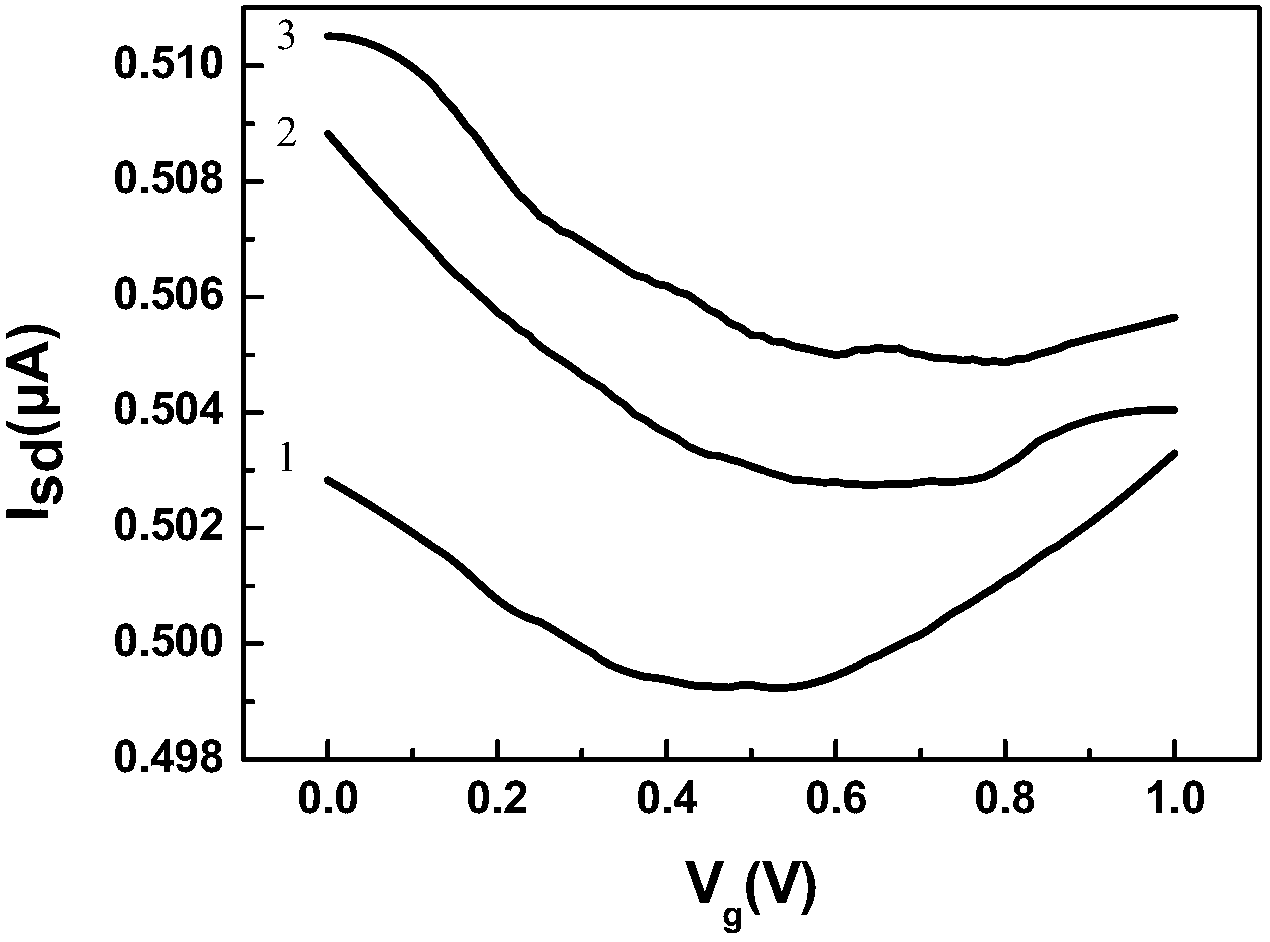
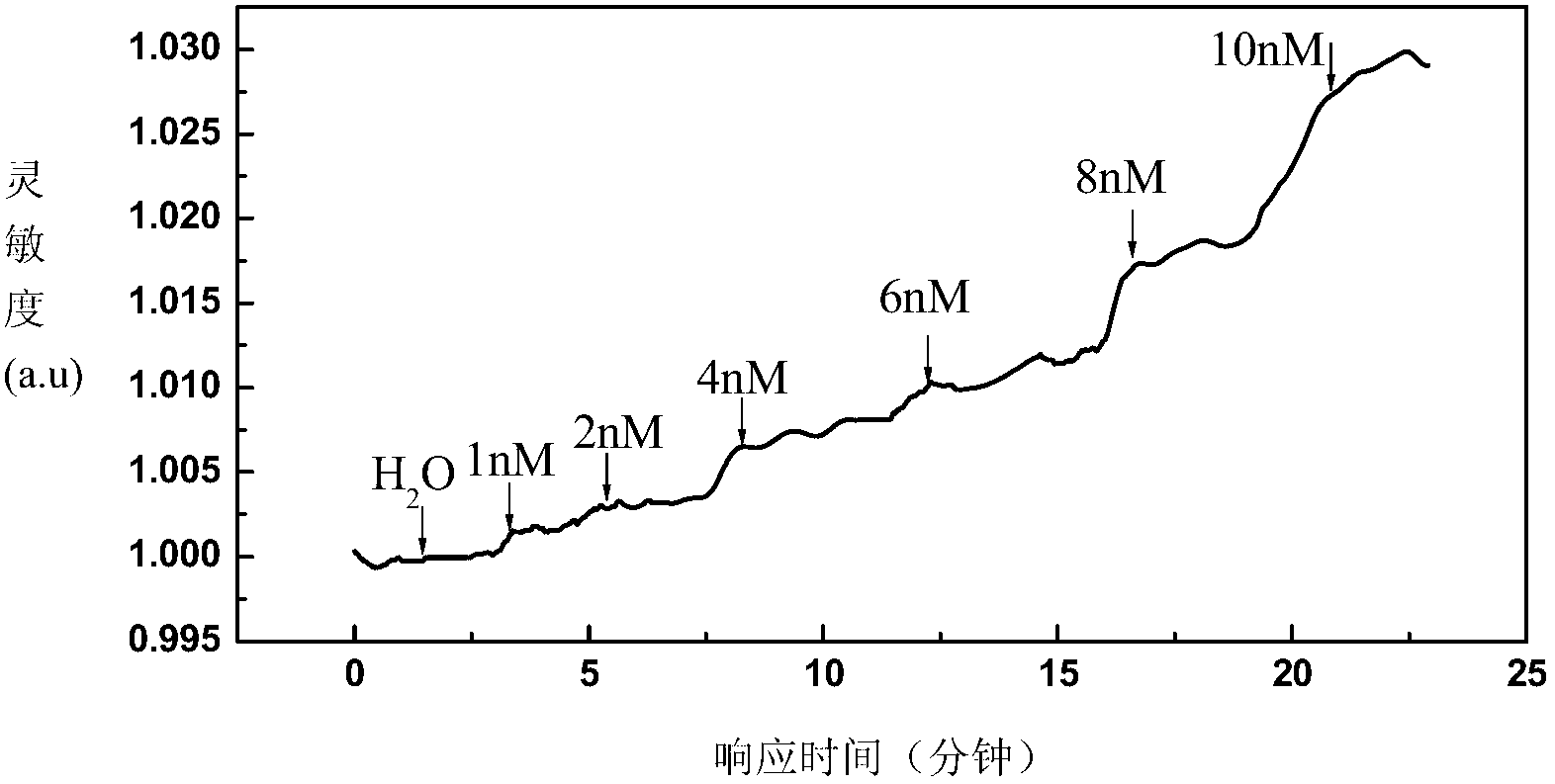
Patents
Literature
271 results about "Ion sensitive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
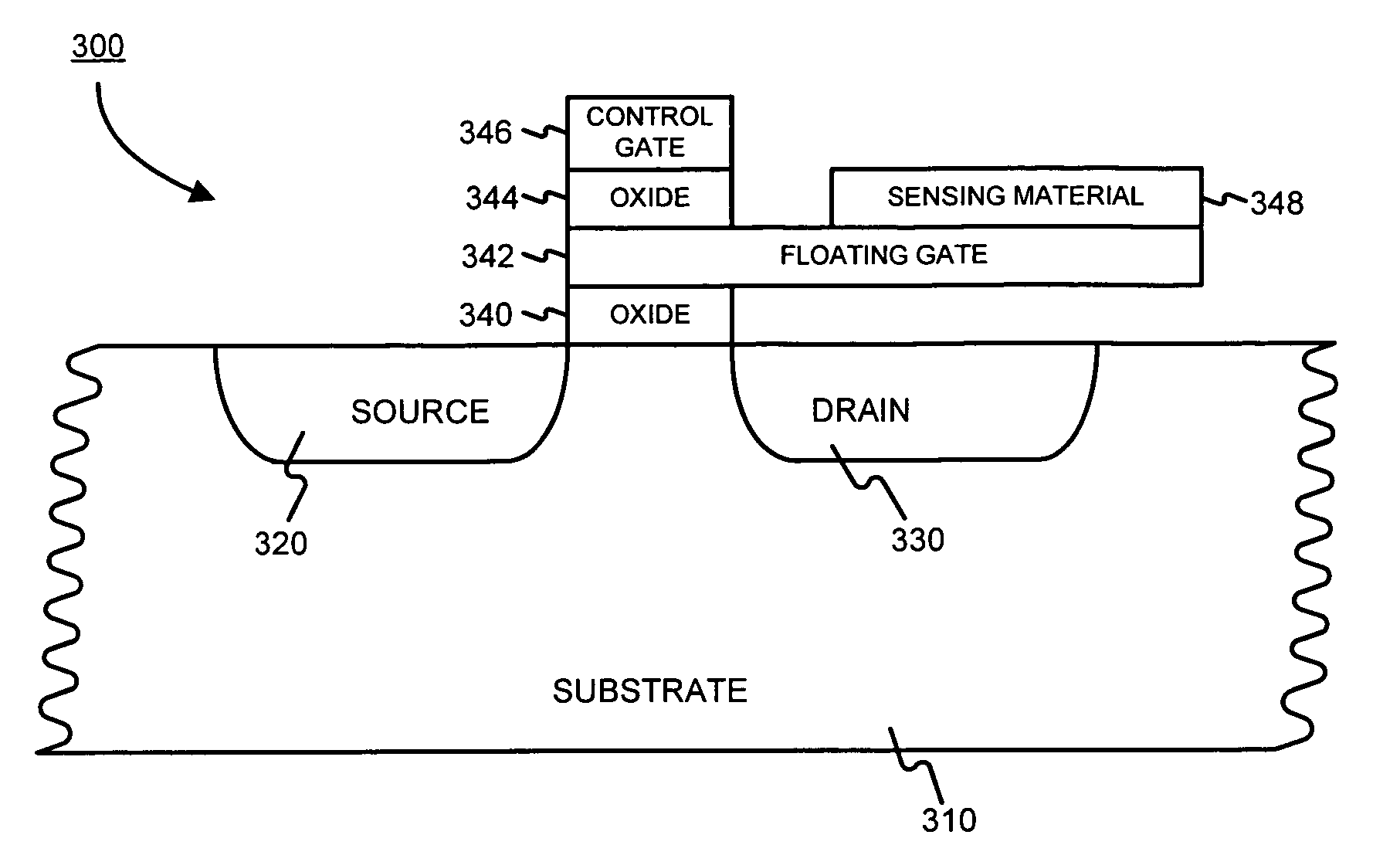
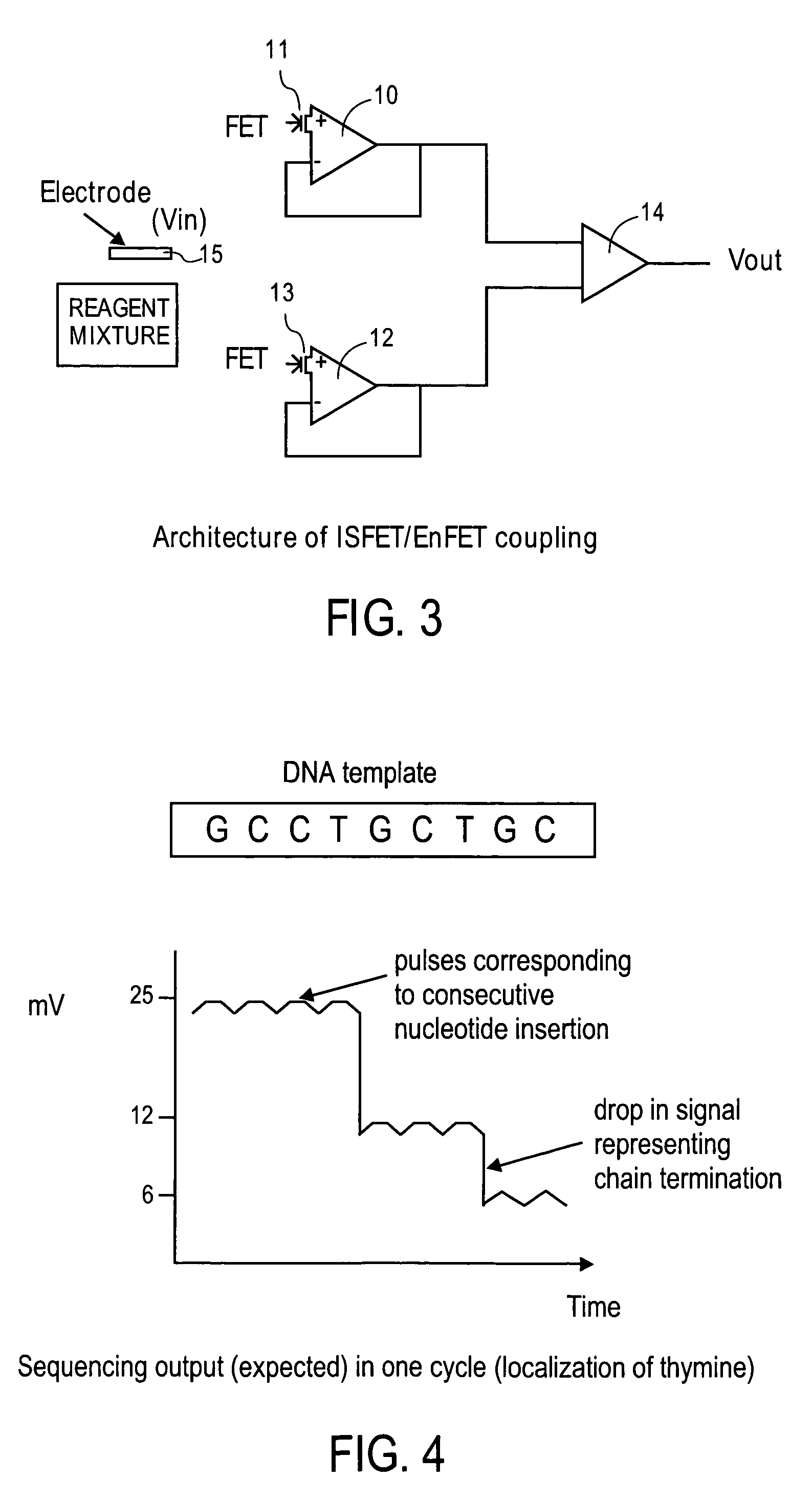
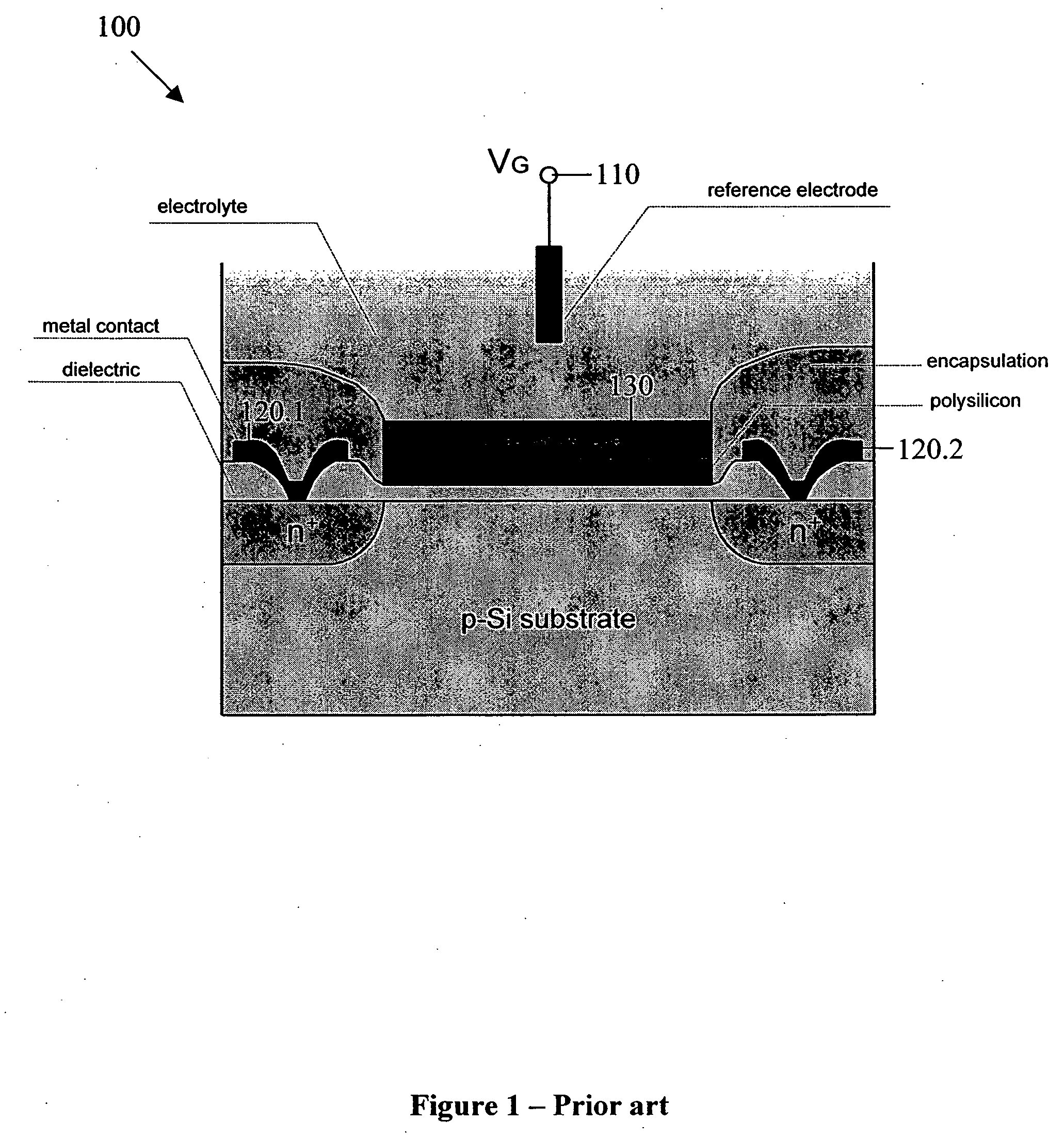
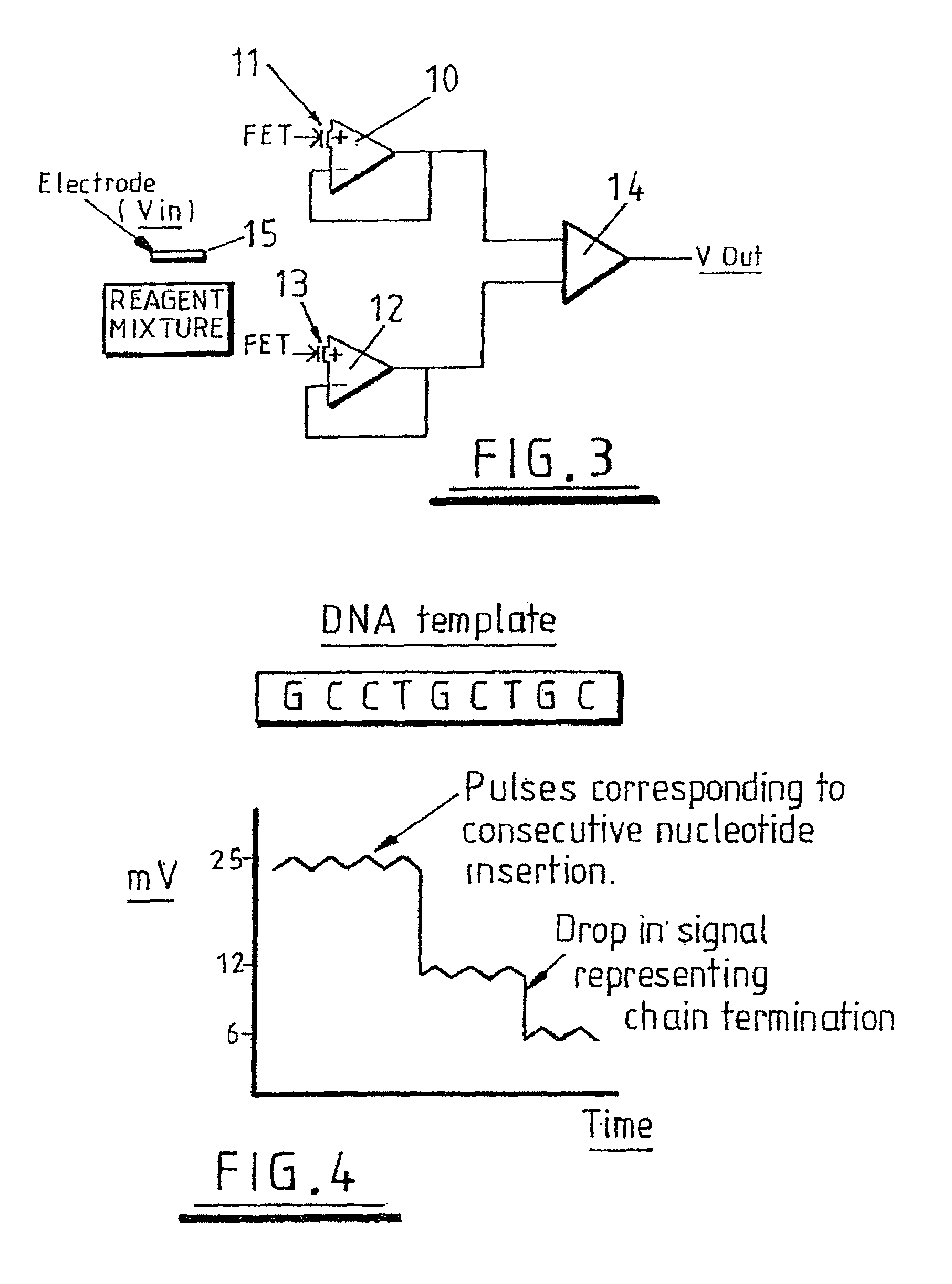
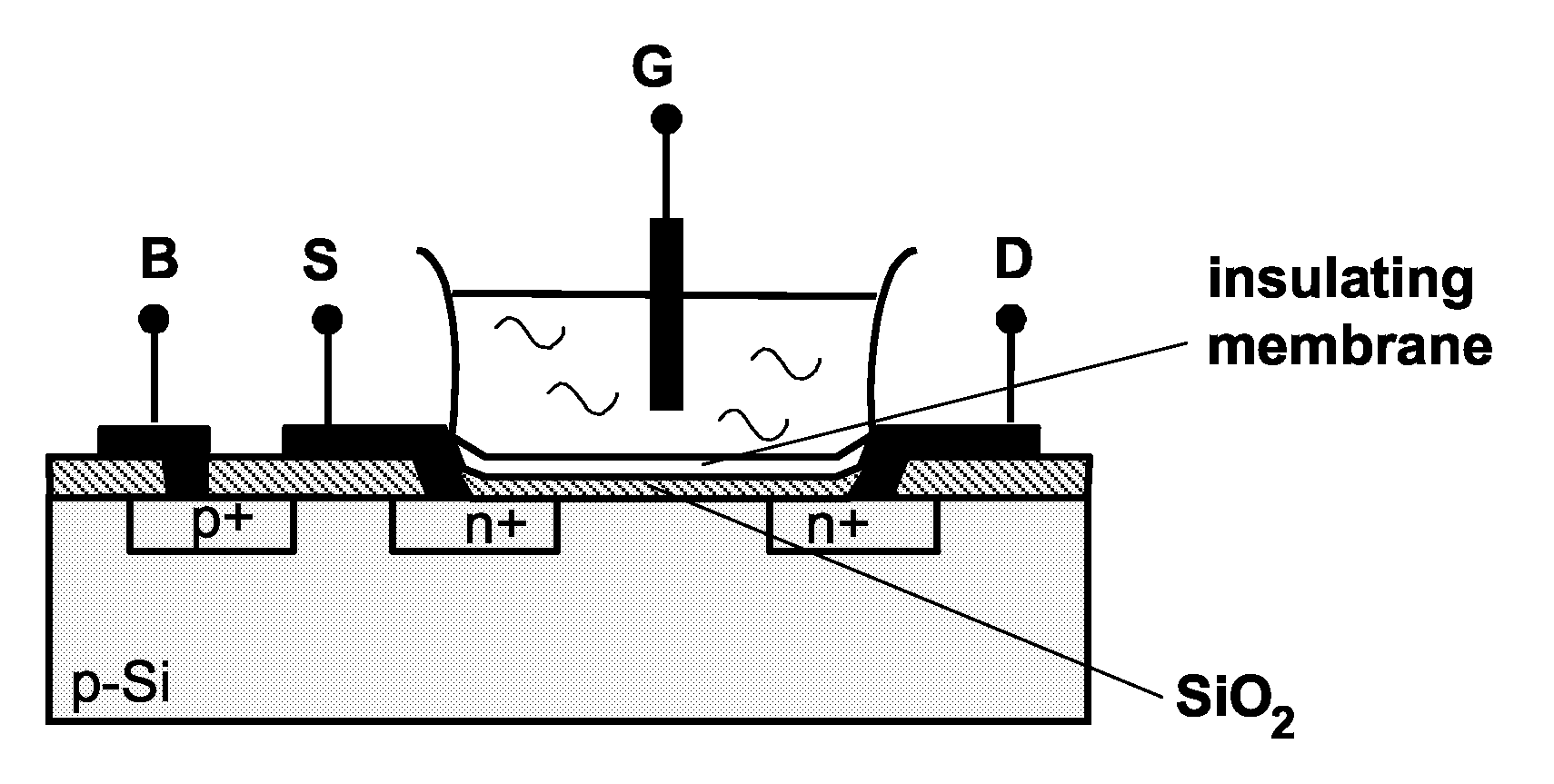
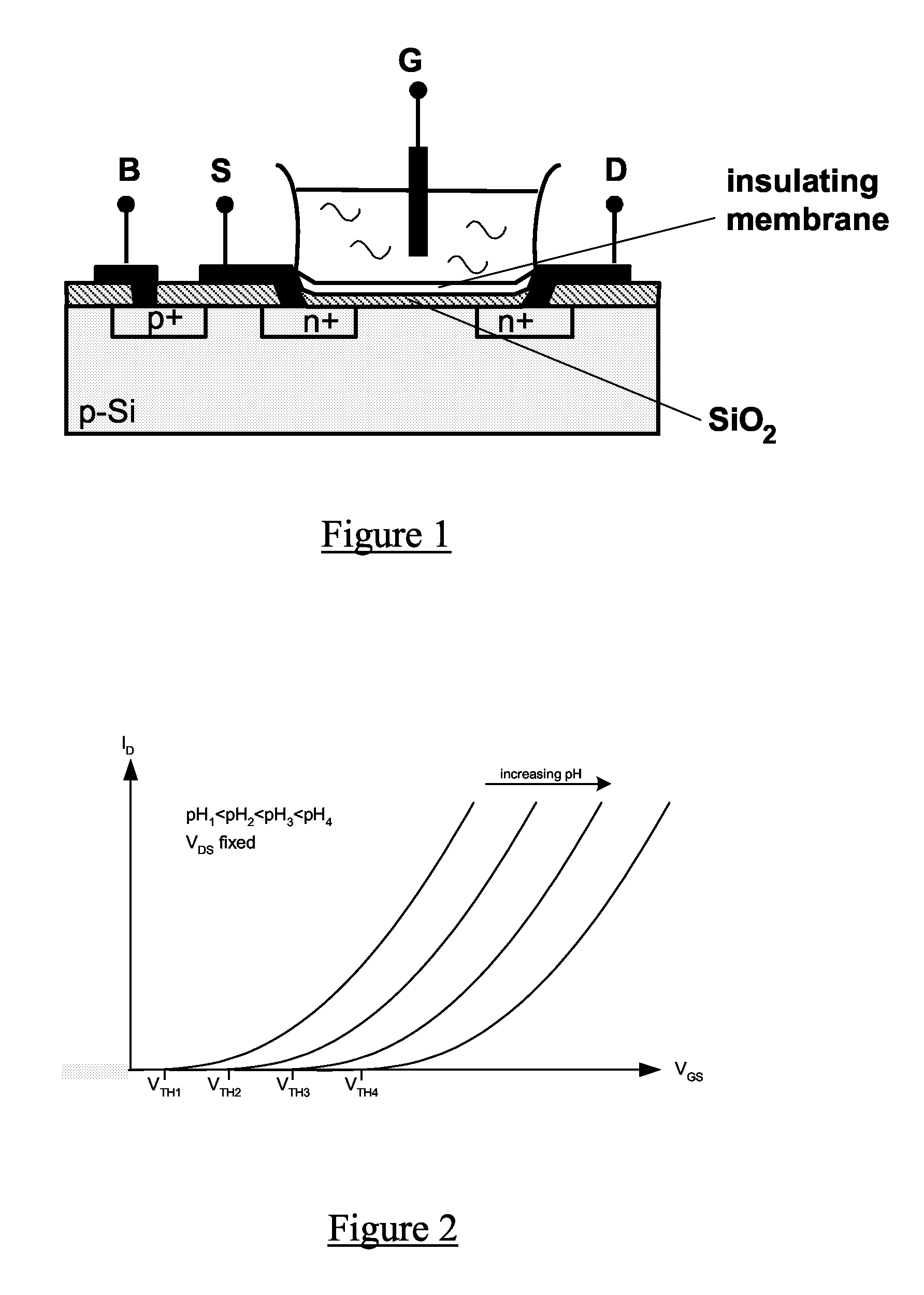
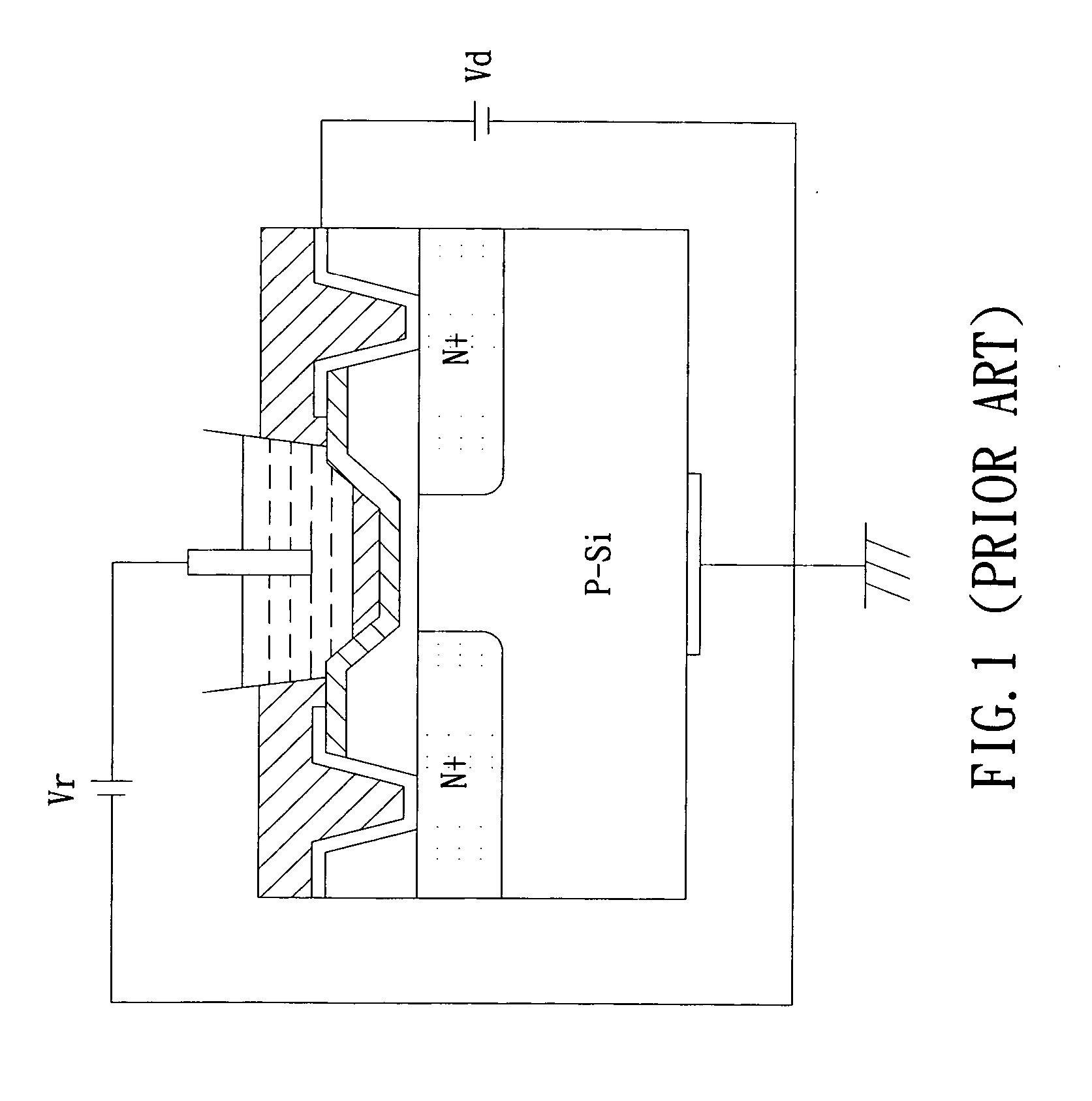
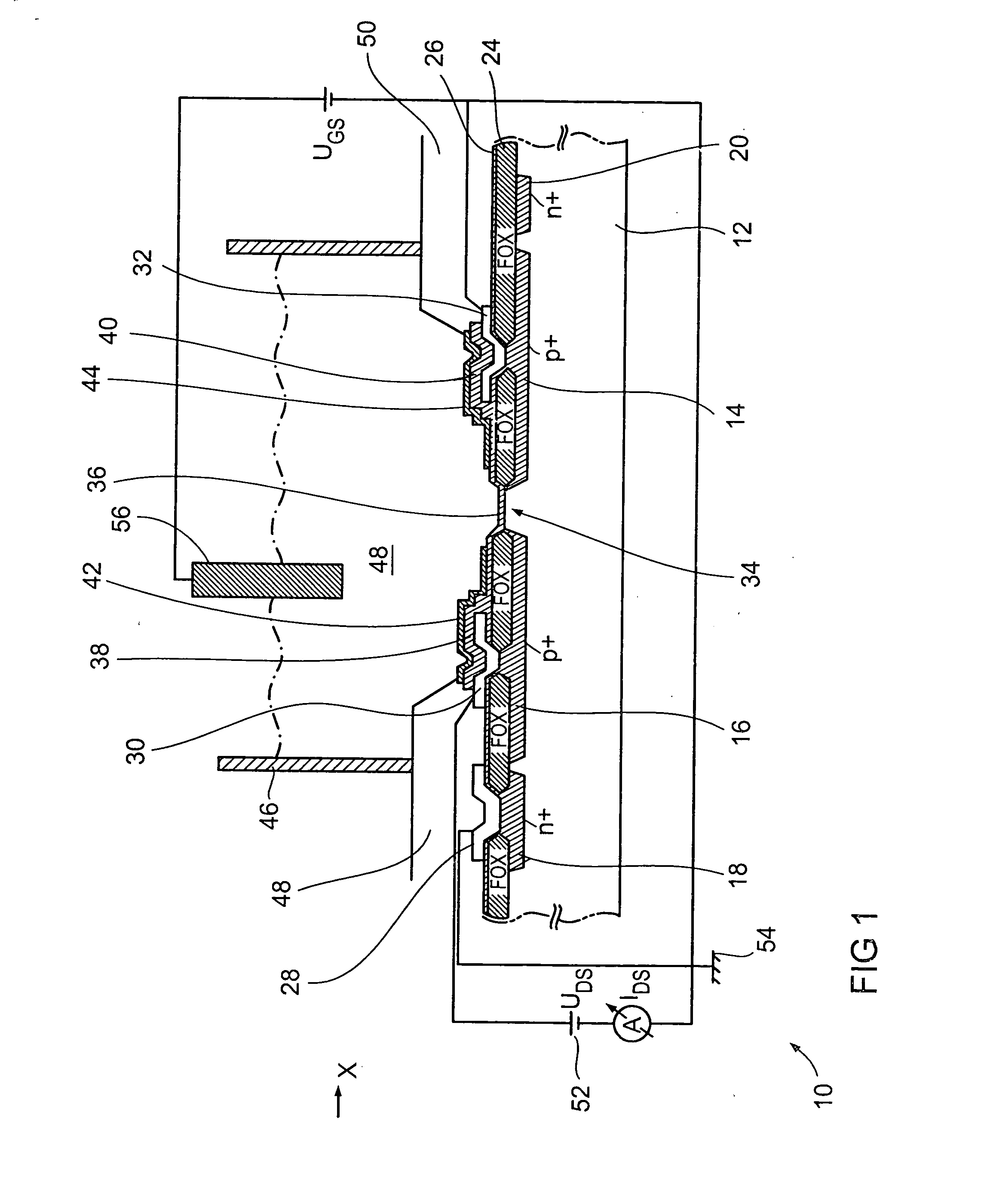
Floating gate field effect transistors for chemical and/or biological sensing
ActiveUS20050230271A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementChemical physicsEngineering
Specific ionic interactions with a sensing material that is electrically coupled with the floating gate of a floating gate-based ion sensitive field effect transistor (FGISFET) may be used to sense a target material. For example, an FGISFET can use (e.g., previously demonstrated) ionic interaction-based sensing techniques with the floating gate of floating gate field effect transistors. The floating gate can serves as a probe and an interface to convert chemical and / or biological signals to electrical signals, which can be measured by monitoring the change in the device's threshold voltage, VT.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
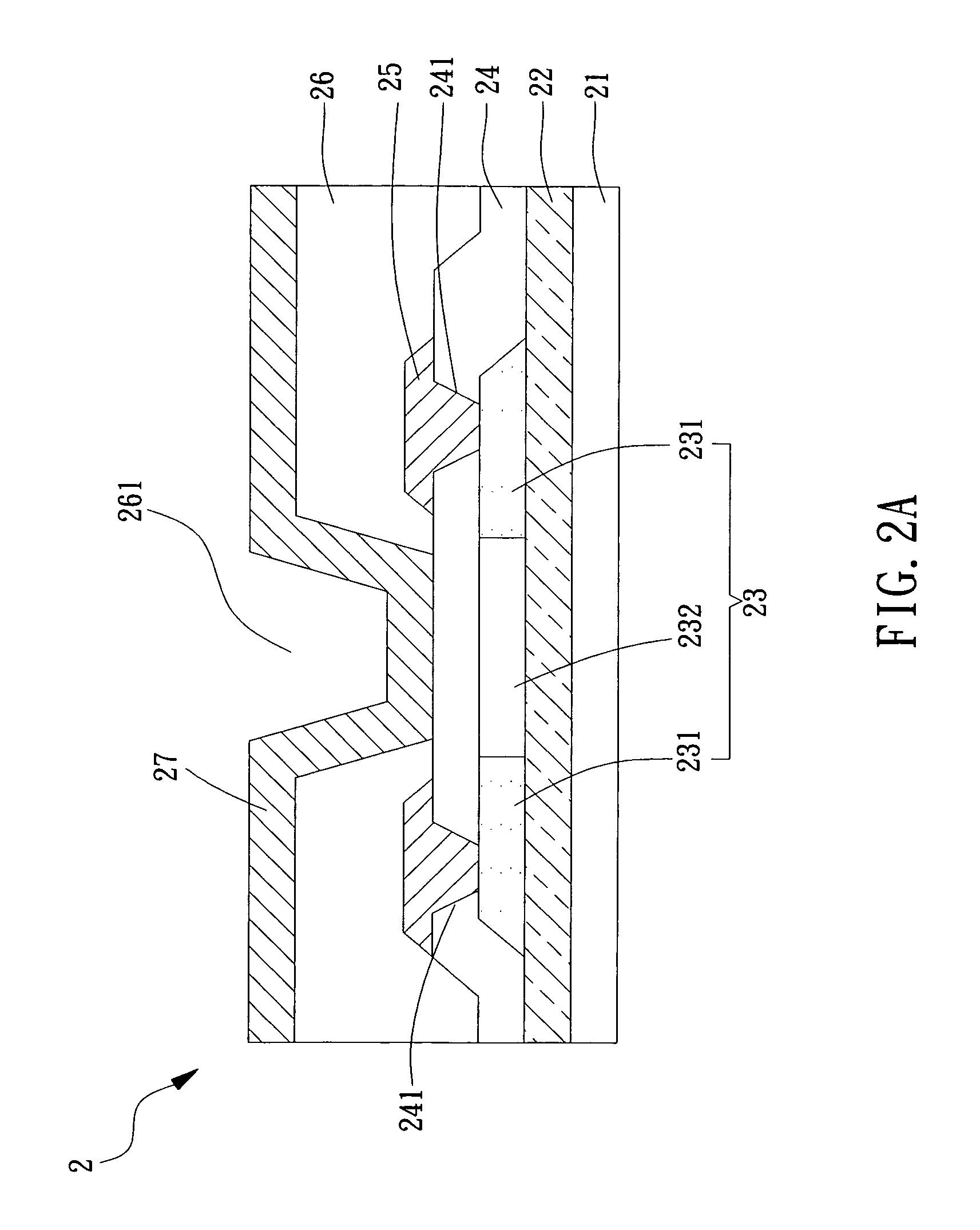
FET type sensor, ion density detecting method comprising this sensor, and base sequence detecting method
InactiveUS7049645B2Low costSure easyTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusionIon density
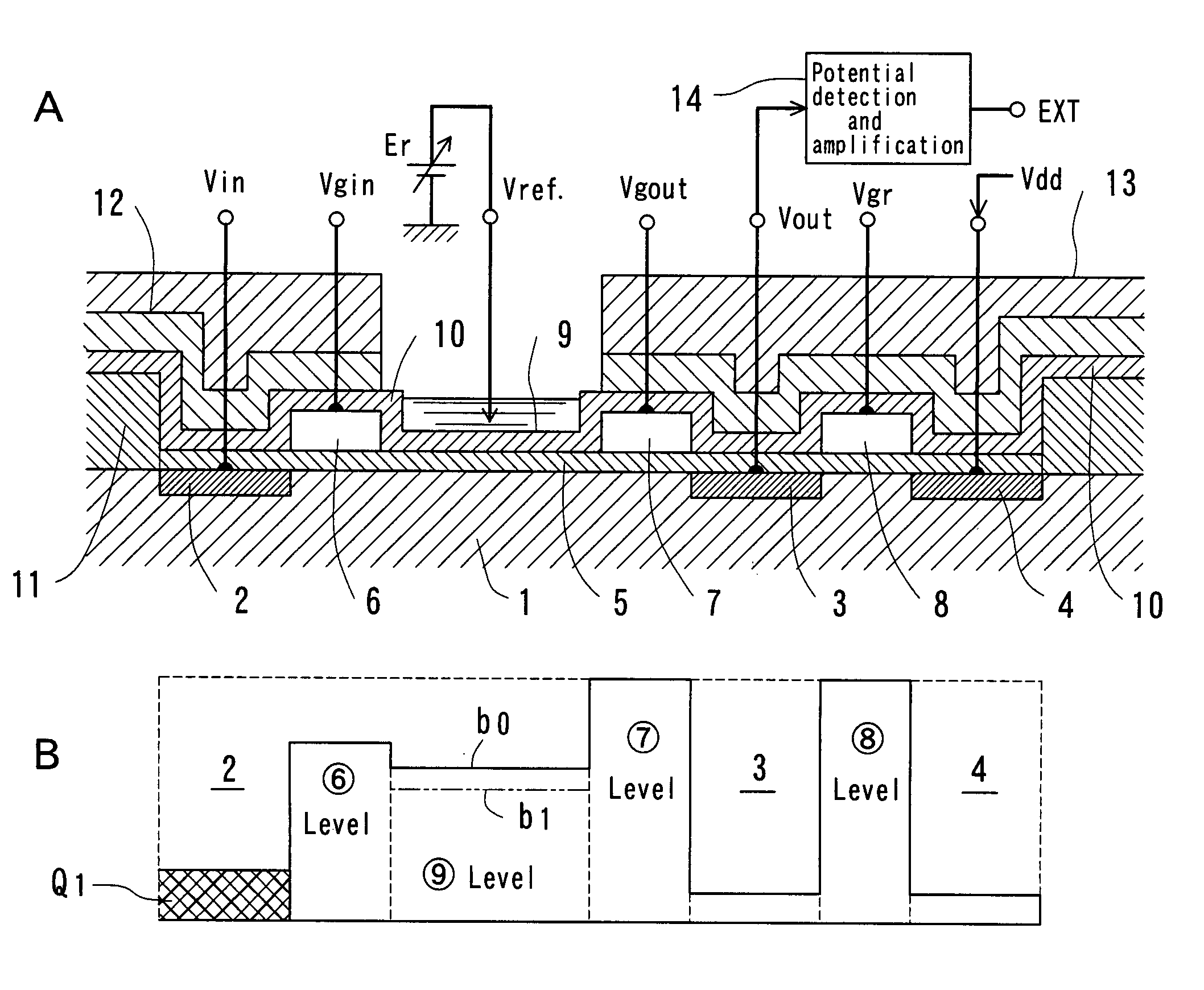
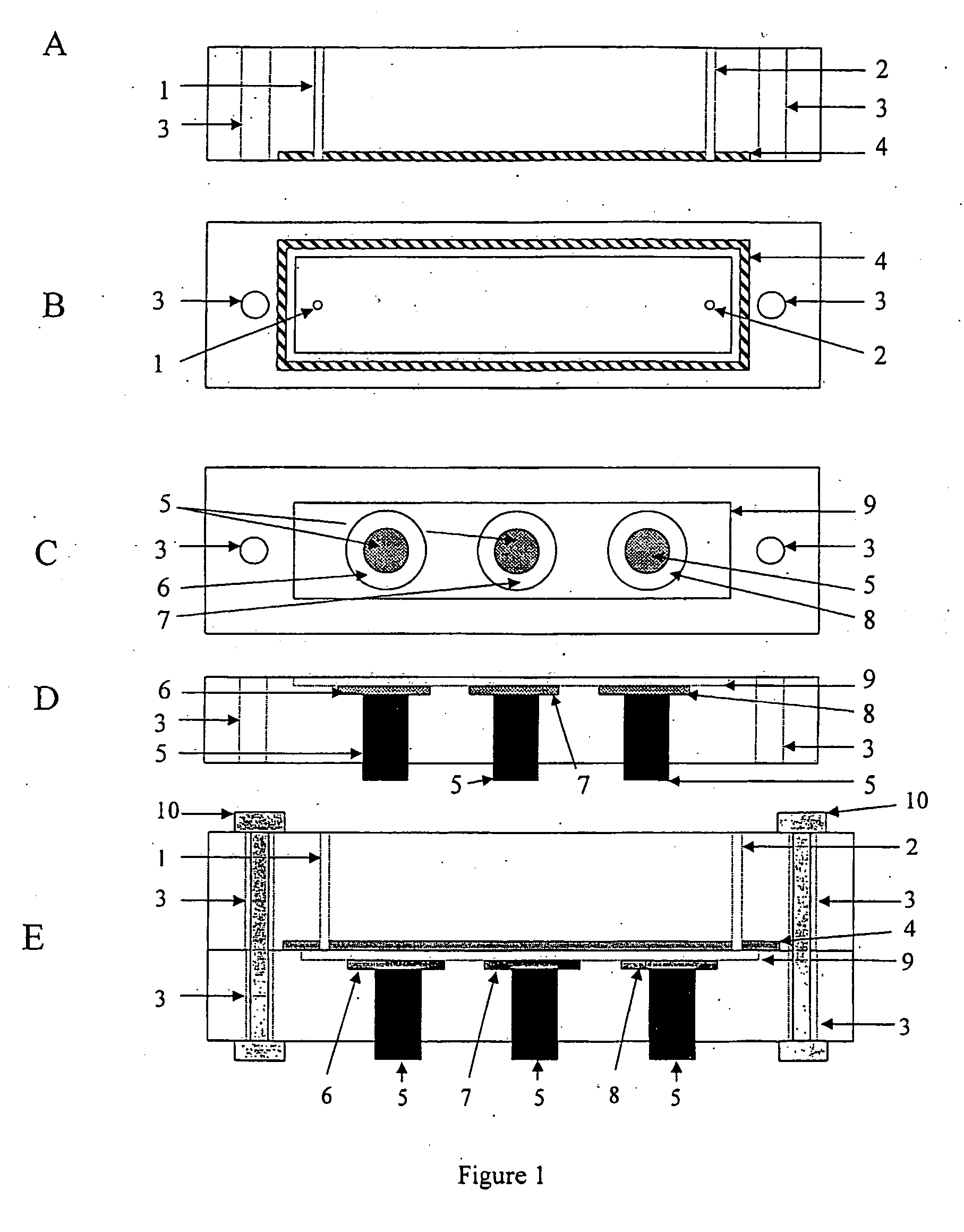
The surface of a semiconductor substrate (1) comprises an input diode section (2) and a floating diffusion section (3) consisting of a diffusion region reverse to the substrate in conductivity type, an input gate (6) and an output gate (7) fixed on an insulation film (5) extending from an input diode section to a floating diffusion section, a sensing section (9) consisting of an ion sensitive film fixed on the insulation film extending from the input.
Owner:BAIO TSUKUSU +1
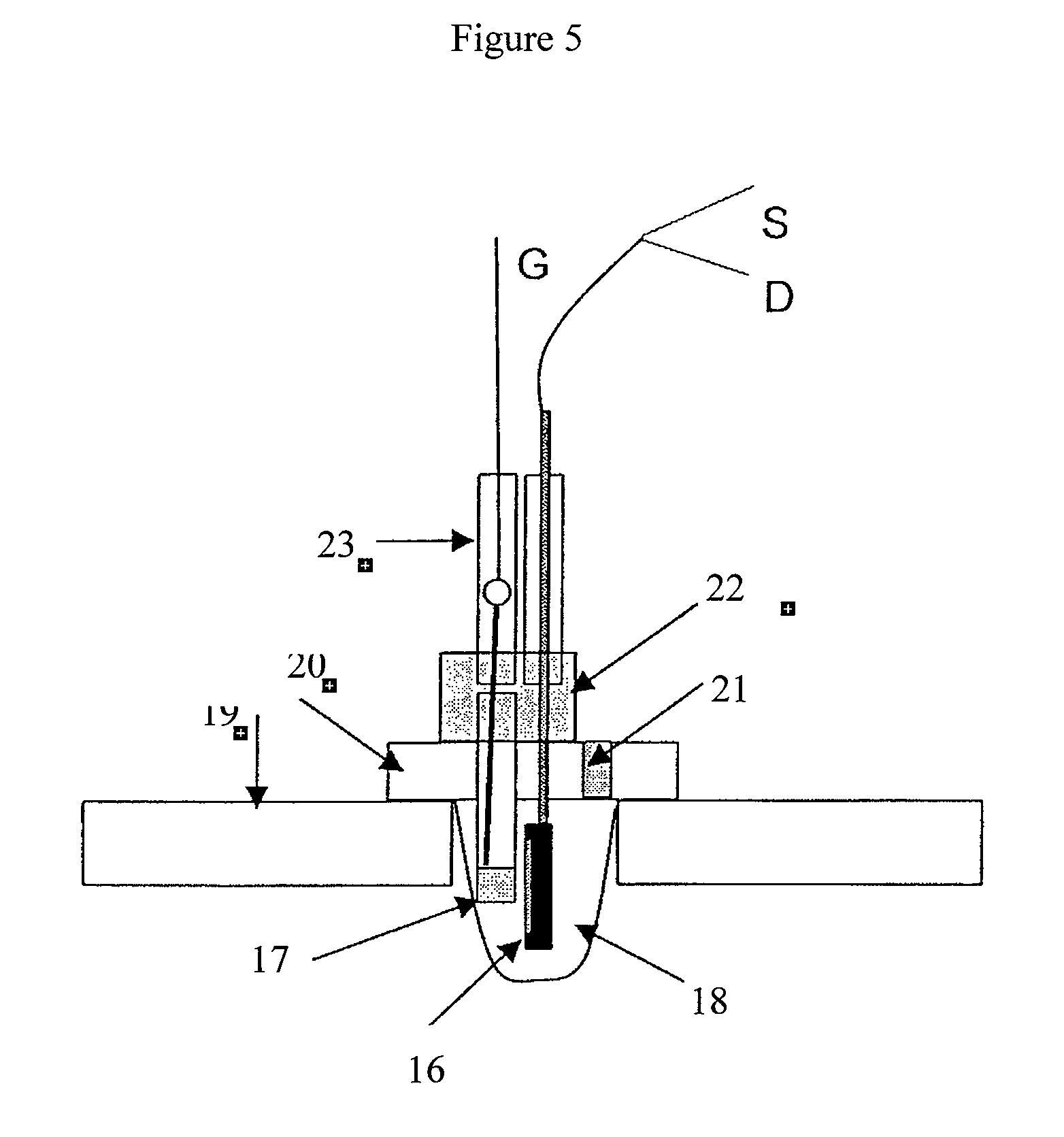
Sensing apparatus and method
A sensing apparatus comprising an ion sensitive field effect transistor arranged to generate an electrical output signal in response to localized fluctuations of ionic charge at or adjacent the surface of the transistor, and means for detecting the electrical output signal from the ion sensitive field effect transistor, the localized fluctuations of ionic charge indicating events occurring during a chemical reaction.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
Floating gate field effect transistors for chemical and/or biological sensing
ActiveUS7462512B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityEngineering
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Sensing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080032295A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsProton
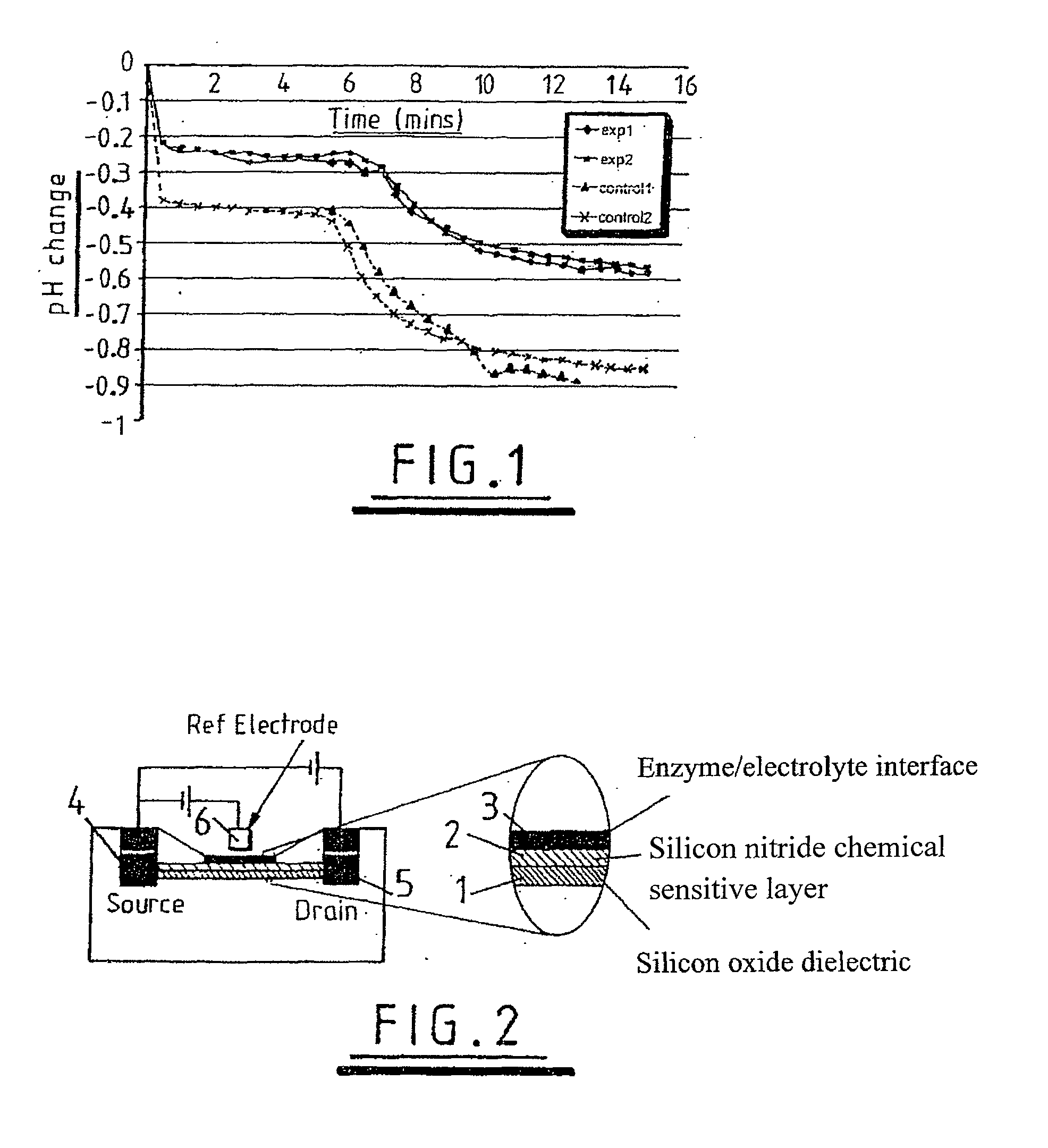
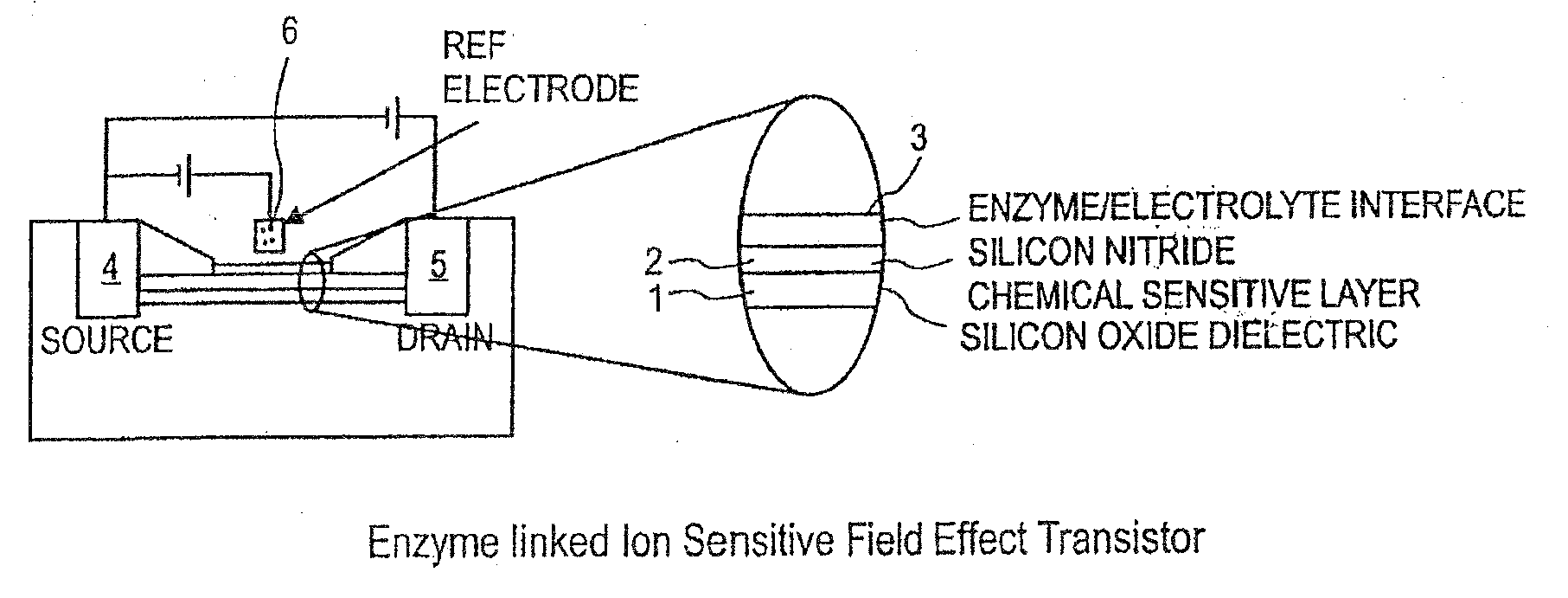
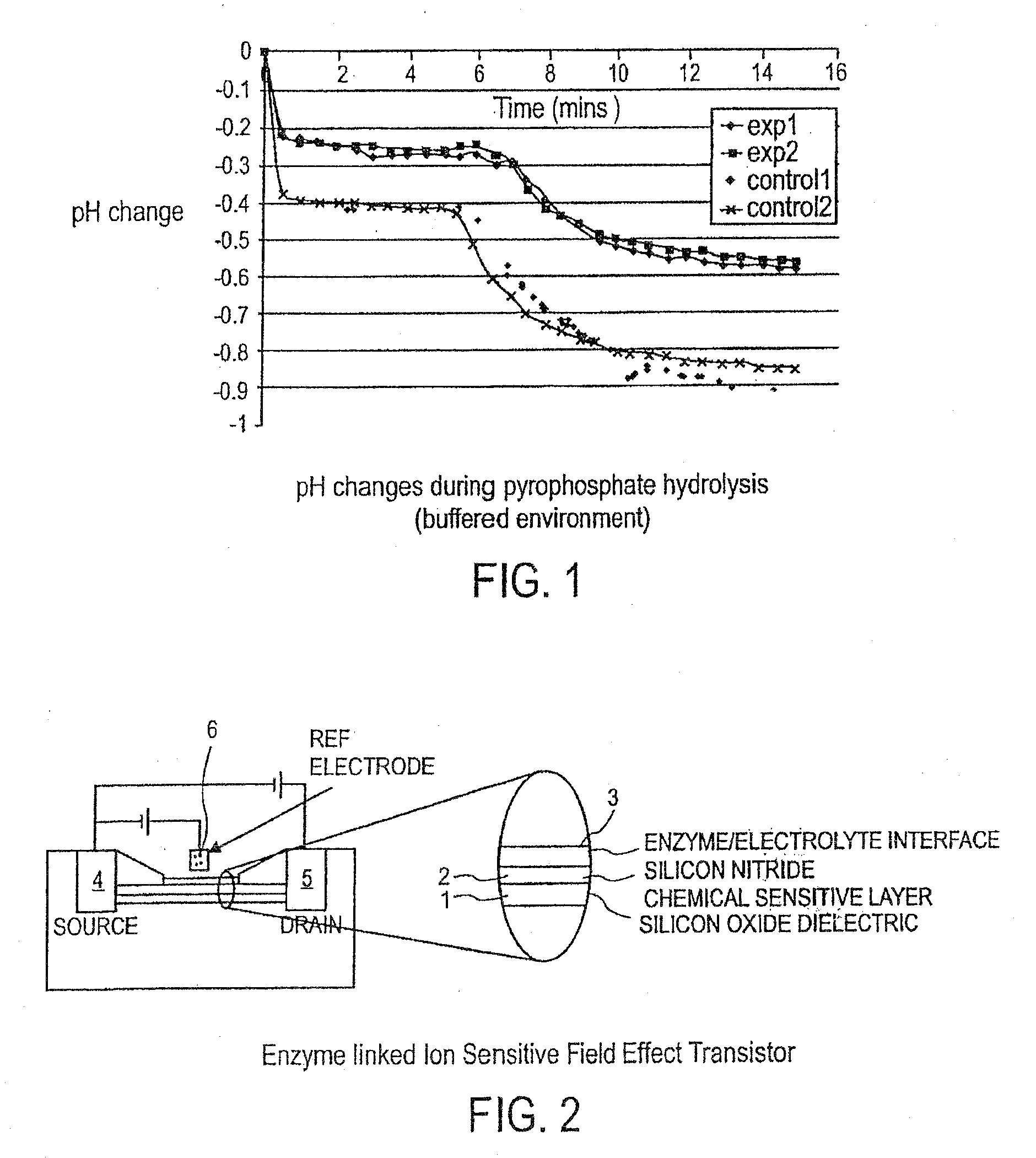
Use of a pH sensor comprising an ion-sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) to perform real time detection / quantification of nucleic acid amplification, e.g. polymerase chain reaction (PCR) nucleic acid amplification, based on detection of protons released during the primer extension phase.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
Sensing Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20100255595A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionReaction intermediate
A method of observing reaction intermediaries during a chemical reaction and comprising detecting an electrical signal output from an ion sensitive field effect transistor exposed to said reaction, and monitoring the detected electrical signal to discriminate discrete fluctuations in the electrical signal, the discrete fluctuations indicating reaction intermediaries occurring during a chemical reaction.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
Fet type sensor, ion density detecting method comprising this sensor, and base sequence detecting method
InactiveUS20050062093A1Accurate detectionLow costTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusionIon density
The surface of a semiconductor substrate (1) comprises an input diode section (2) and a floating diffusion section (3) consisting of a diffusion region reverse to the substrate in conductivity type, an input gate (6) and an output gate (7) fixed on an insulation film (5) extending from an input diode section to a floating diffusion section, a sensing section (9) consisting of an ion sensitive film fixed on the insulation film extending from the input.
Owner:BAIO TSUKUSU +1
Ion concentration sensor
InactiveUS20050230245A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterial electrochemical variablesDiffusionPhysical chemistry
An ion concentration sensor produces a signal reflective of the ion concentration within a solution. The ion concentration sensor is based on an ion sensitive transistor having a solution input, a reference input, a diffusion input, and a diffusion output. The ion sensitive transistor is connected as a pass transistor, such that the diffusion output provides an electrical signal indicating an ion concentration in a solution contacting the solution input.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Preparation of a PH sensor, the prepared PH sensor, system comprising the same and measurement using the system
InactiveUS20070095663A1Reduce sheet resistanceImprove conductivityMaterial electrochemical variablesSputteringTitanium nitride
Preparation of a pH sensor, the prepared pH sensor, system comprising the same, and measurement using the system. The pH sensor is an extended gate field effect transistor (EGFET) structure. The preparation includes the steps of providing an extended gate ion sensitive field effect transistor comprising an extended gate region, forming a titanium nitride film on the extended gate region by RF sputtering deposition to obtain a pH sensor.
Owner:NATIONAL YUNLIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Sensing apparatus and method
ActiveUS8114591B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionReaction intermediate
A method of observing reaction intermediaries during a chemical reaction and comprising detecting an electrical signal output from an ion sensitive field effect transistor exposed to said reaction, and monitoring the detected electrical signal to discriminate discrete fluctuations in the electrical signal, the discrete fluctuations indicating reaction intermediaries occurring during a chemical reaction.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
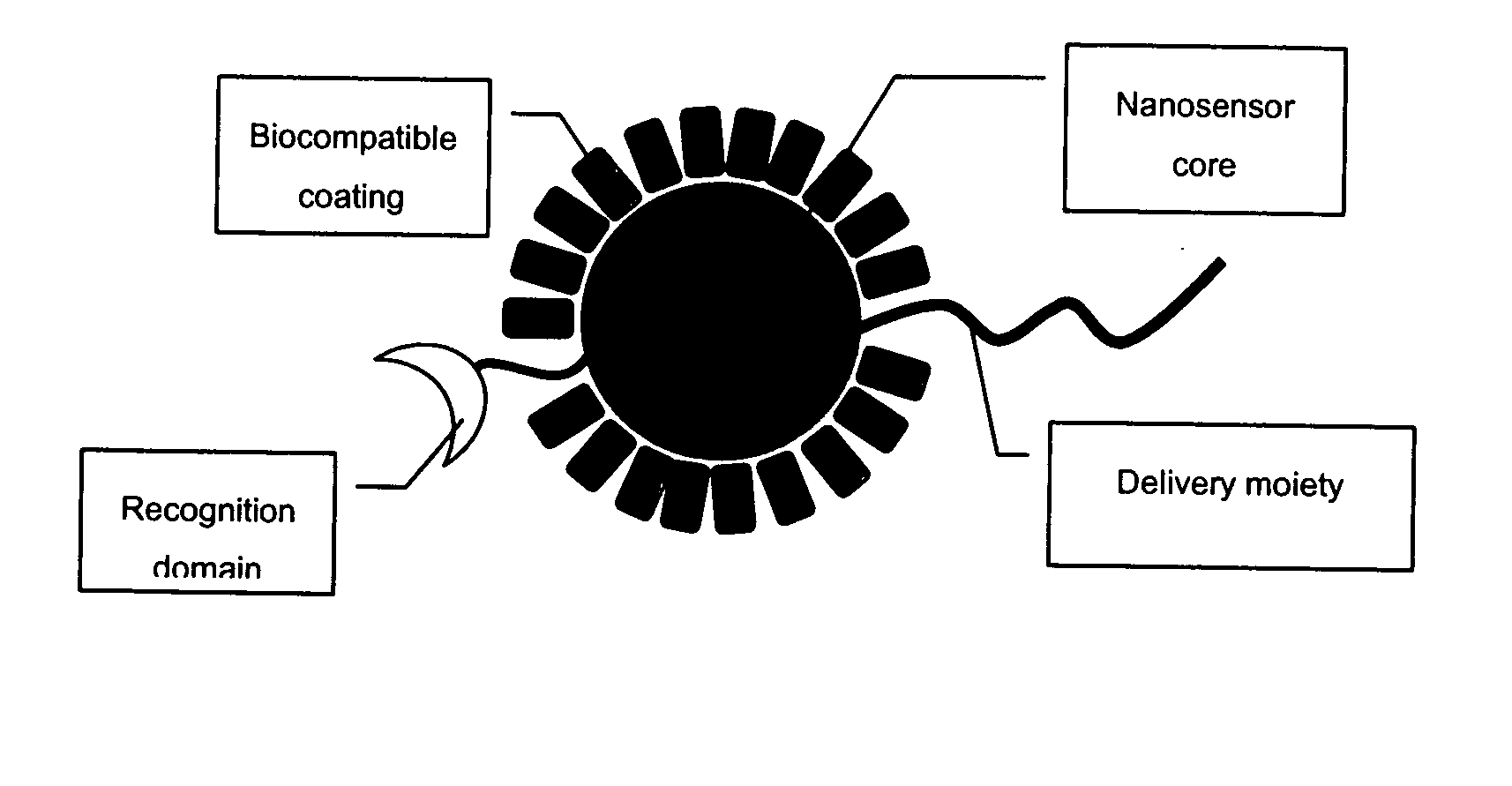
Detection of ion channel or receptor activity
InactiveUS20060148104A1Easy accessImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeterologousBiological activation
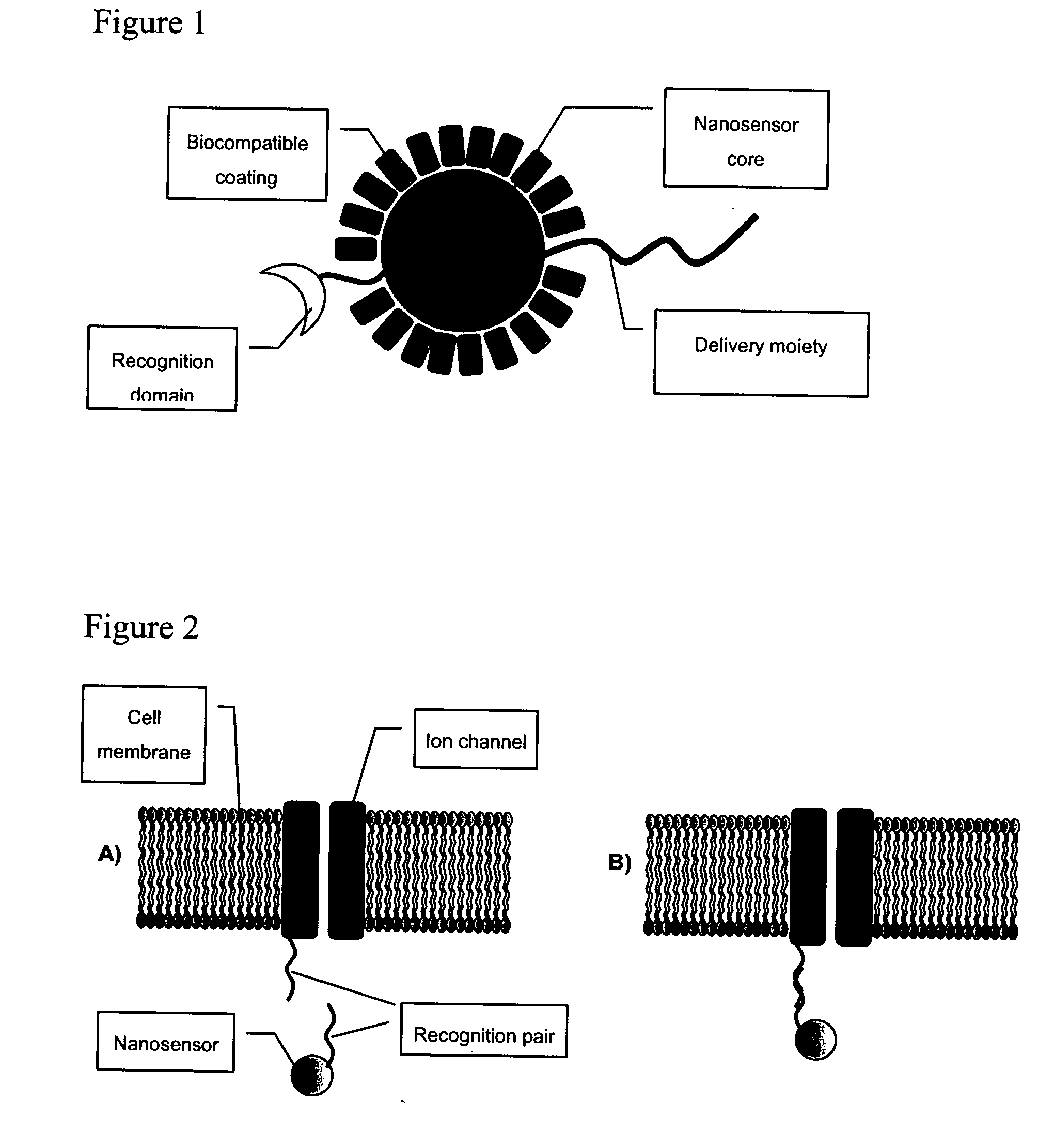
The invention provides nanosensors and nanosensor components for the detection of ion channel activity, receptor activity, or protein protein interactions. Certain of the nanosensor components comprise a nanoparticle and recognition domain. Following contact with cells and, optionally, internalization of the nanosensor component by a cell, the recognition domain binds to a target domain, e.g., a heterologous target domain, of a polypeptide of interest such as an ion channel subunit, G protein coupled receptor (GPCR), or G protein subunit. Ion channel activity, GPCR activity, or altered protein interaction results in a detectable signal. The nanoparticles may be functionalized so that they respond to the presence of an ion by altering their proximity. Certain of the nanosensors utilize the phenomenon of plasmon resonance to produce a signal while others utilize magnetic properties, RET, and / or ion-sensitive moieties. Also provided are polypeptides, e.g., ion channel subunits, comprising a heterologous target domain, and cell lines that express the polypeptides. Further provided are a variety of methods for detecting ion channel activity, receptor activity, or protein interaction and for identifying compounds that modulate one or more of these. In certain embodiments the invention allows the user to detect the activity of specific ion channels even in the presence of other channels that permit passage of the same ion(s) or result in activation of the same downstream targets, thereby achieving improved specificity in high throughput screens while at the same time providing a high signal to noise ratio.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP +1
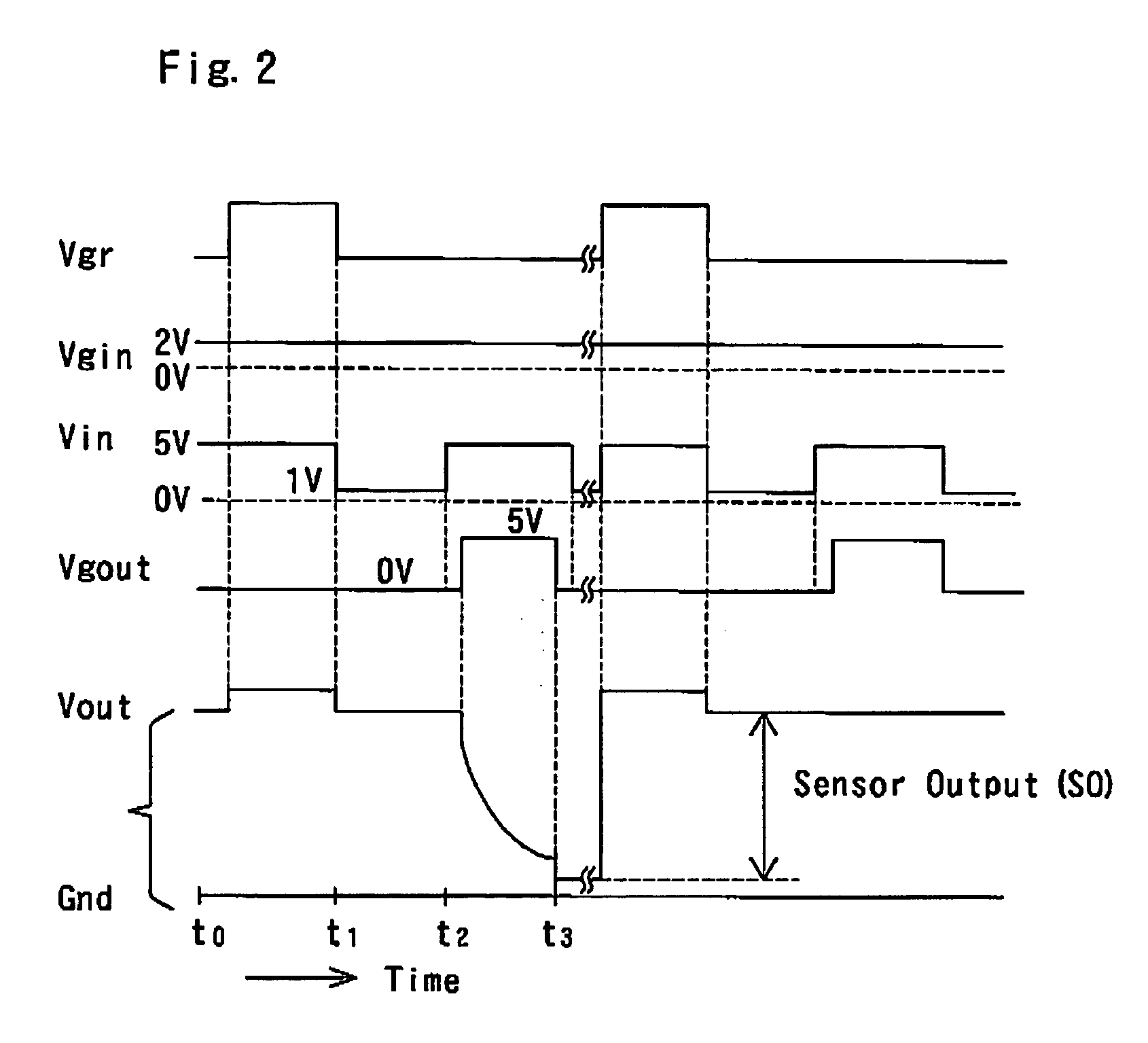
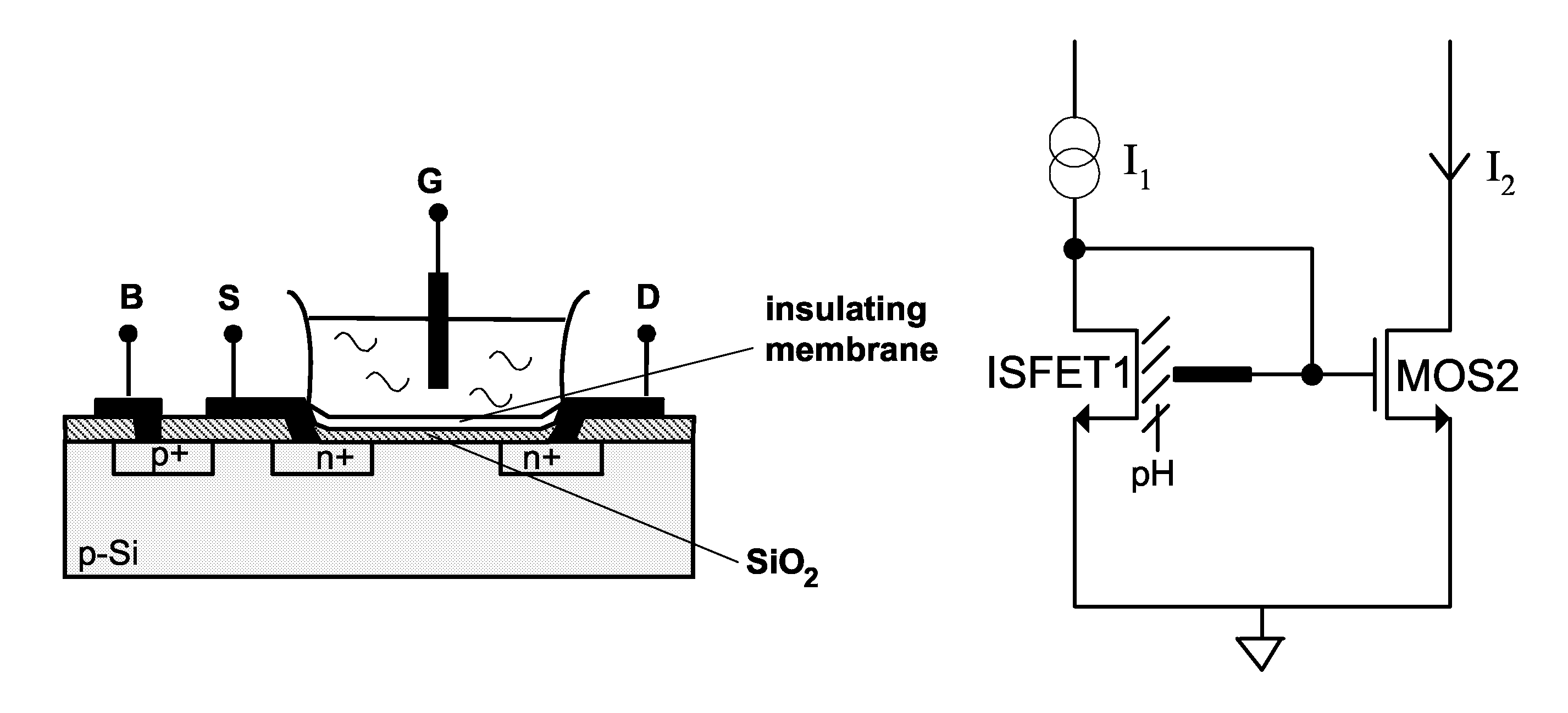
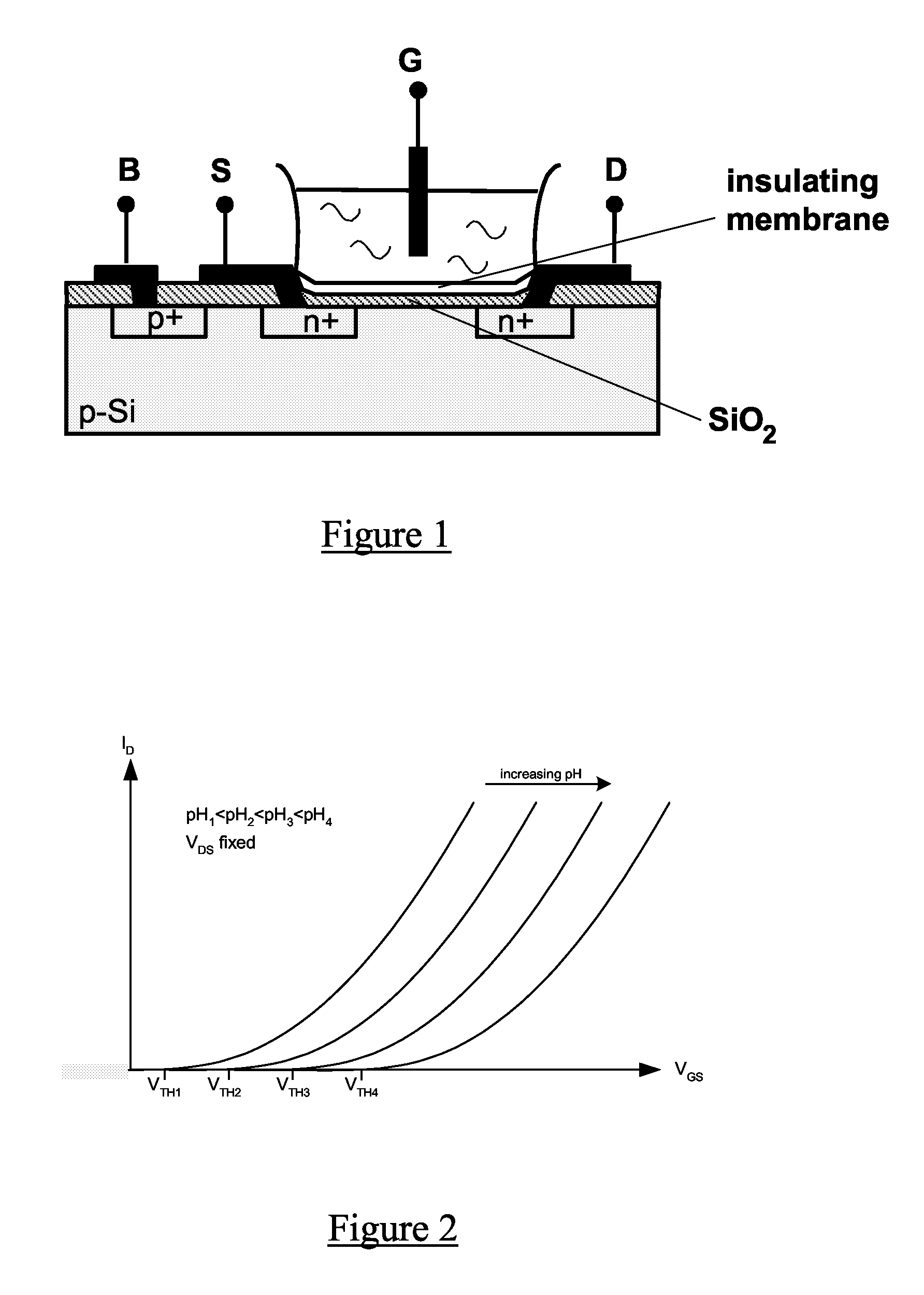
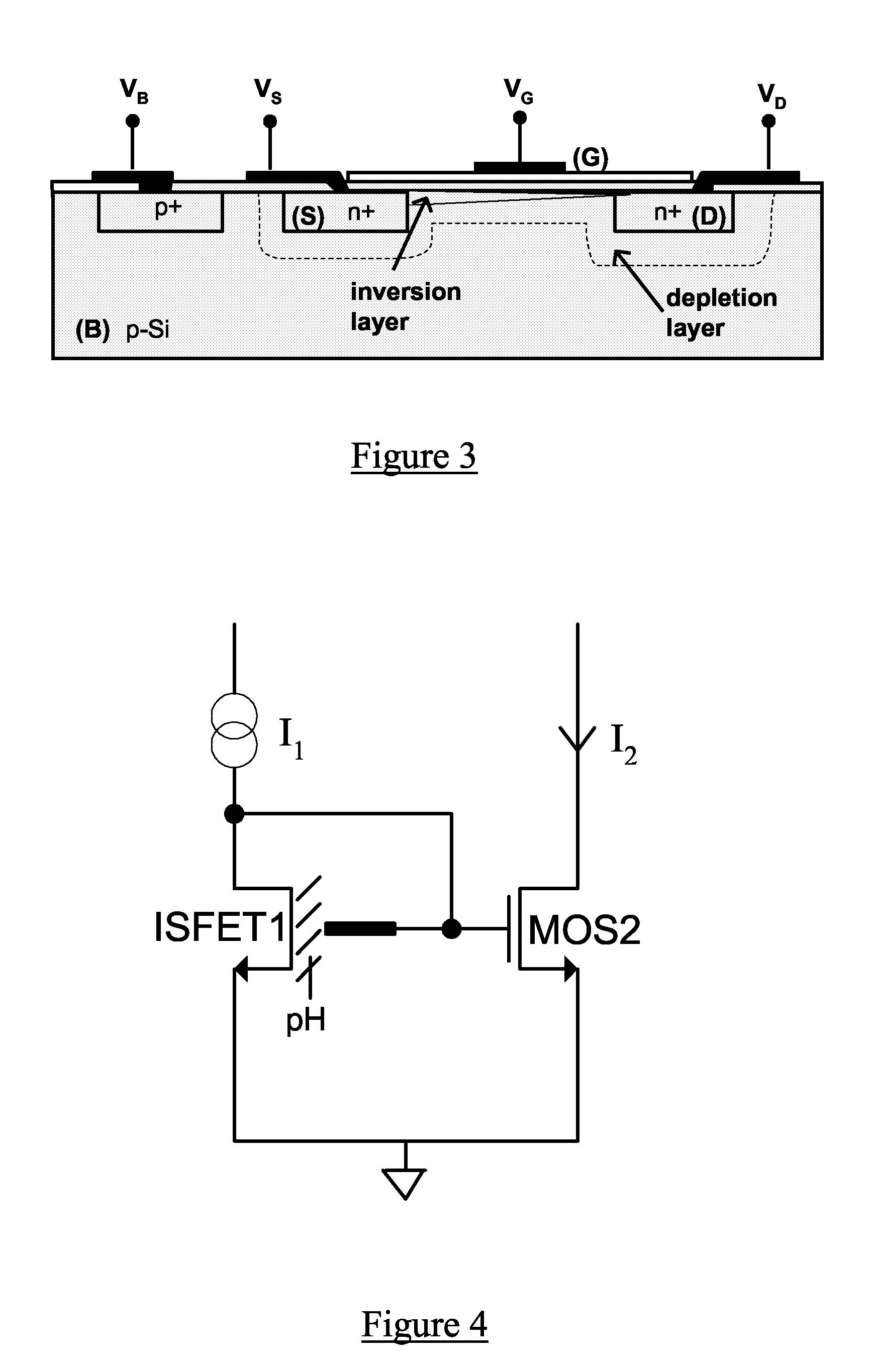
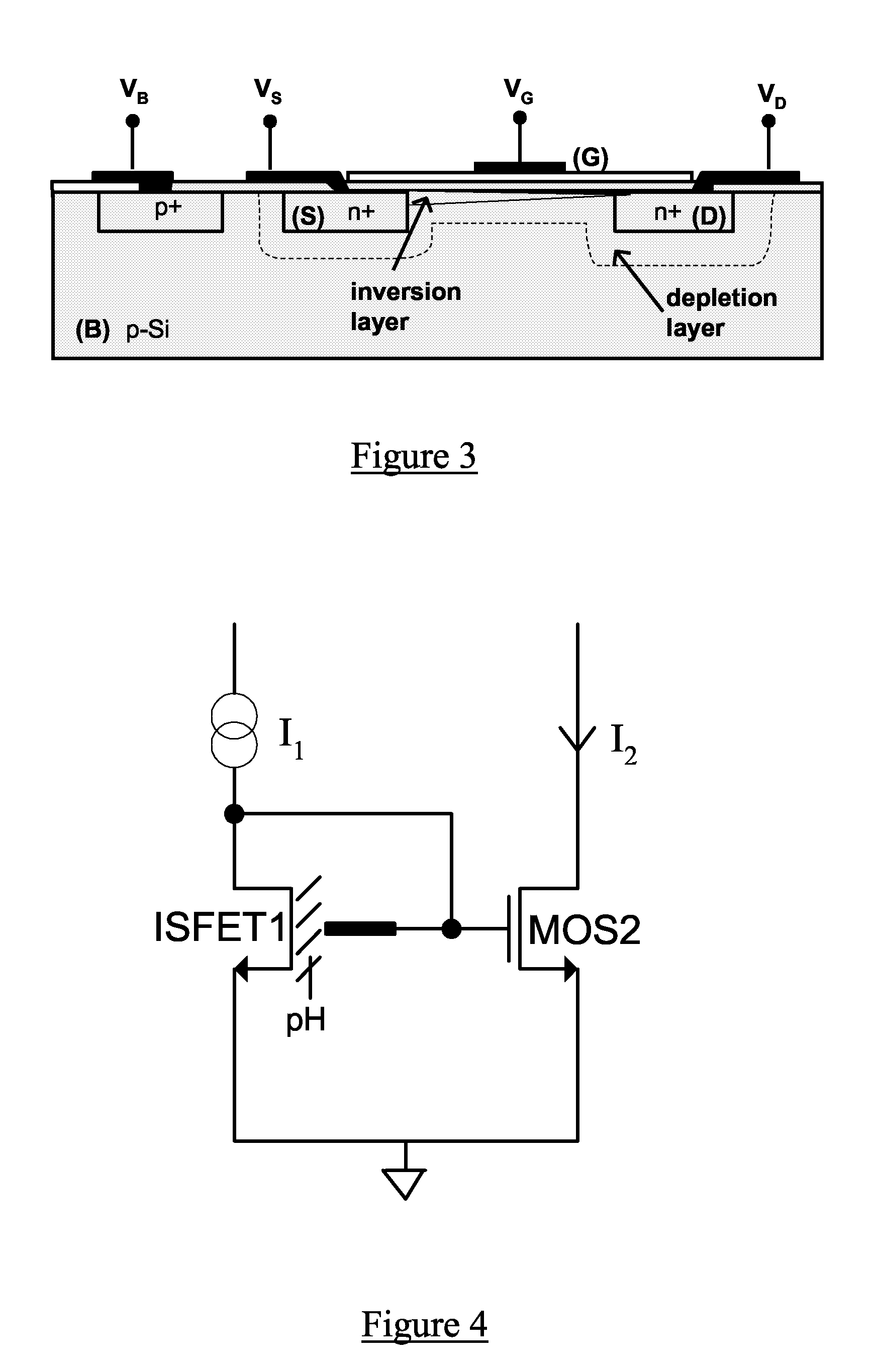
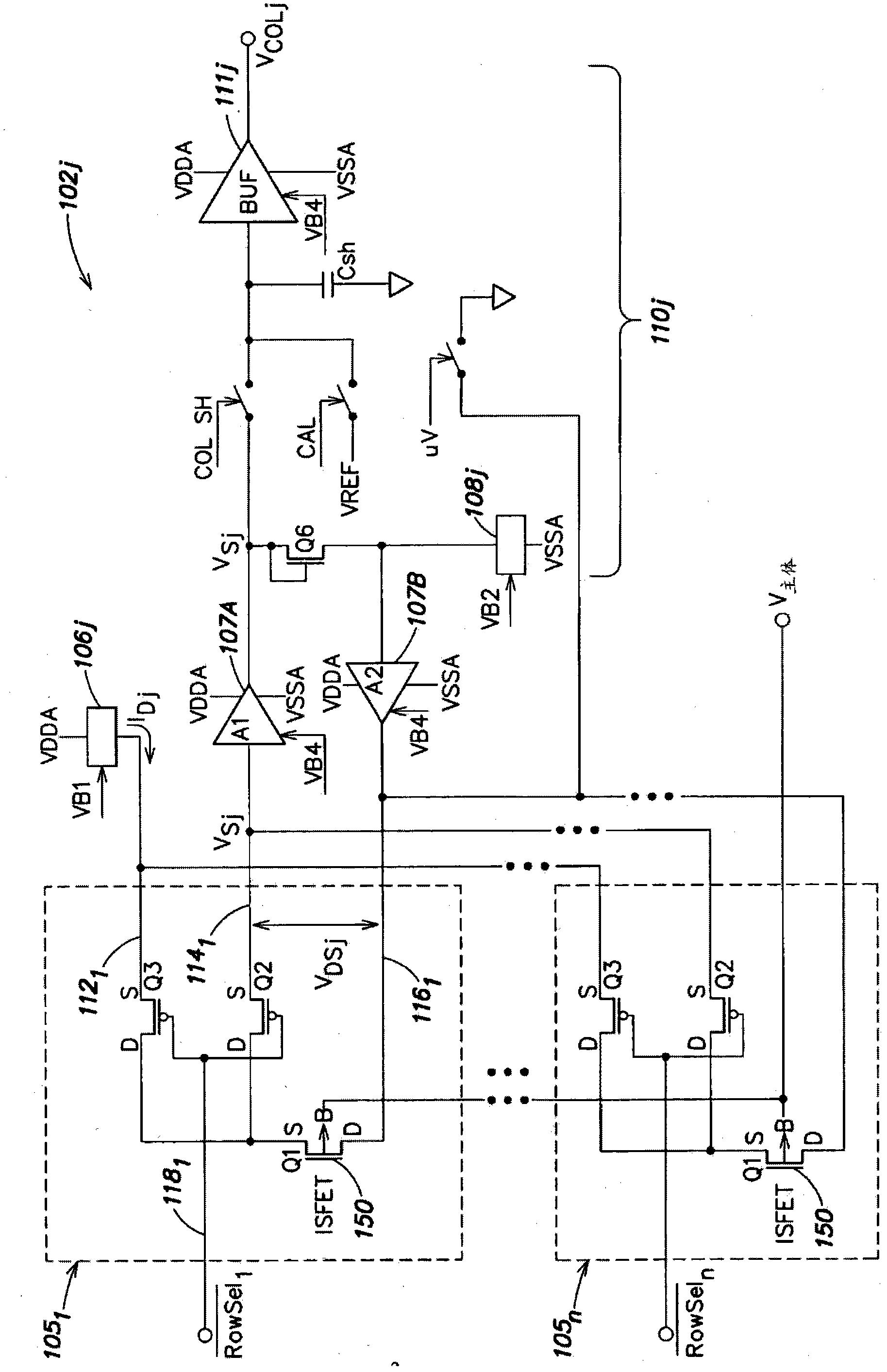
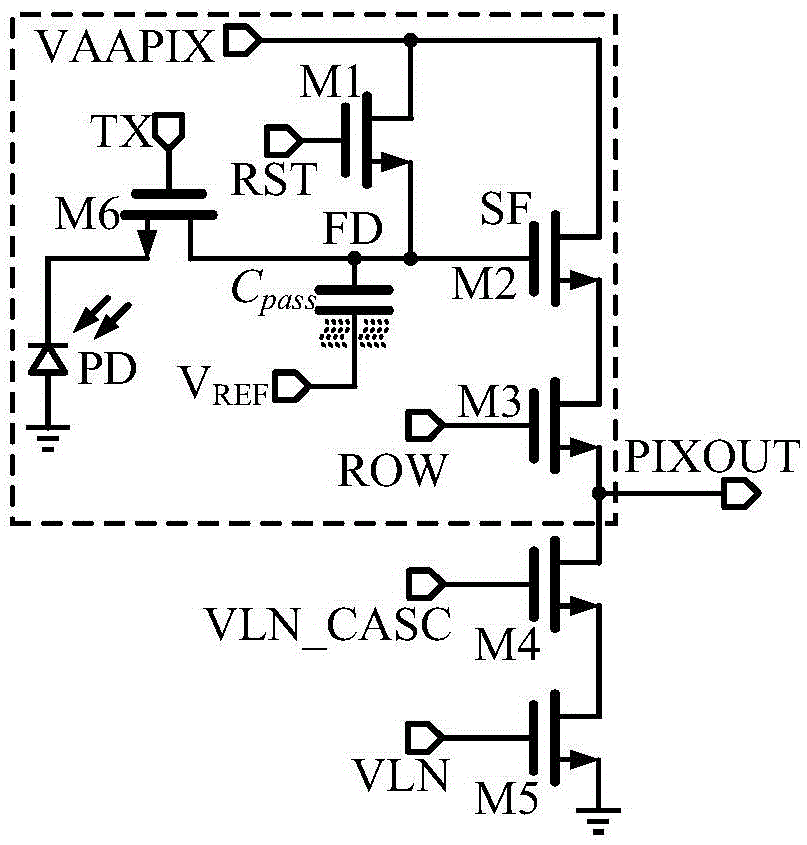
Signal processing circuit comprising ion sensitive field effect transistor and method of monitoring a property of a fluid
ActiveUS7649358B2Compensation effectWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementSignal processing circuitsCondensed matter physics
A signal processing circuit includes an ion sensitive field effect transistor, a reference electrode for the ion sensitive field effect transistor, a metal oxide semiconductor transistor having its gate coupled to the reference electrode, and a biasing circuit. The biasing circuit is configured to bias the ion sensitive field effect transistor and the metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor to operate in a weak inversion region and to provide an output current signal.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
Signal Processing Circuit Comprising Ion Sensitive Field Effect Transistor and Method of Monitoring a Property of a Fluid
ActiveUS20080265985A1Compensation effectWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementIon sensitiveIon
A signal processing circuit comprising one or more ion sensitive field effect transistors, ISFETs, and a biasing circuit for biasing the or each ion sensitive field effect transistor to operate in the weak inversion region.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
Apparatus of ion sensitive thin film transistor and method of manufacturing of the same
InactiveUS20060035400A1Reduce weightLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDriver circuitSignal processing circuits
The present invention discloses an apparatus of ion sensitive thin film transistor and method of manufacturing of the same. The apparatus of the invention, formed on a glass substrate, comprises an ion detector, formed on said glass substrate, including a plurality of ion sensitive transistors and a signal processor with display, also formed on said glass substrate, being coupled with said ion detector. The signal processor with display further comprises a circuit of signal processing, a driver circuit, and a display, wherein by means of the method of Low Temperature PolySilicon, i.e. LTPS technology, the invention integrates said ion detector and said signal processor with display on said glass substrate to become an tiny, light and thin apparatus with portable and disposable characteristics.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
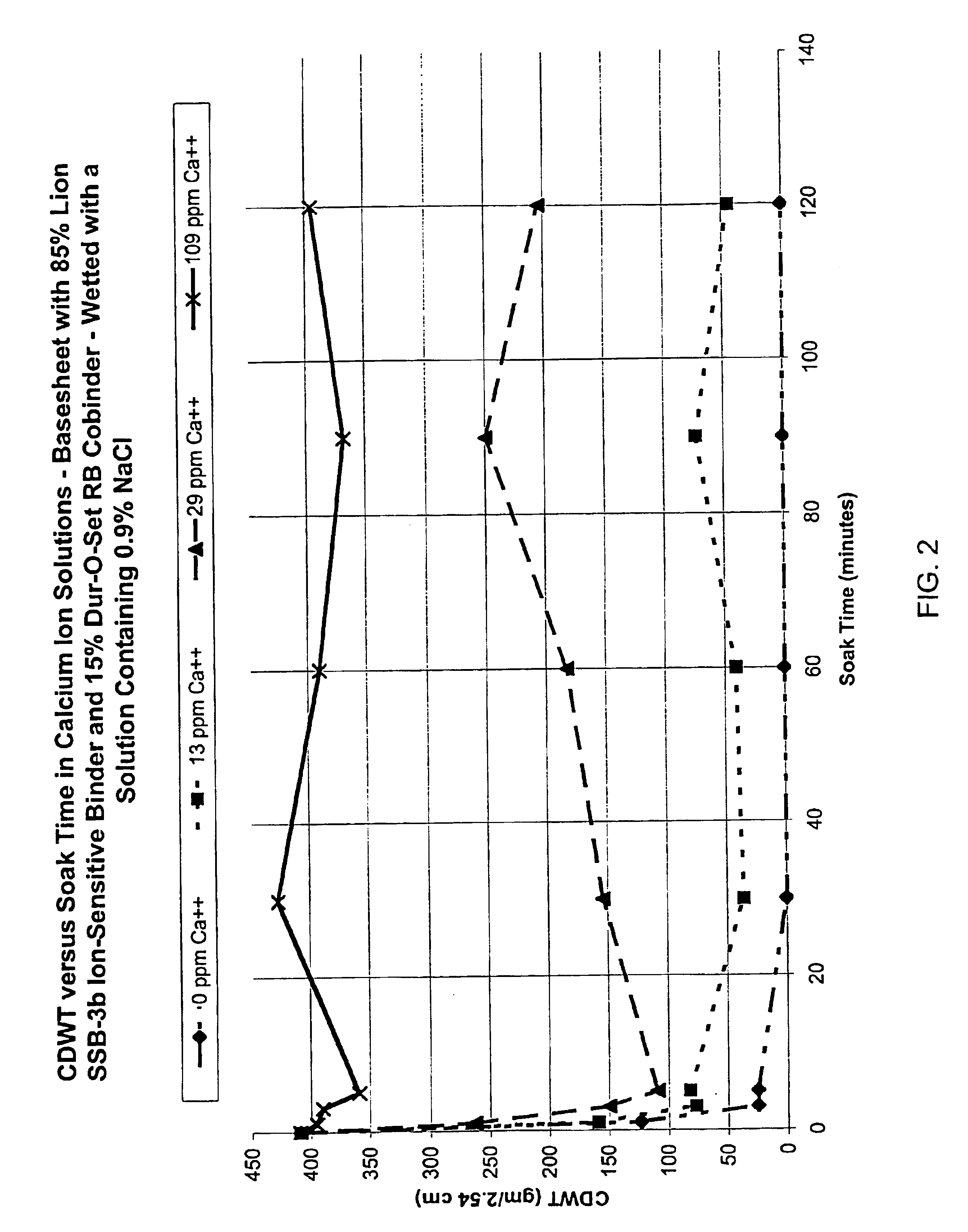
Pre-moistened wipe product
InactiveUS7101612B2Improve propertiesReduced high-shear viscosityInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsFiberWater dispersible
The present invention provides ion-sensitive, water-dispersible polymers. The present invention also provides a method of making ion-sensitive, water-dispersible polymers and their applicability as binder compositions. The present invention further provides fiber-containing fabrics and webs comprising ion-sensitive, water-dispersible binder compositions and their applicability in water-dispersible personal care products.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
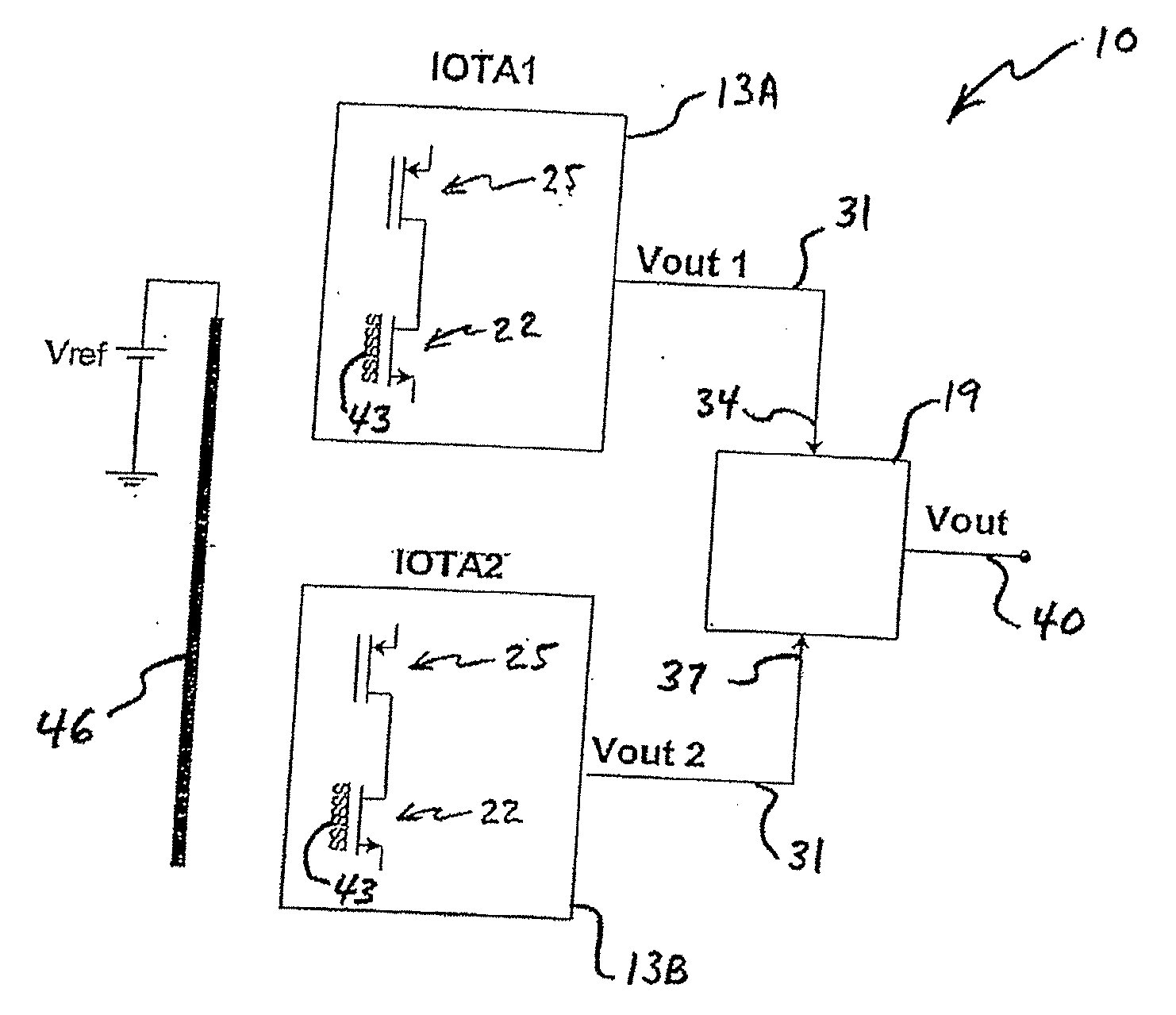
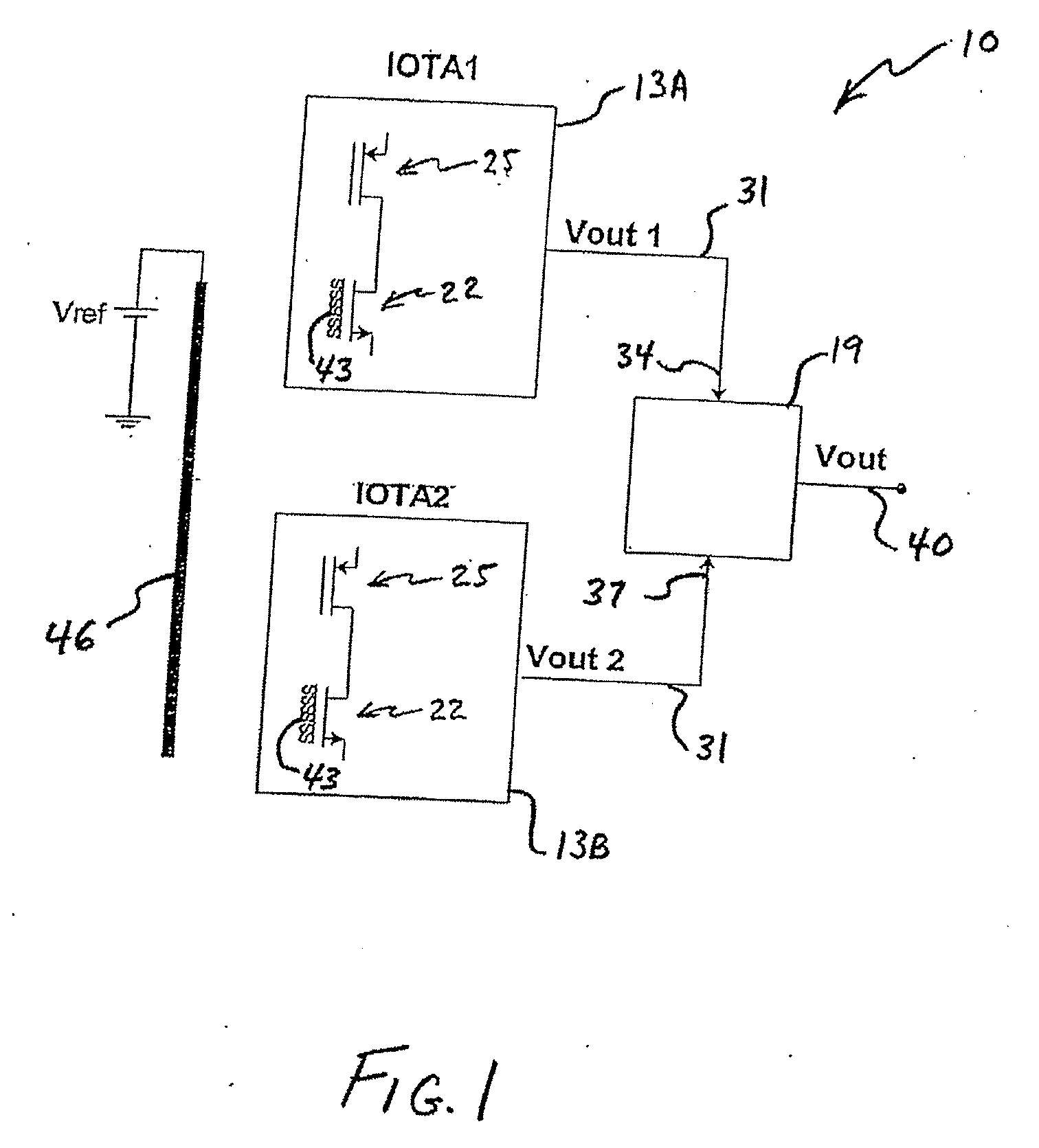
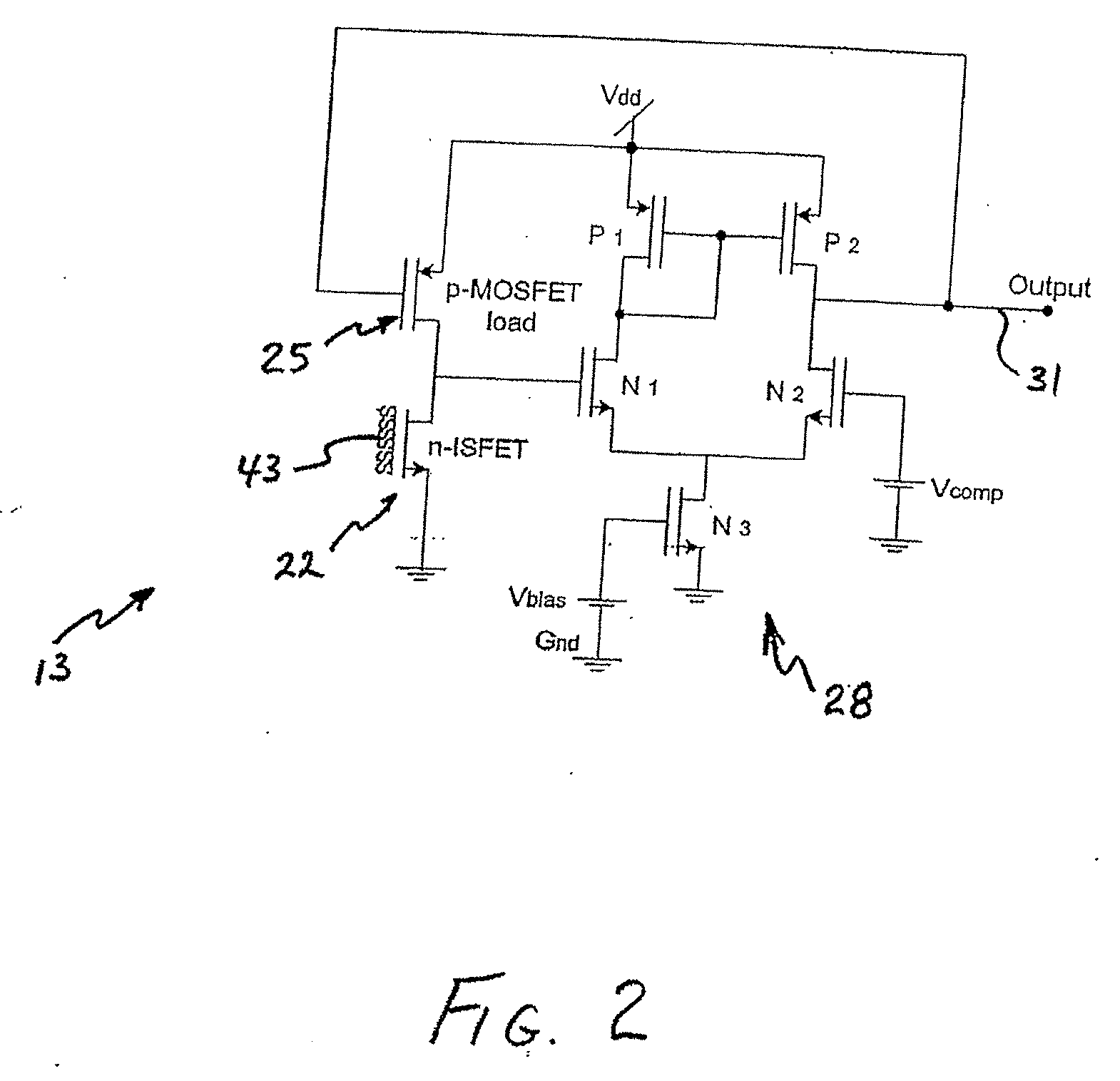
Ph-change sensor and method
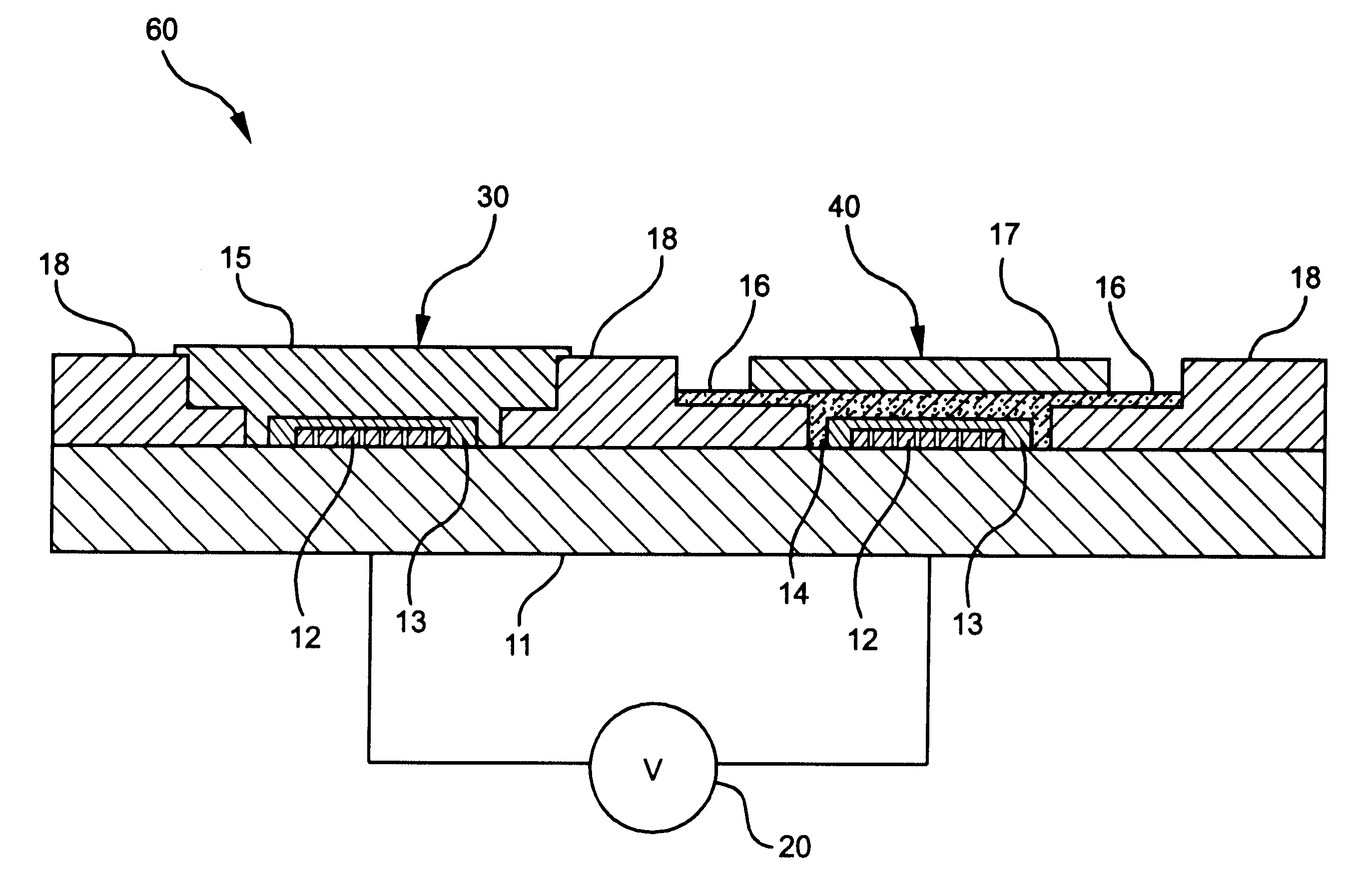
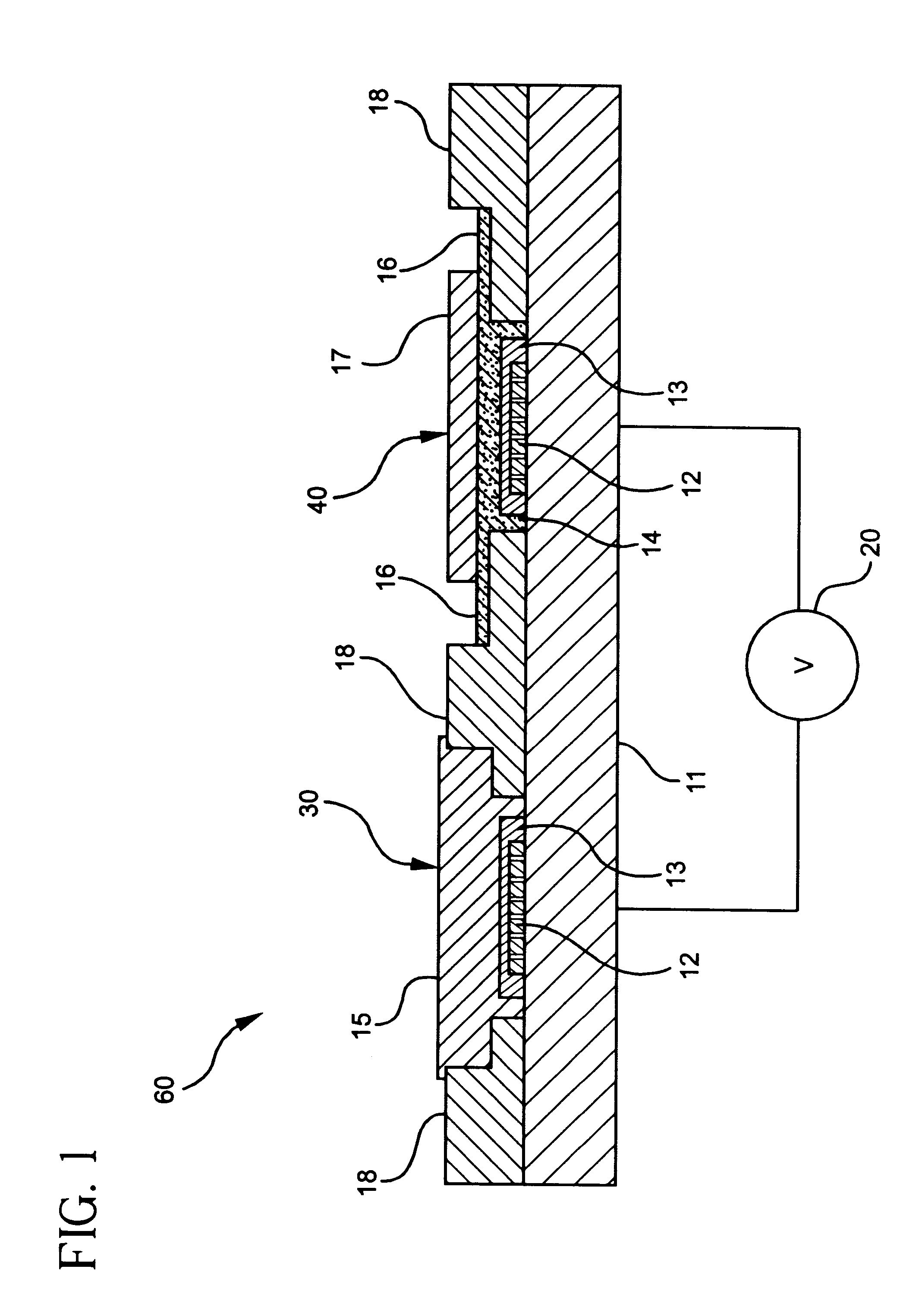
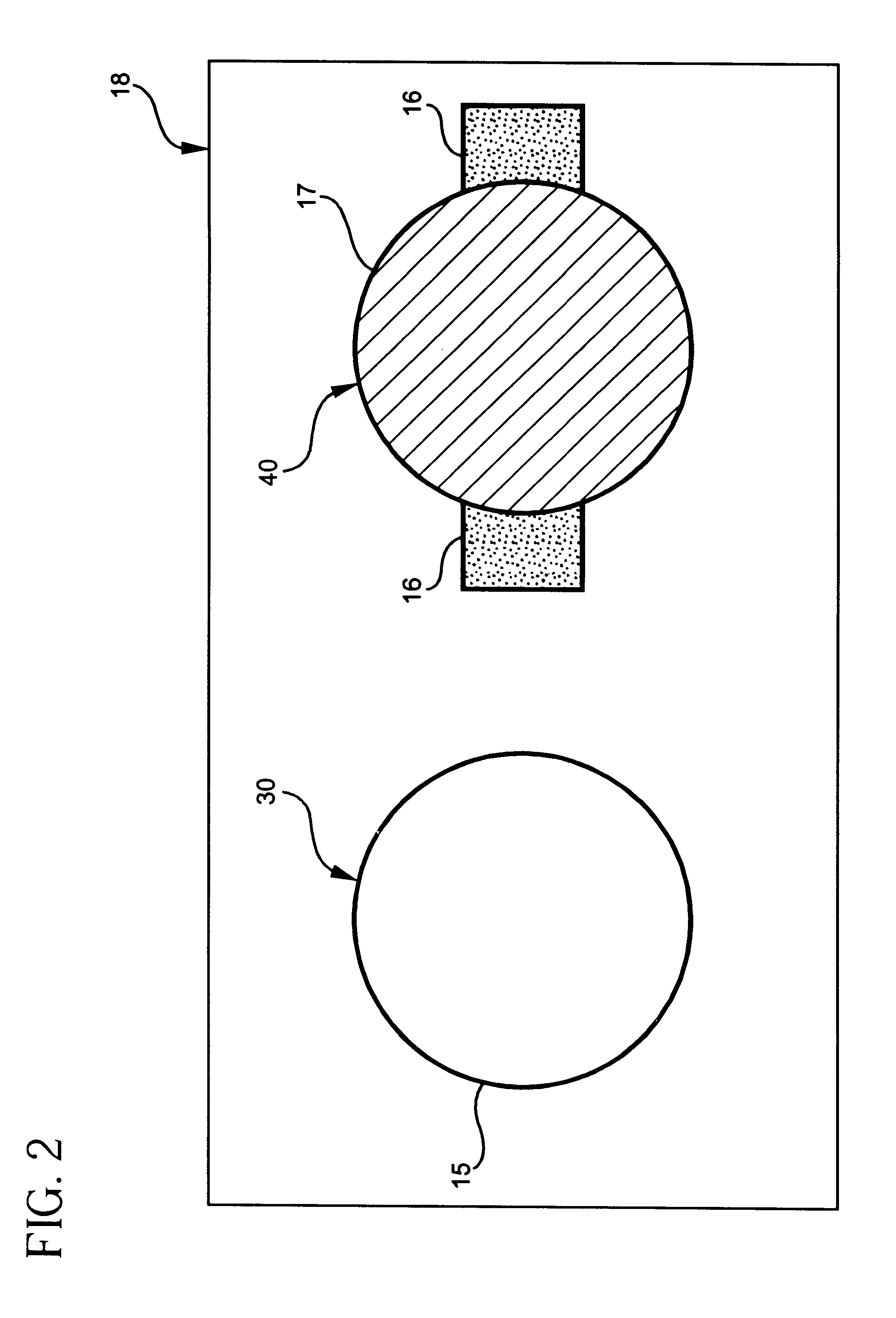
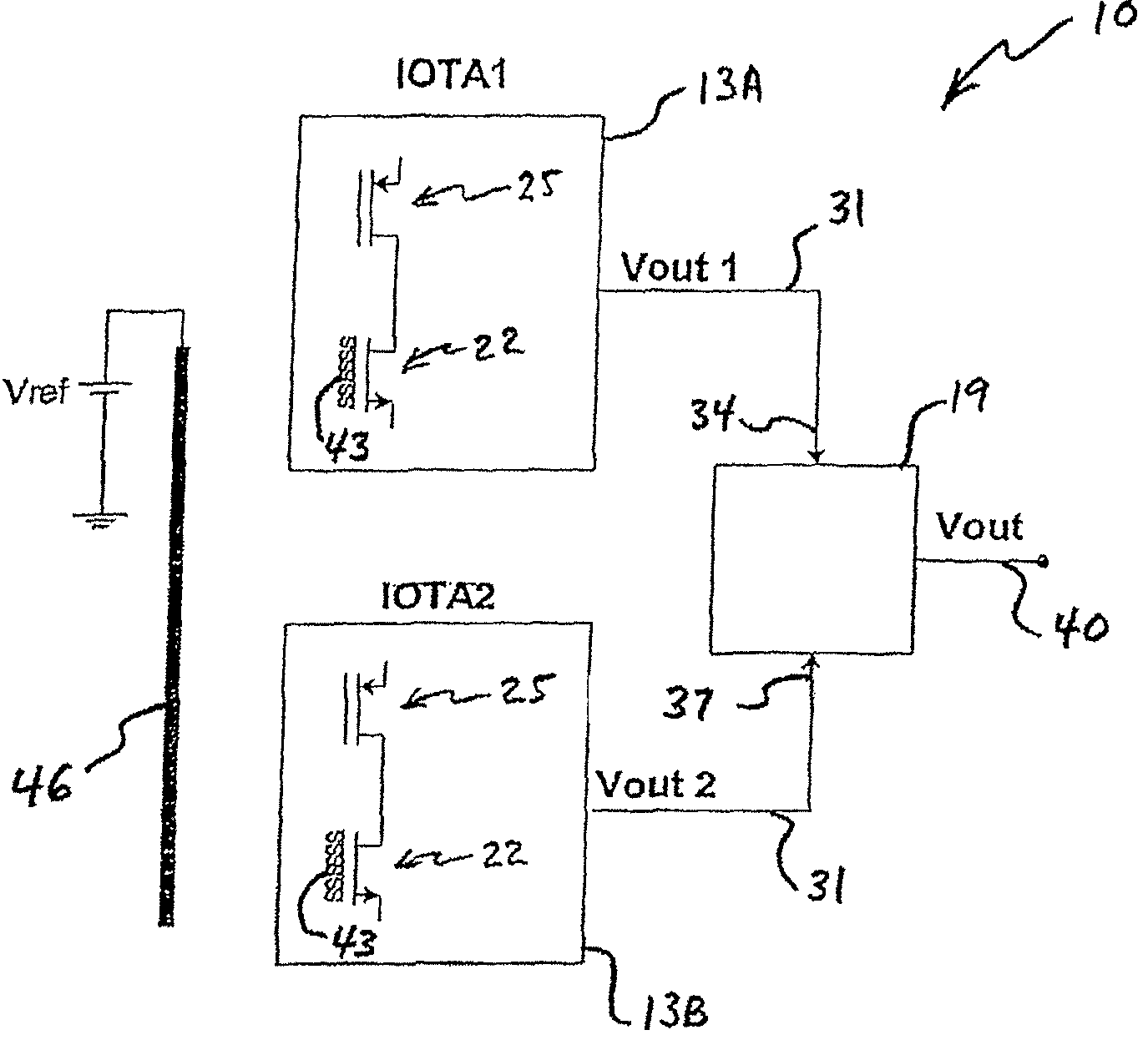
ActiveUS20070138028A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEngineeringOperational transconductance amplifier
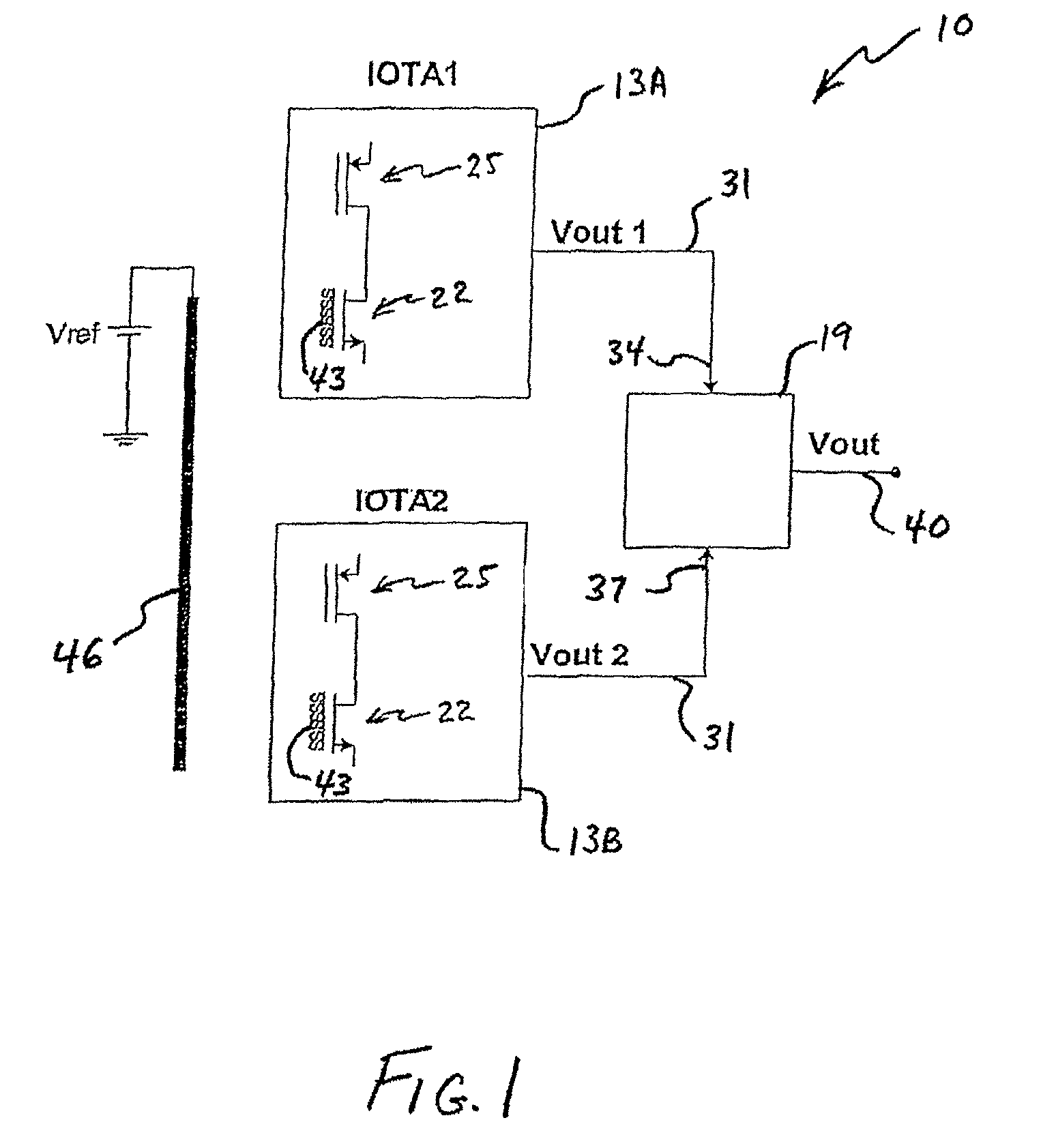
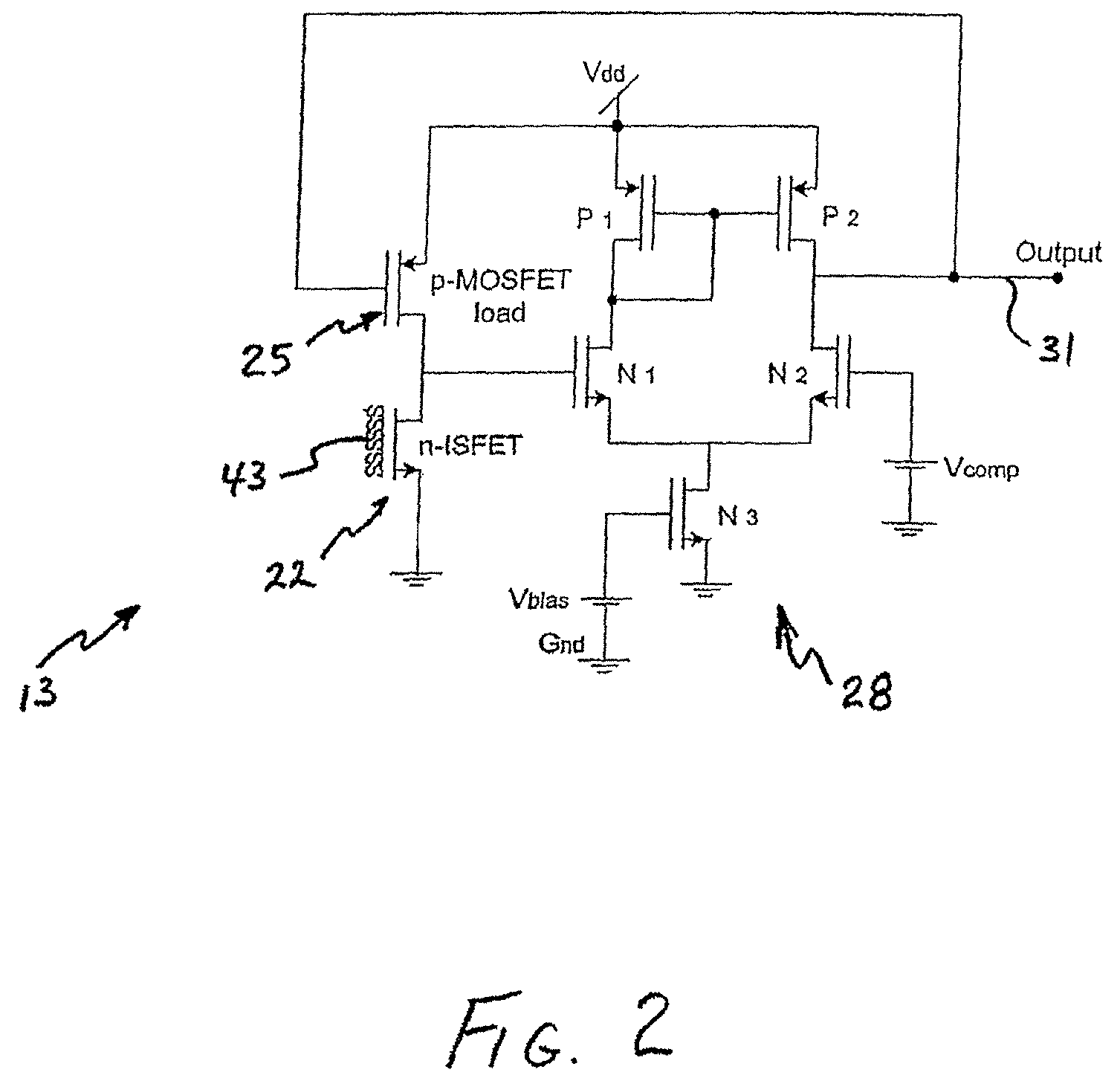
pH-change sensors and related methods are disclosed. One such sensor may have a first ion-sensitive transistor-operational-transconductance-amplifier (the “first IOTA”) and a second ion-sensitive transistor-operational-transconductance-amplifier (the “second IOTA”). Each IOTA may have an ion-sensitive transistor, a load transistor, and an output. In each IOTA, the drain region of the ion-sensitive transistor may be connected to the drain region of the load transistor. A differential sensor may be connected to the IOTAs, and an output from the differential sensor may indicate a voltage difference between the IOTA outputs. The output from the differential sensor may be used to provide an indication of a change in pH.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
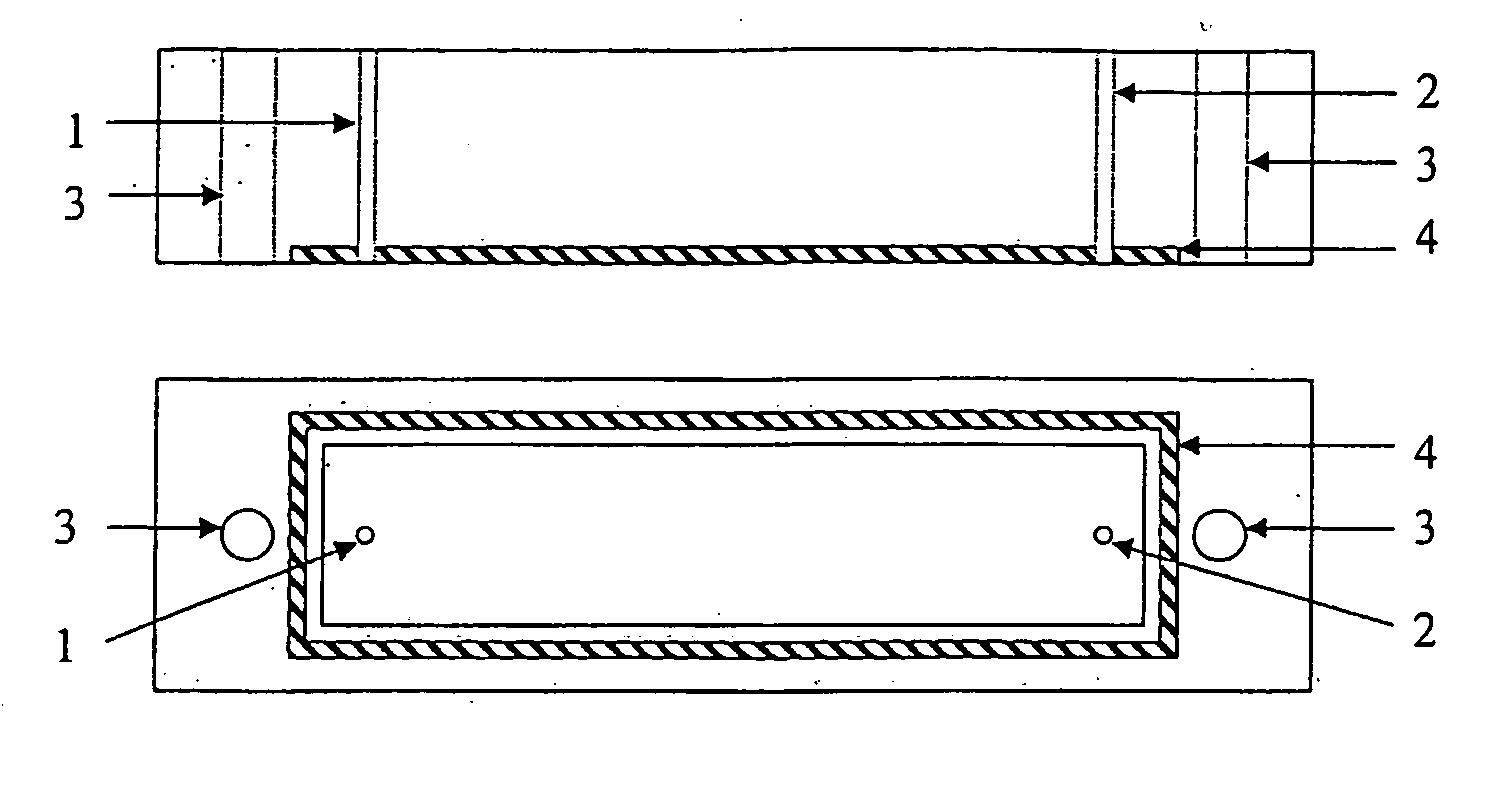
Miniaturized solid-state reference electrode with self-diagnostic function
The present invention relates to a reference electrode for a potentiometric electrode system, characterized in that the junction in contact with a sample solution is enlarged and an ion-sensitive membrane containing an ion selective material as a protective membrane for the inner reference solution is employed, which comprises a substrate; a metal layer; an insoluble metal salt layer; an insulating film for insulating the metal layer from an aqueous solution; a hydrogel serving as an inner reference solution; the junction on the hydrogel contacting with a sample solution; the ion-sensitive, protective membrane formed over all surface areas of the hydrogel, except for the junction, to separate the sample solution from the inner reference solution or act as an ion-sensing membrane upon the contamination of the junction, whereby the operational abnormality caused by junction contamination may be easily checked and fast activation may be achieved.
Owner:INFOPIA CO LTD
pH-change sensor and method
ActiveUS7794584B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOperational transconductance amplifierTransistor
pH-change sensors and related methods are disclosed. One such sensor may have a first ion-sensitive transistor-operational-transconductance-amplifier (the “first IOTA”) and a second ion-sensitive transistor-operational-transconductance-amplifier (the “second IOTA”). Each IOTA may have an ion-sensitive transistor, a load transistor, and an output. In each IOTA, the drain region of the ion-sensitive transistor may be connected to the drain region of the load transistor. A differential sensor may be connected to the IOTAs, and an output from the differential sensor may indicate a voltage difference between the IOTA outputs. The output from the differential sensor may be used to provide an indication of a change in pH.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Sensing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20100151479A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityChemical reaction
A sensing apparatus comprising an ion sensitive field effect transistor arranged to generate an electrical output signal in response to localised fluctuations of ionic charge at or adjacent the surface of the transistor, and means for detecting the electrical output signal from the ion sensitive field effect transistor, the localised fluctuations of ionic charge indicating events occurring during a chemical reaction.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
Ion sensitive sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103293209AGuaranteed uptimeImprove throughputMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSurface layerHigh flux
The invention relates to an ion sensitive sensor comprising a silicon oxide layer and a silicon substrate which are vertically stacked, a source electrode and a drain electrode arranged on the silicon oxide layer at an interval, and a graphene layer arranged on the surface of the silicon oxide layer and between the source electrode and the drain electrode; wherein the graphene layer is respectively connected with a gear shaping part of the source electrode and a gear shaping part of the drain electrode, and the surface layer of the graphene layer is penetrated with metal oxide particles; the ion sensitive sensor also comprises a micro fluidic channel layer which is erected on the gear shaping part of the source electrode and the gear shaping part of the drain electrode, and the gear shaping part of the source electrode and the gear shaping part of the drain electrode are coated with insulating layers; the micro fluidic channel layer is matched with the graphene layer to form a cavity for accommodating an object for measurement, and is opened with through holes; and suspended grid electrodes are inserted into the through holes and extend into the cavity. The ion sensitive sensor has a structure which is similar to a field effect transistor, and has advantages of high flux, high sensitivity, short response time and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
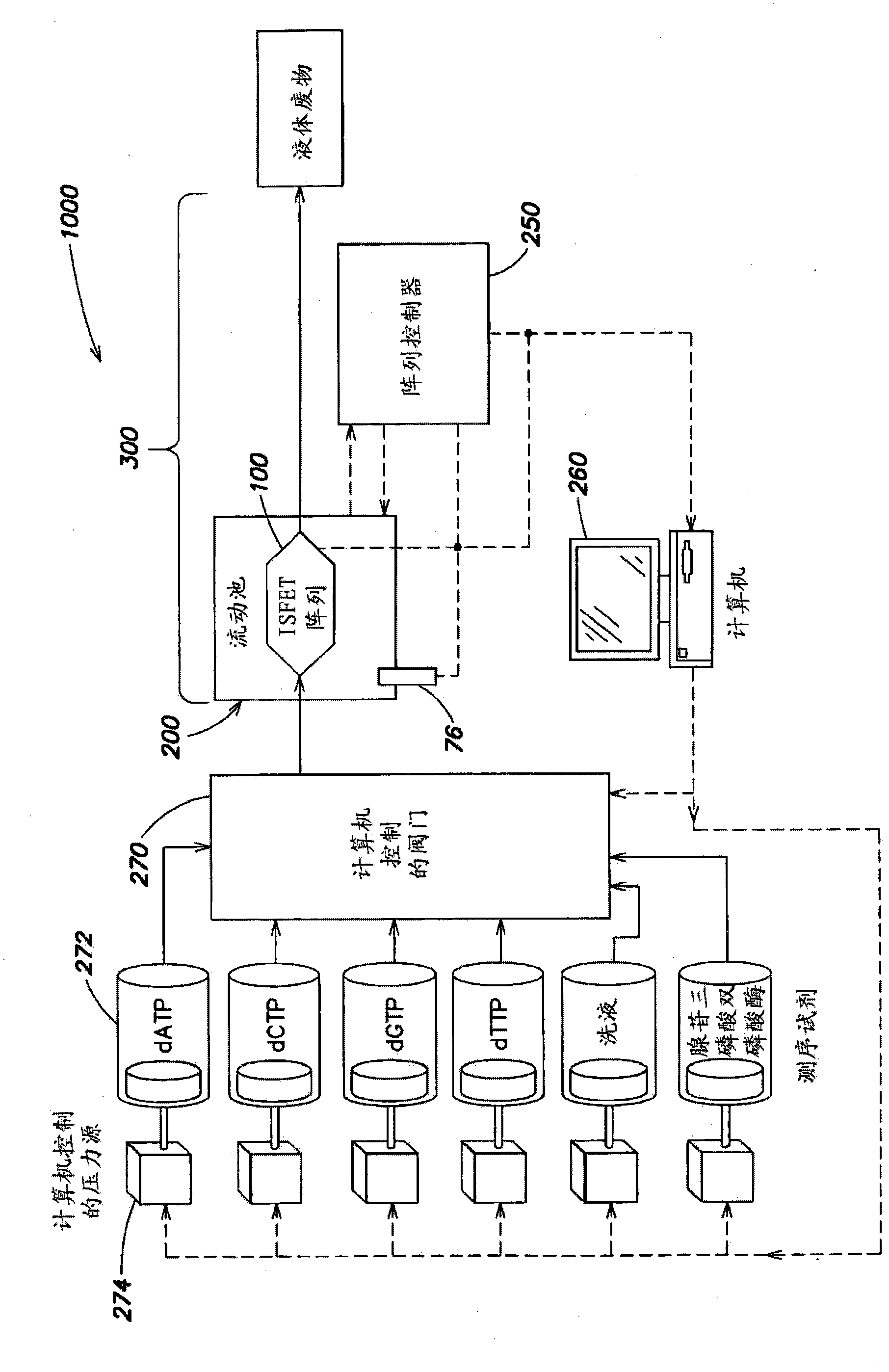
Integrated Sensor Arrays for Biological and Chemical Analysis
InactiveCN102301228ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTransistor arraySensor array
The present invention relates to devices and chips comprising large scale chemical field effect transistor arrays including an array of sample retention regions capable of retaining a chemical or biological sample from a sample fluid for analysis. In one aspect, such an array of transistors has a pitch of 10 μm or less, and each sample retention region is located on at least one chemical field effect transistor arranged to generate at least one output signal, which signal is consistent with such related to the characteristics of the chemical or biological sample in the sample retention area. In one embodiment, said chemical or biological sample is characterized by the concentration of charged species, and wherein each of said chemical field effect transistors is an ion-sensitive field effect transistor having a floating The dielectric layer is in contact with the sample fluid and is capable of accumulating charge in proportion to the concentration of charged species in the sample fluid. In one embodiment, such charged species are hydrogen ions, whereby the sensor measures the change in pH of the sample fluid in or near its sample retention zone. The devices and chips of the present invention may be suitable for large-scale pH-based DNA sequencing and other bioscience and biomedical applications.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Multi-ionophore membrane electerode
InactiveUS20060060471A1Reduce driftImprove adhesionMaterial electrochemical variablesChemical speciesMembrane configuration
A polymeric membrane for ion sensitive measurement comprising a polymer, a lipophilic salt and at least two ionophores selective for different chemical species. The membrane may be used in a pseudo reference for measurement of a plurality of ions.
Owner:DREW SCI
DNA sequencing employing nanomaterials
InactiveUS20120264617A1Compact and field portableLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanowireNucleotide
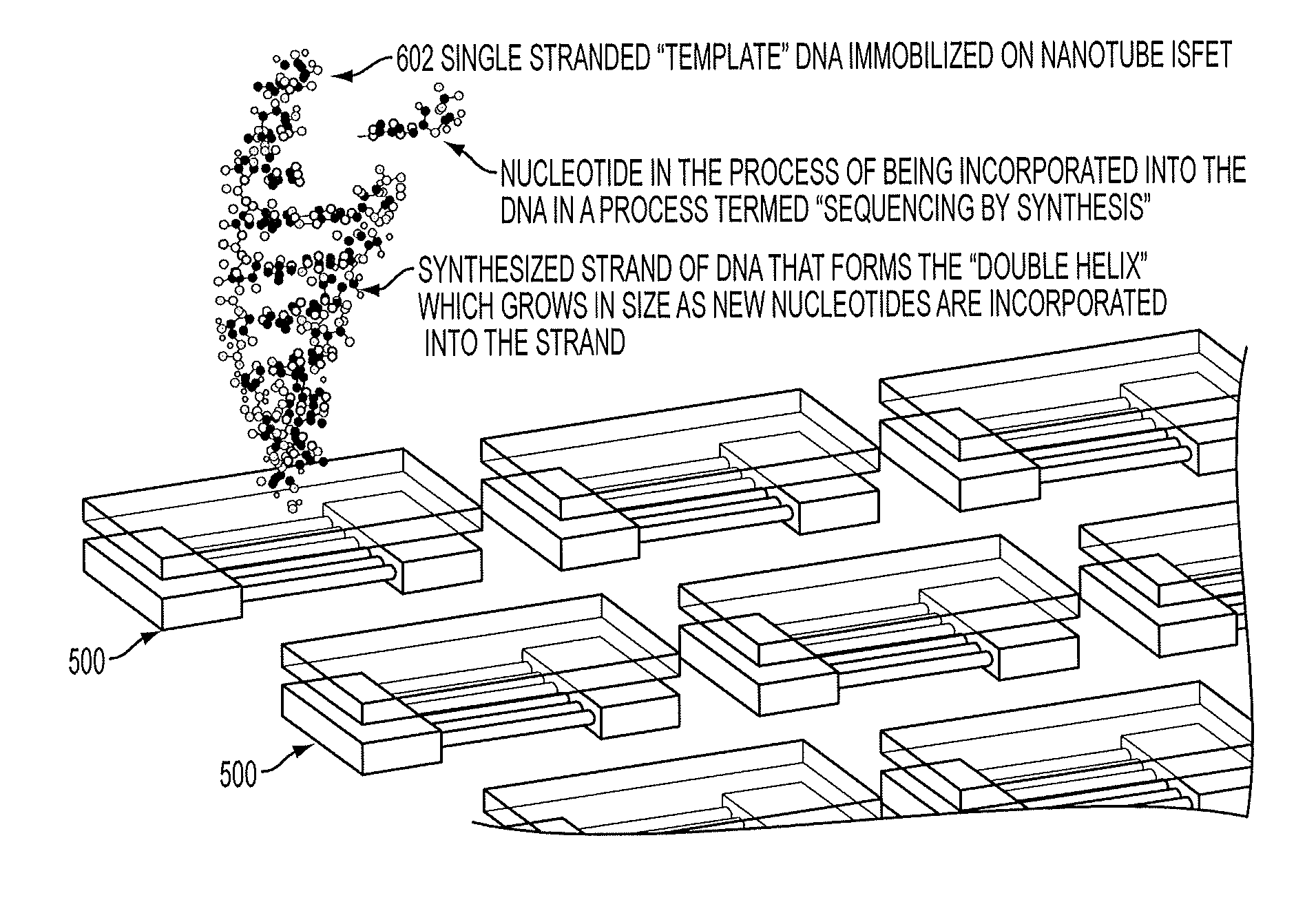
Charge transfer doped nanomaterials such as hydrogen terminated diamond, nanotubes, nanowires or similar nanostructures are used to create a highly sensitive pH sensor, or ion sensitive sensor to directly detect the addition of a newly incorporated nucleotide when performing DNA sequencing by synthesis. A single highly integrated chip can be made to sequence many strands of DNA in a massively parallel fashion in a short amount of time with a direct electronic readout that will bring the cost, size, power consumption of sequencing DNA to very attractive and useful levels.
Owner:PETTIT JOHN W
TFT ion sensor and TFT ion sensor apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20150276663A1High sensitivityTransistorMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMOSFETCapacitance
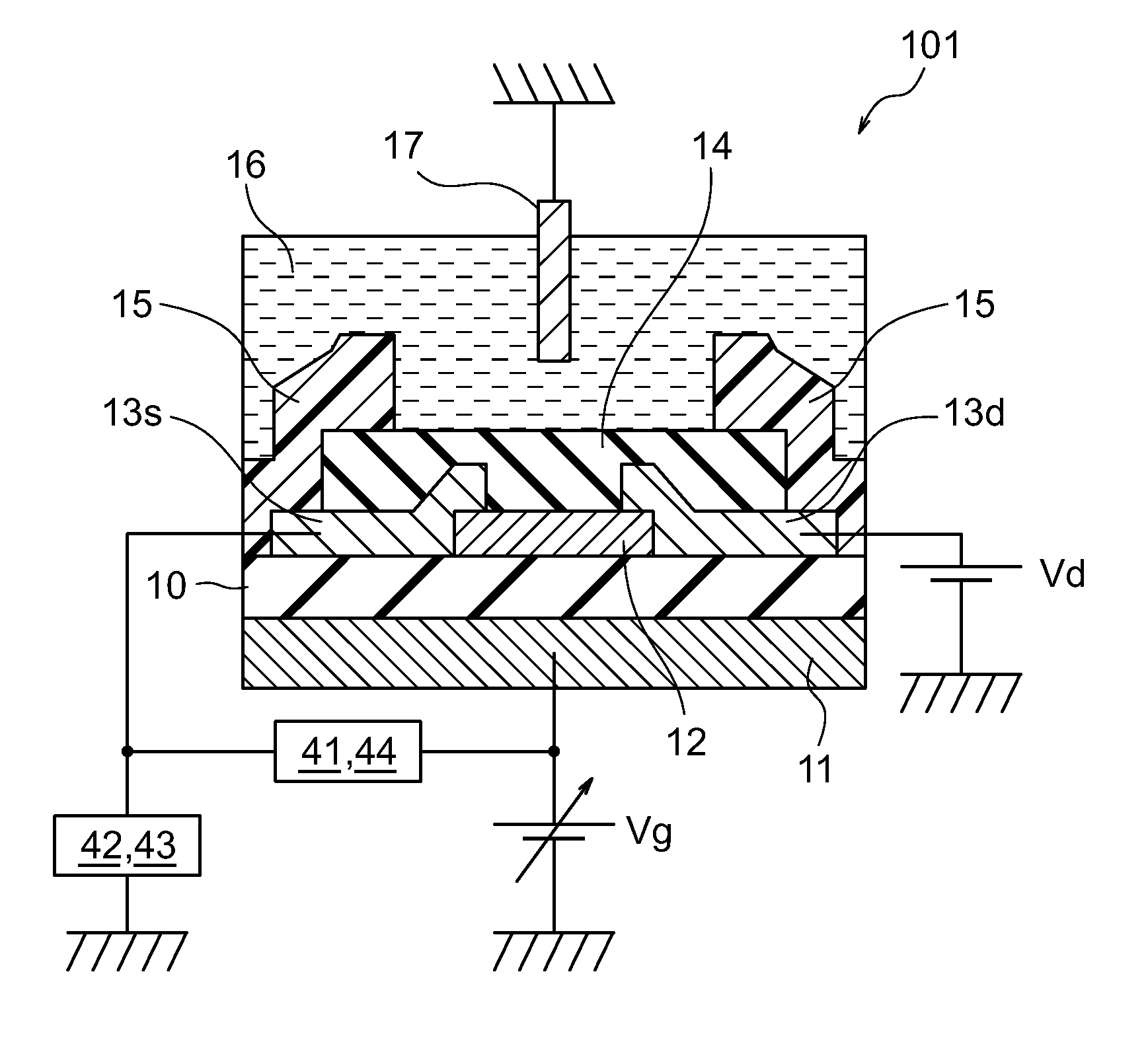
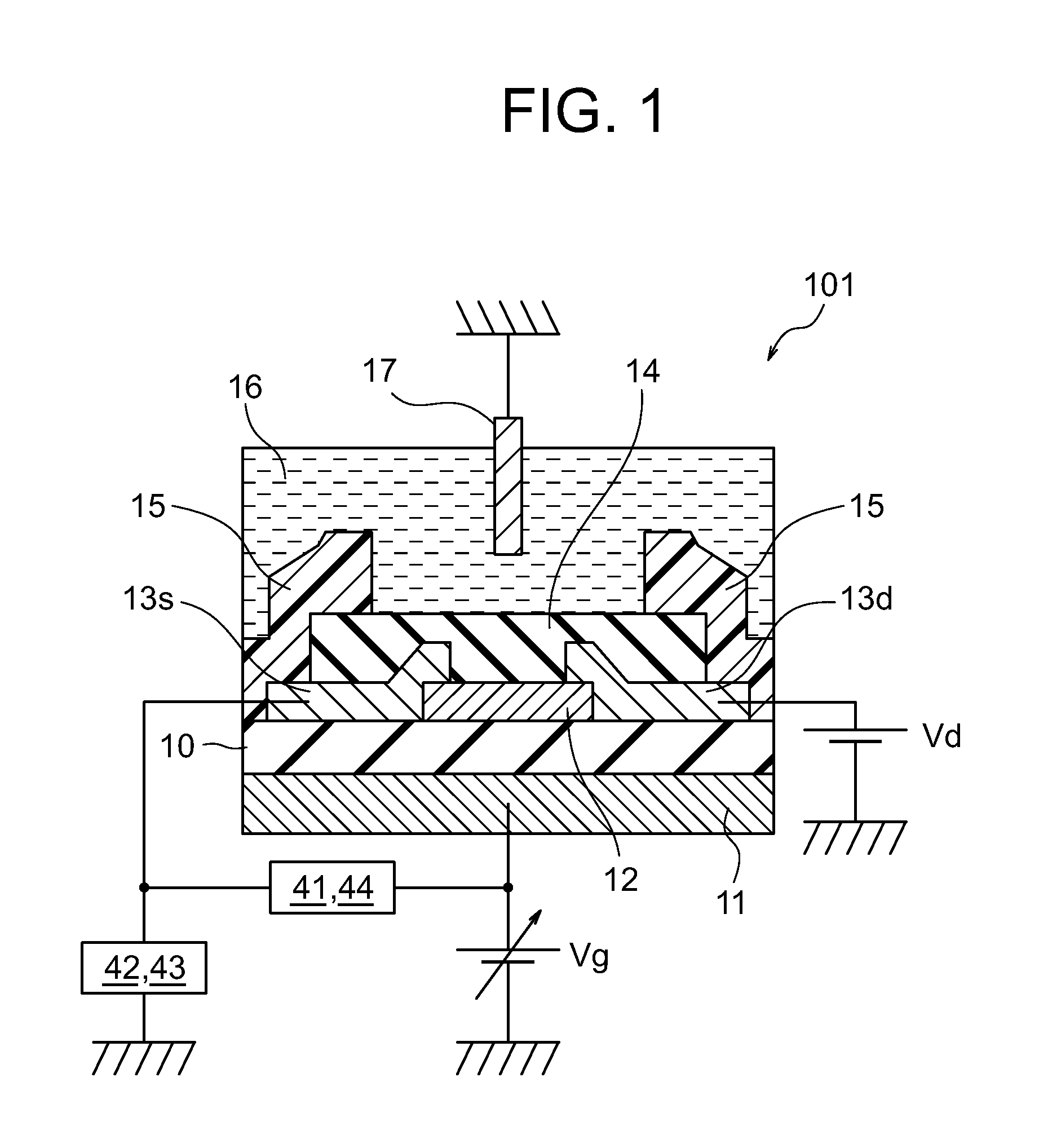
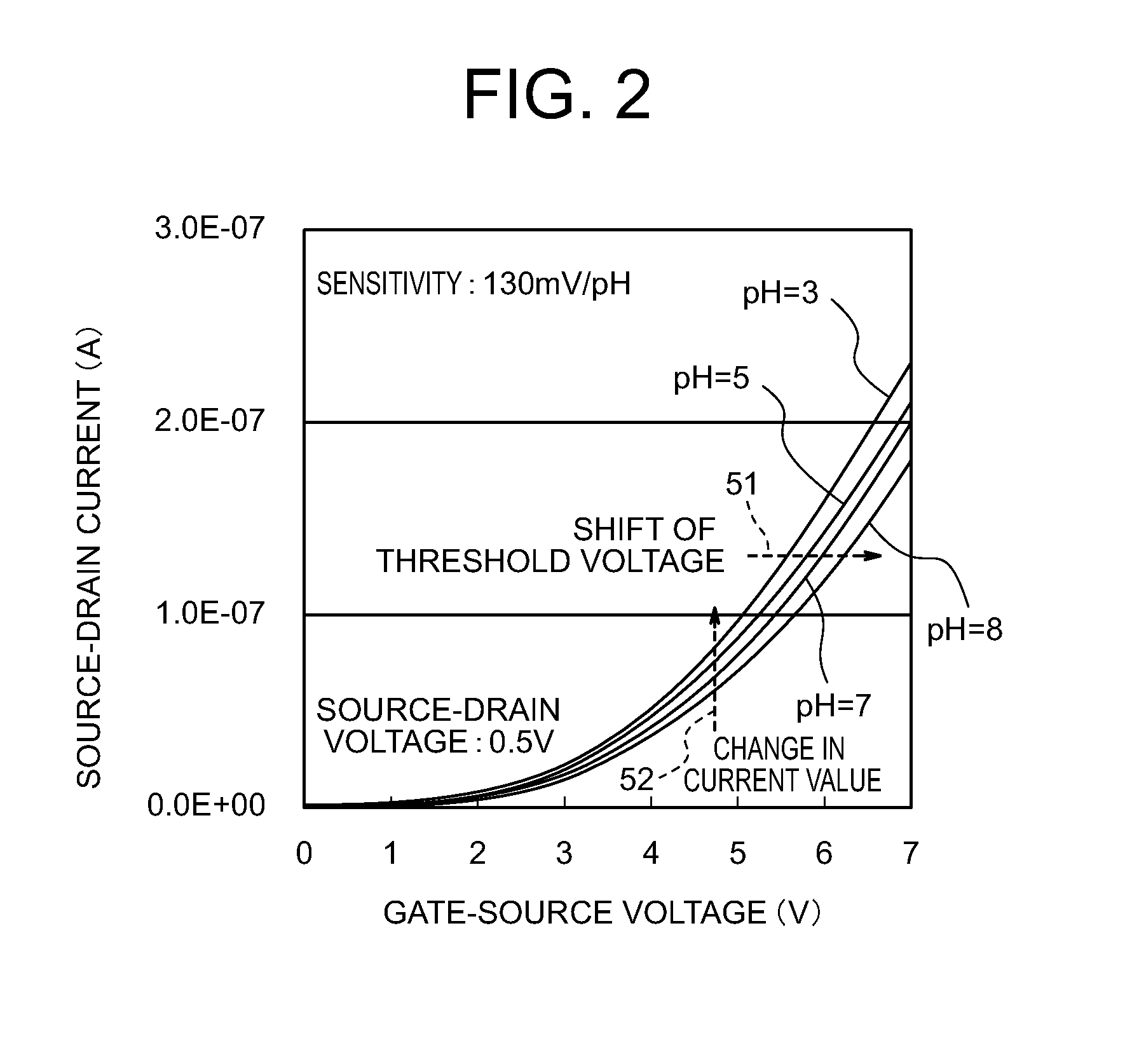
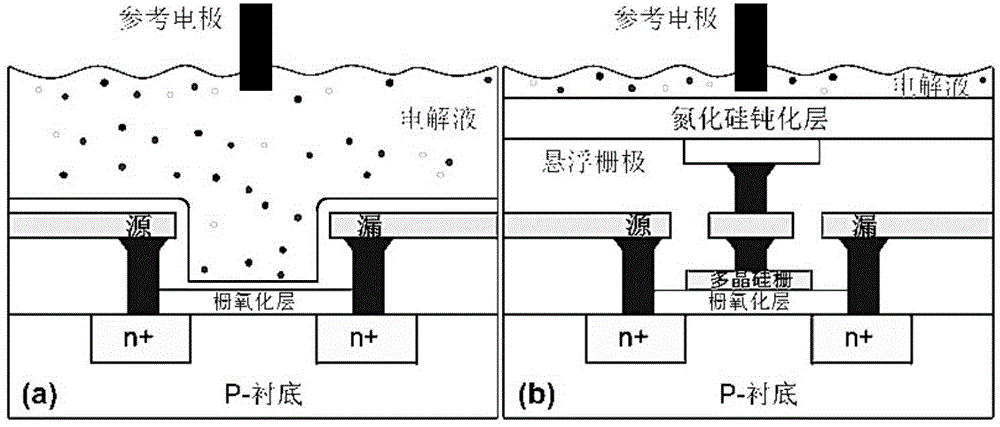
The ion sensors using TFT or MOSFET are low in the measurement sensitivity so that it is difficult to detect an extremely small amount of sensing-target substance. A TFT ion sensor includes both a gate electrode (a silicon substrate) and a reference electrode, in which the electrostatic capacitance of a gate insulating film (a thermal oxide film) is set to be larger than the electrostatic capacitance of an ion sensitive insulating film. Therefore, it is possible to detect the concentration of ions, hormones, and the like in a sensing-target substance from the shift in the threshold voltage of the gate-source voltage to source-drain current property.
Owner:TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Ion-sensitive hard water dispersible polymers and applications therefor
InactiveUS6855790B2Difficulty in dispersibilityIncrease contentAnionic surface-active compoundsDetergent materialsFiberWater dispersible
The present invention is directed to ion-sensitive, hard water dispersible polymers. The present invention is also directed to a method of making ion-sensitive, hard water dispersible polymers and their applicability as binder compositions. The present invention is further directed to fiber-containing fabrics and webs comprising ion-sensitive, hard water dispersible binder compositions and their applicability in water dispersible personal care products.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
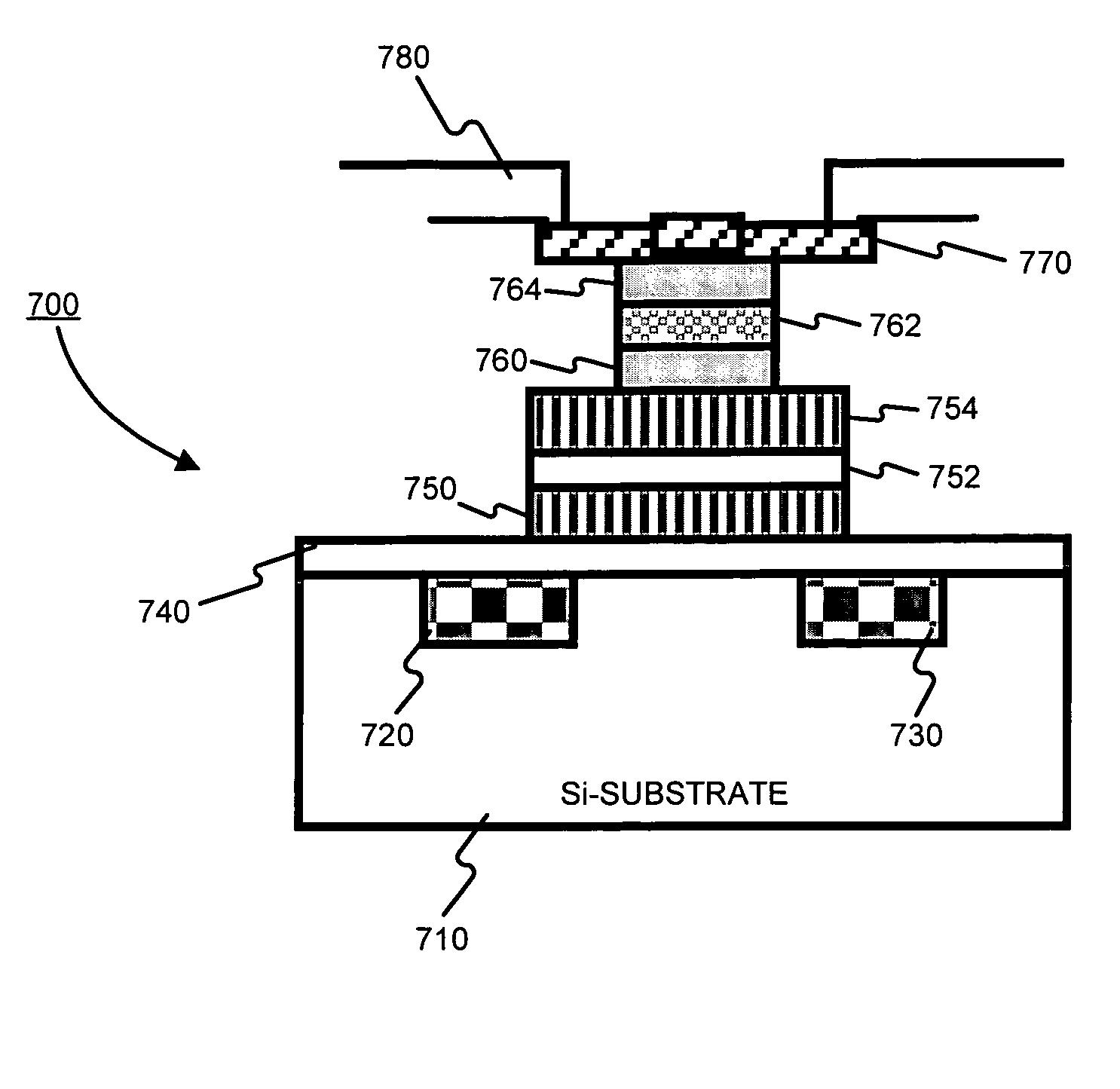
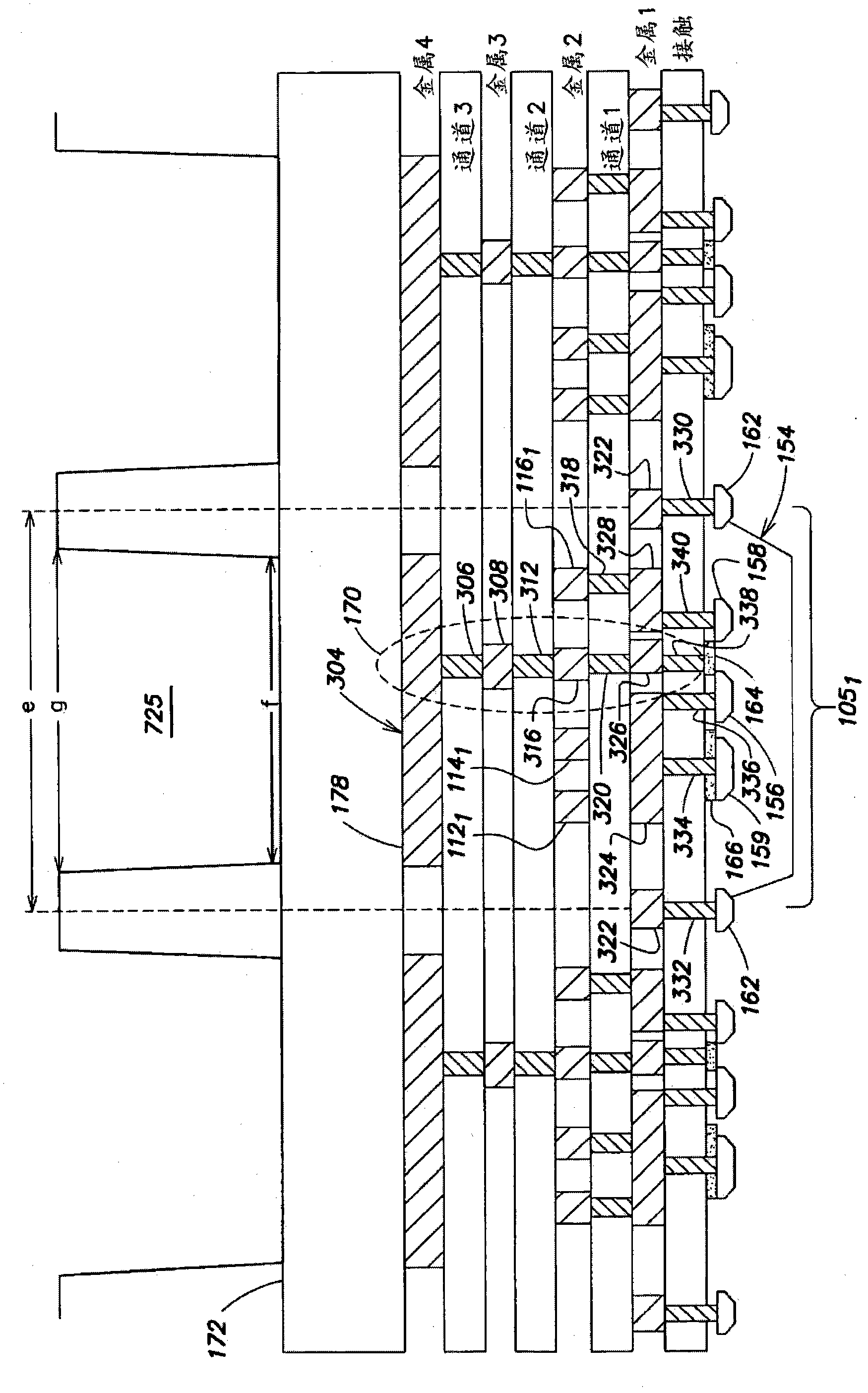
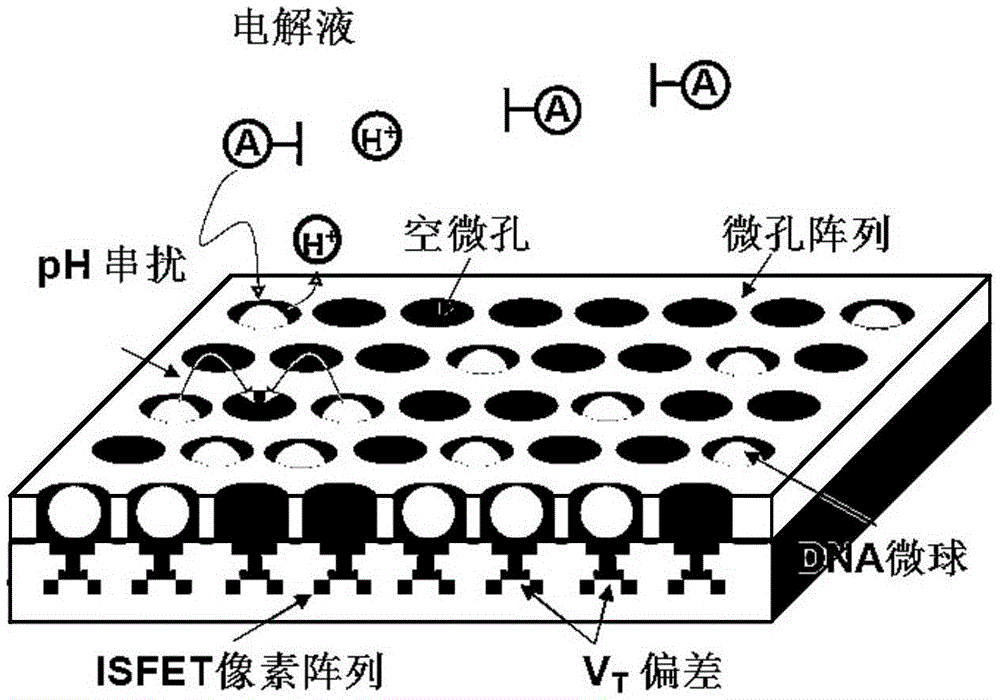
CMOS and ISFET dual-mode image chemical sensor chip for high-throughput gene sequencing
InactiveCN105543071AReduce mismatchQuick responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStatic random-access memoryHemt circuits
The invention provides a CMOS and ISFET dual-mode image chemical sensor chip for high-throughput gene sequencing; the chip comprises a dual-mode pixel array, a row decoder / driver, a column decoder / driver, a column parallel gain adjustable amplifier, a column parallel single-slope analog-digital converter, a static random access memory, a sensitive amplifier, a low voltage differential signal readout module, a static register, a phase-locked loop, a ramp generator and a digital control current source. The chip comprises an image sensor and an ion sensitive field effective transistor (ISFET) produced by a standard semiconductor process, so that optical image acquisition and chemical pH value detection can be performed. A high-speed correlated double sampling signal readout circuit adapting to the image and chemical dual-mode sensing is provided to reduce a system error caused by the mismatch between threshold voltages VT of the sensors. The chip has the advantages of high accuracy and high throughput when applied in gene sequencing.
Owner:严媚
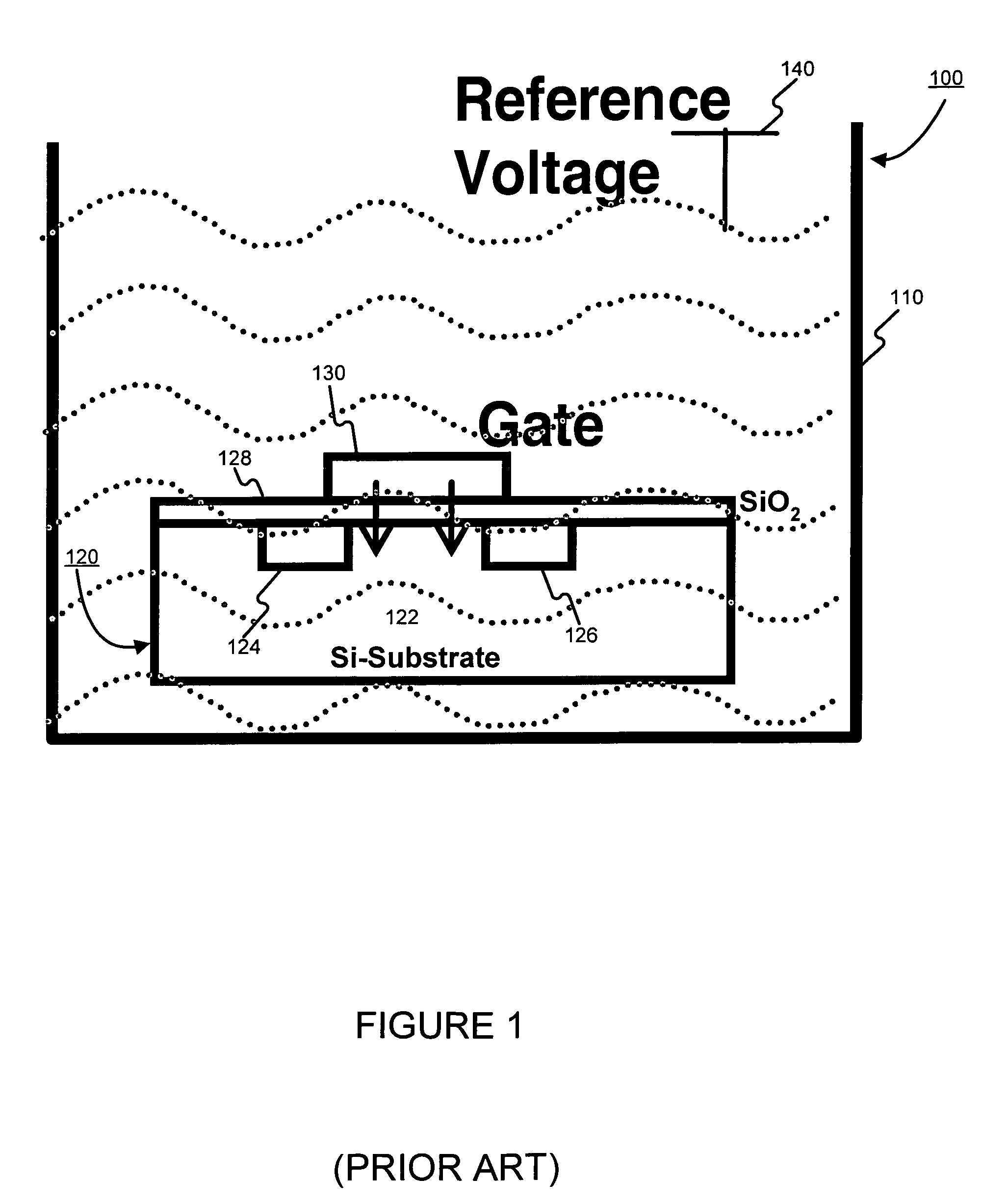
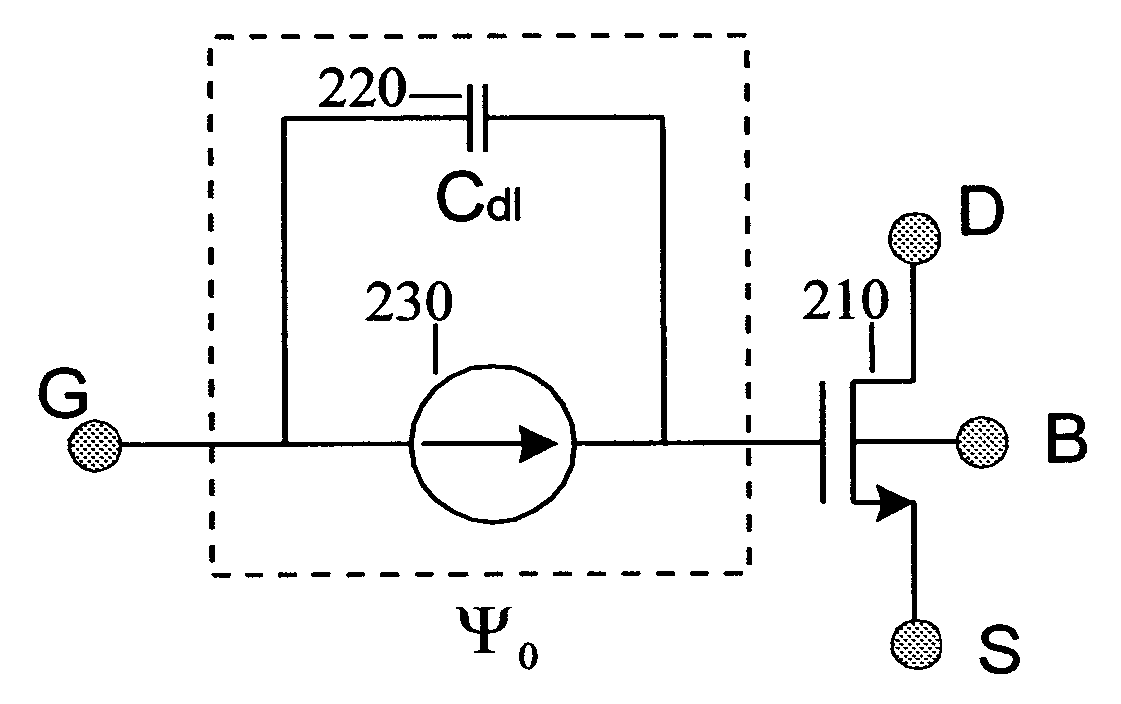
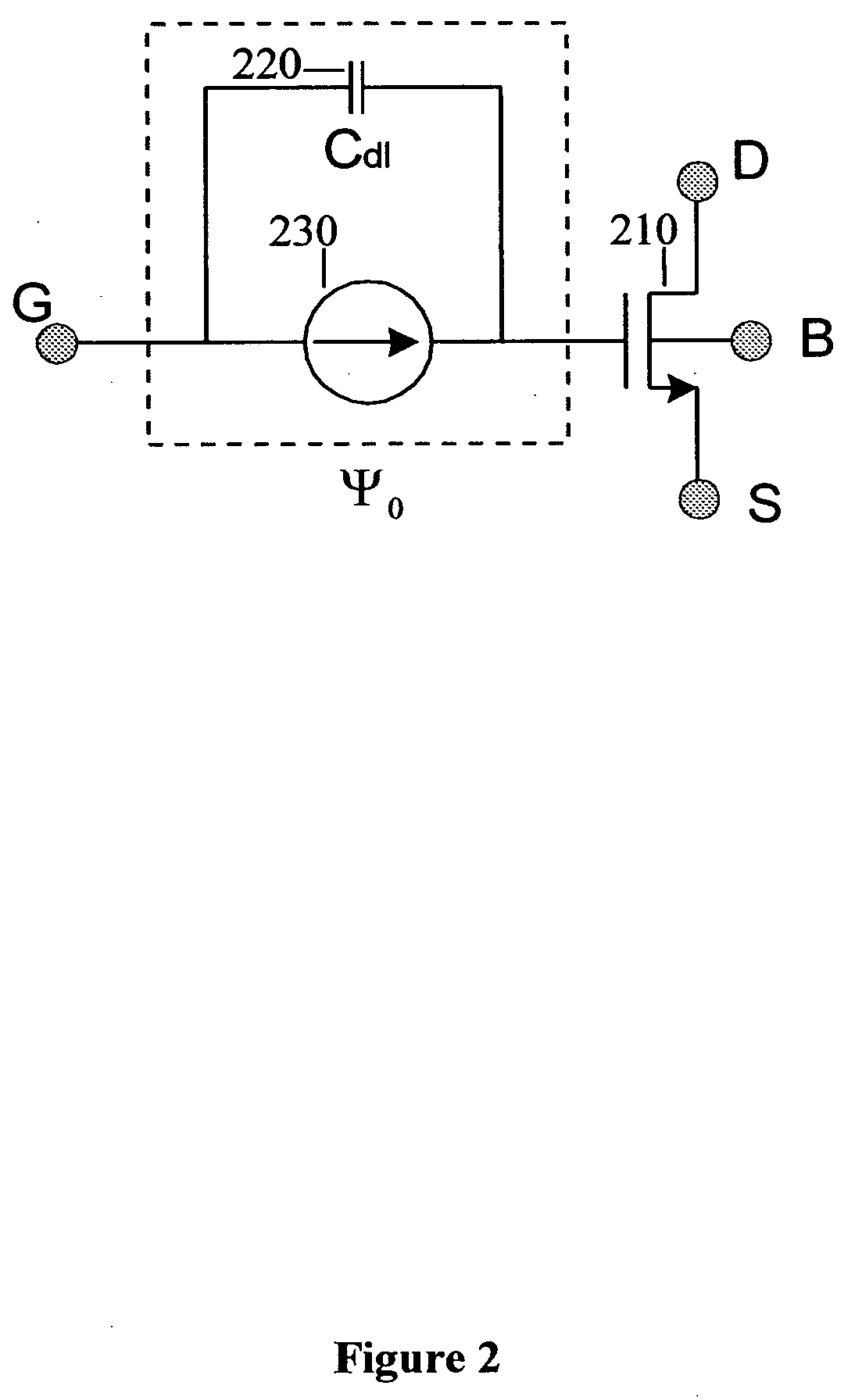
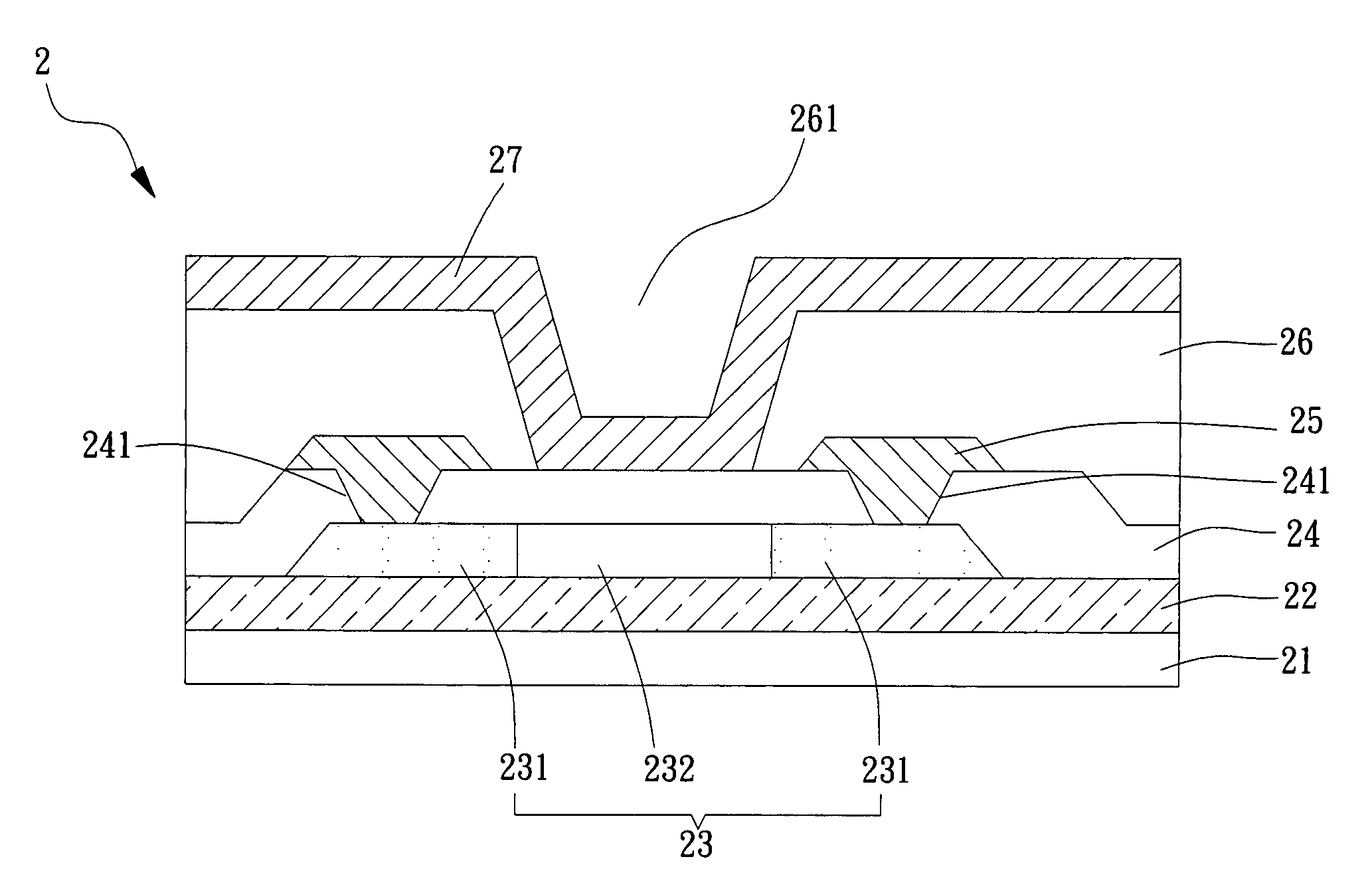
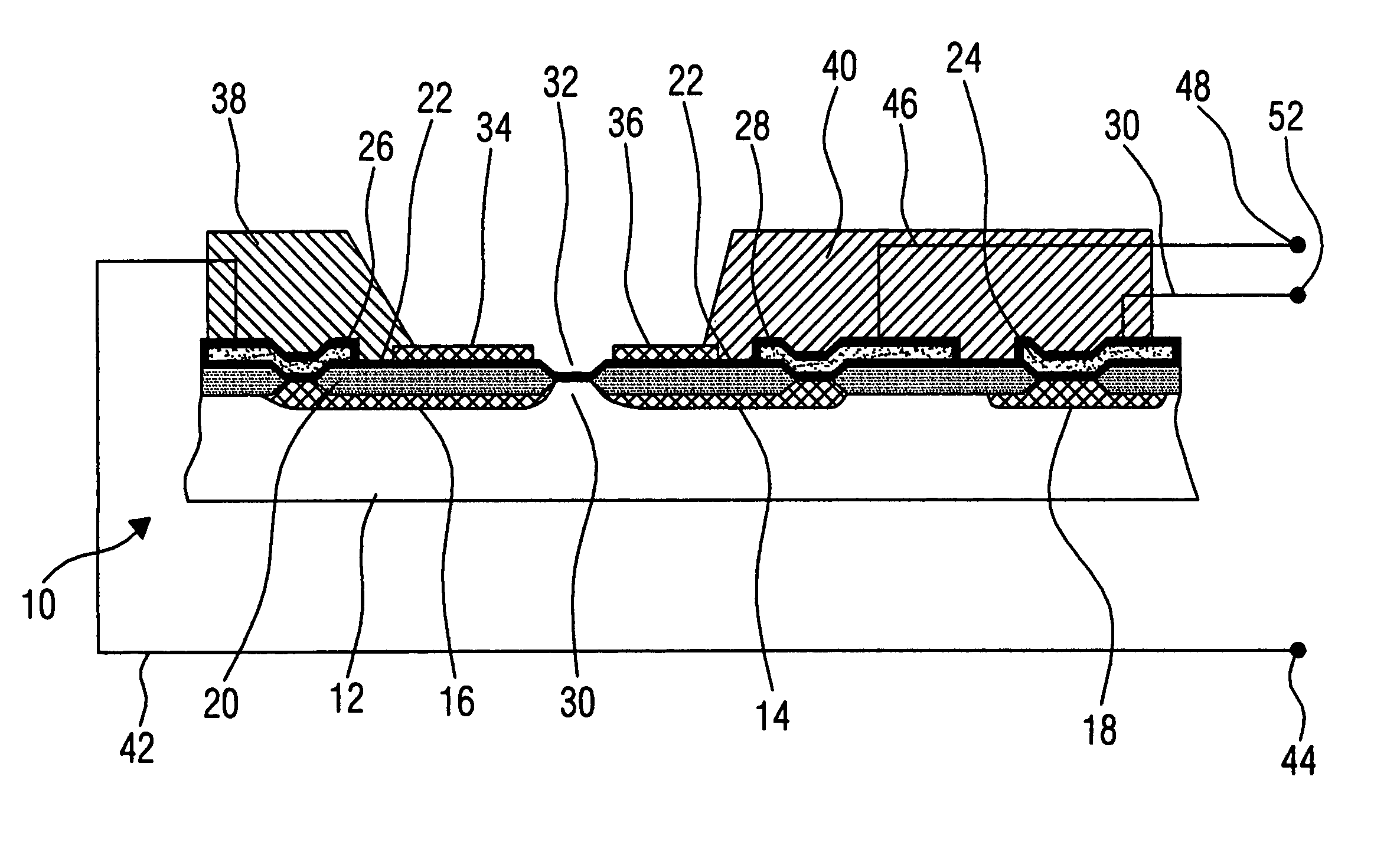
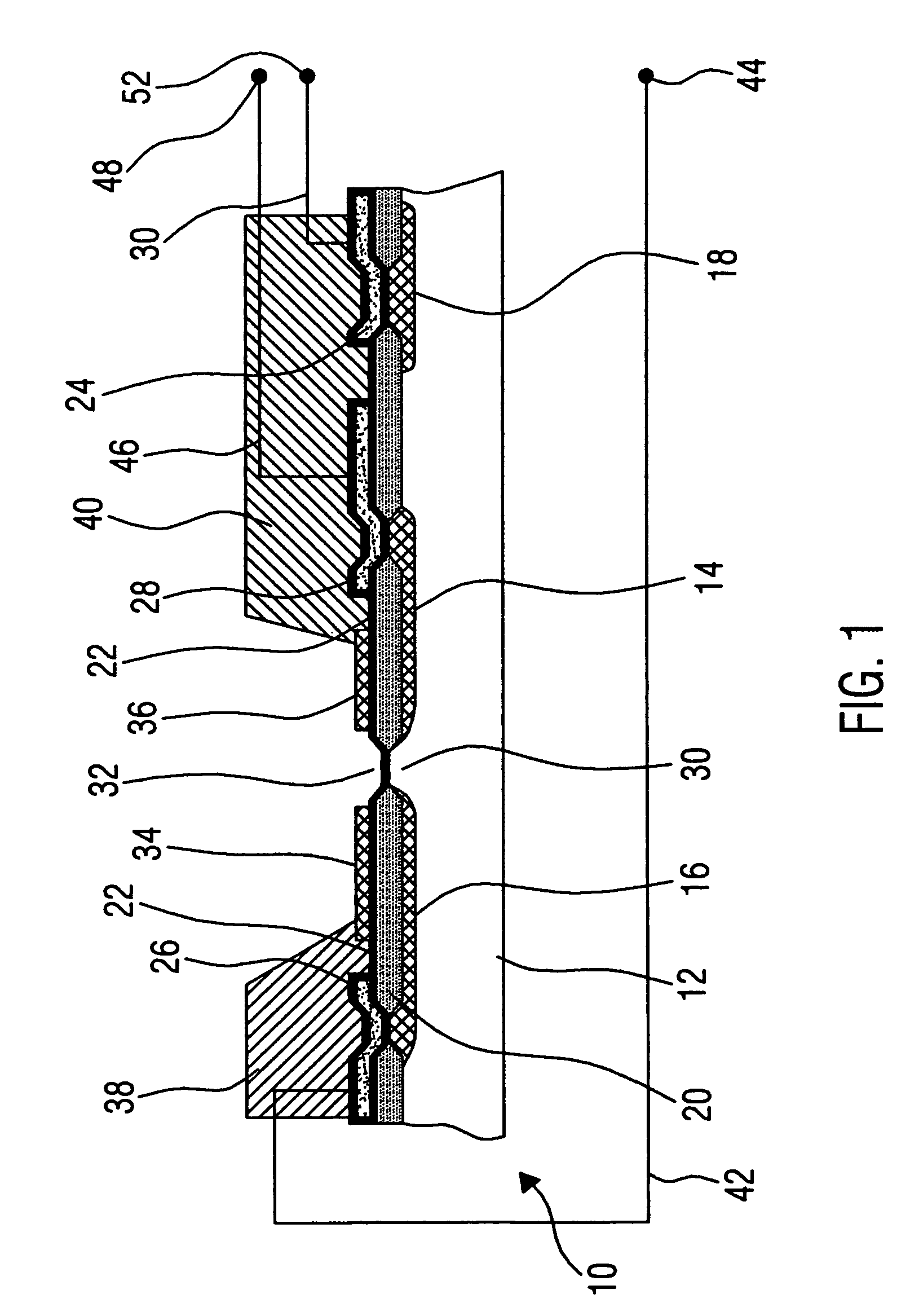
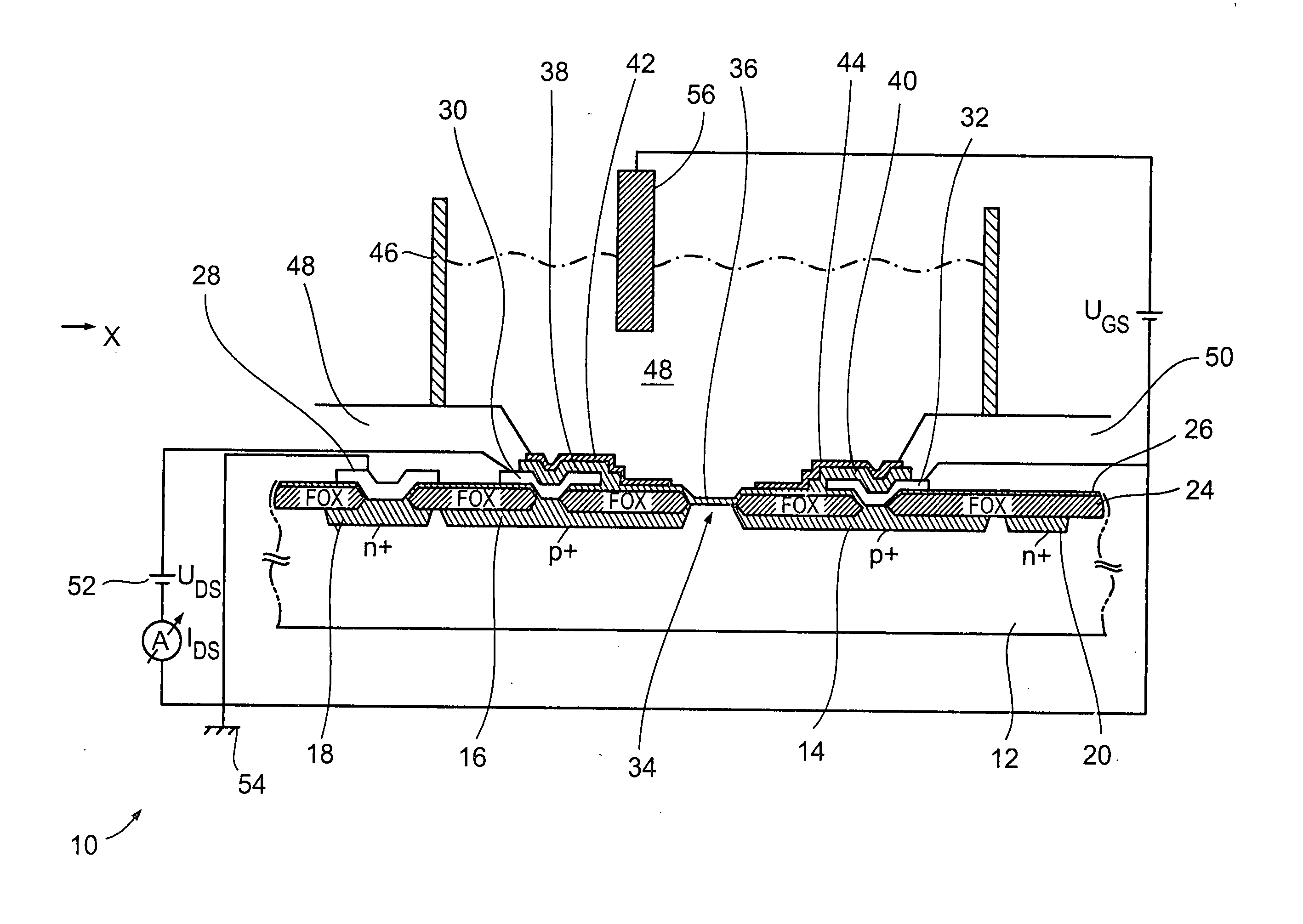
Ion-sensitive field effect transistor and method for producing an ion-sensitive field effect transistor
InactiveUS7321143B2Improved sensor propertySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNitrideCondensed matter physics
An ion-sensitive field effect transistor includes a substrate on which there are formed a source region and a drain region. Above a channel region, the ion-sensitive field effect transistor has a gate with a sensitive layer including a metal oxide nitride mixture and / or a metal oxide nitride mixture compound.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Ion-sensitive, water-dispersible polymers, a method of making same and items using same
The present invention is directed to ion-sensitive, water-dispersible polymers. The present invention is also directed to a method of making ion-sensitive, water-dispersible polymers and their applicability as binder compositions. The present invention is further directed to fiber-containing fabrics and webs comprising ion-sensitive, water-dispersible binder compositions and their applicability in water-dispersible personal care products.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Ion sensitive field effect transistor and method for producing an ion sensitive field effect transistor
InactiveUS20050012115A1Operational safety is highLow production costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPill deliveryCarbon nitrideCondensed matter physics
The invention relates to an ion-sensitive field effect transistor, comprising a gate (36) consisting of carbon nitride. The carbon nitride gate (36) is highly resistant to aggressive substances to be measured and also exhibits good adhesive properties. In addition, the ion-sensitive field effect transistor has high long-term stability and negligible drift. Said ion-sensitive field effect transistor can be produced in a method that uses CMOS-compatible planar technology.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Multi-parameter sensor with readout circuit
InactiveUS20070000778A1Improve linearitySmall sizeMaterial electrochemical variablesDual modeAmperometric biosensor
The present discloses an ion sensor and its readout circuit. The sensor includes potentiometric, amperometric ion sensors or dual mode electrochemical sensor. The dual mode electrochemical sensors can be measured by the same measurement circuit system. The dual mode sensors are extended gate ion sensitive field effect transistors and amperometric biosensors. The measurement circuit system is adaptable to the different mode sensors.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com