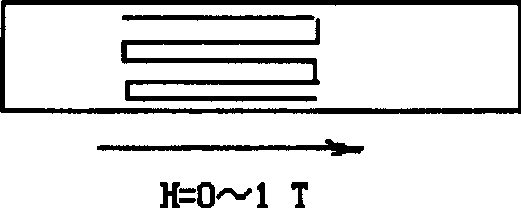Magnetic and heating treatment method to improve magnetically driven reversible strain property of polycrystalline Ni2 MnGa
A magnetic drive and strain variable technology, applied in the direction of material selection for magnetostrictive devices, inorganic material magnetism, device material selection, etc., can solve the problems of misorientation of martensitic twins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Improvement of polycrystalline Ni by using magnetic field heat treatment according to the present invention 2 A method for magnetically driving reversible strain of MnGa, the method comprising the following steps:
[0027] a) Preparation of Ni by non-stoichiometry according to the chemical formula 2 MnGa alloy containing 52at% Ni, 25at% Mn and 23at% Ga;
[0028] b) placing Ni, Mn and Ga raw materials of high-purity elements in an electric arc furnace, and performing repeated smelting under an argon protective atmosphere to produce a polycrystalline ingot;
[0029] c) performing homogenization annealing treatment on the above-mentioned polycrystalline ingot, the annealing temperature is 1173K, and the time is 3 days;
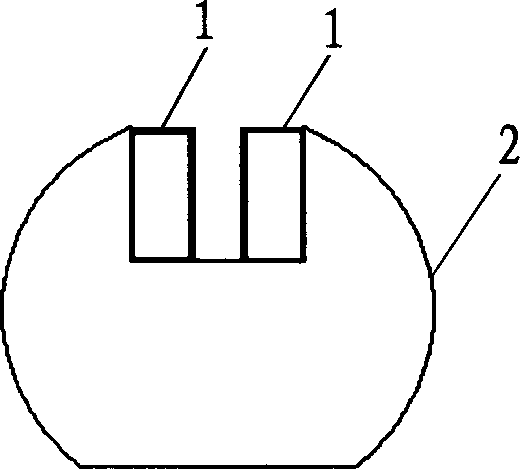
[0030] d) The homogenized heat-treated polycrystalline ingot is made into 2×4×8mm 3 Ni 52 mn 25 Ga 23 sample, placed in the figure 1 The magnetic yoke-permanent magnet assembly shown is subjected to magnetic field heat treatment, the magnetic field ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Improvement of Polycrystalline Ni by Magnetic Field Heat Treatment 2 The method of the magnetic drive reversible strain of MnGa, this method adopts the same step as embodiment 1, just Ni 52 mn 25 Ga 23 The magnetic field heat treatment of the sample is cooled by water quenching (W).
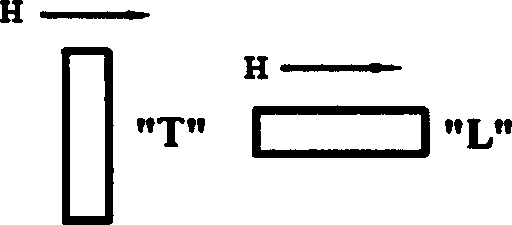
[0038] In the method step of this embodiment, the same sample is subjected to the same heat treatment in the magnetic field of zero magnetic field H=0 and H 0.7T, which are respectively expressed as:
[0039] T 1 W-0 means that the sample is water quenched under the condition of H=0 (0) after being kept at 413K for 30 minutes.
[0040] T i W-L means that after the sample is kept at 413K for 30 minutes, it is longitudinally treated in a magnetic field under the condition of H≈0.7T (L) water quenching.
[0041] T 1 W-T means that after the sample is kept at 413K for 30 minutes, it is water-quenched under the condition of H≈0.7T under the condition of magnetic field transverse treatmen...
Embodiment 3
[0051] As the embodiment of water quenching (W) and air-cooling (A) method, use the same step and material as embodiment 1 and 2, just the heat treatment heating temperature of sample piece after annealing adopts 348K (T 2 ) (higher than the end temperature of reverse phase transition A f ), the same sample is subjected to the same heat treatment in the longitudinal (L) or transverse (T) magnetic field of zero magnetic field H=0 and H≈0.7T, air cooling or water quenching are respectively expressed as: T 2 A-L, T 2 A-0, T 2 W-L, T 2 W-0, T 2 A-T, T 2 A-0, T 2 W-T and T 2 W-0. In Example 3, the magnetically induced strain of each sample was measured in the electromagnet with a variable magnetic field H=0-1T along the longitudinal direction of the sample. The test results are listed in Table 2. Correspondingly, according to the measured data of Table 2, the comparison chart of magnetically induced strain is shown in Figure 4 second half of .
[0052] Applied m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com