Fibre finishing agent and moist fibre structure
A fiber treatment agent and fiber structure technology, applied in fiber treatment, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to satisfy skin moisturizing, not being able to form a water-retaining structure, not being able to obtain sufficient moisturizing properties, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~6 and comparative example 1~8
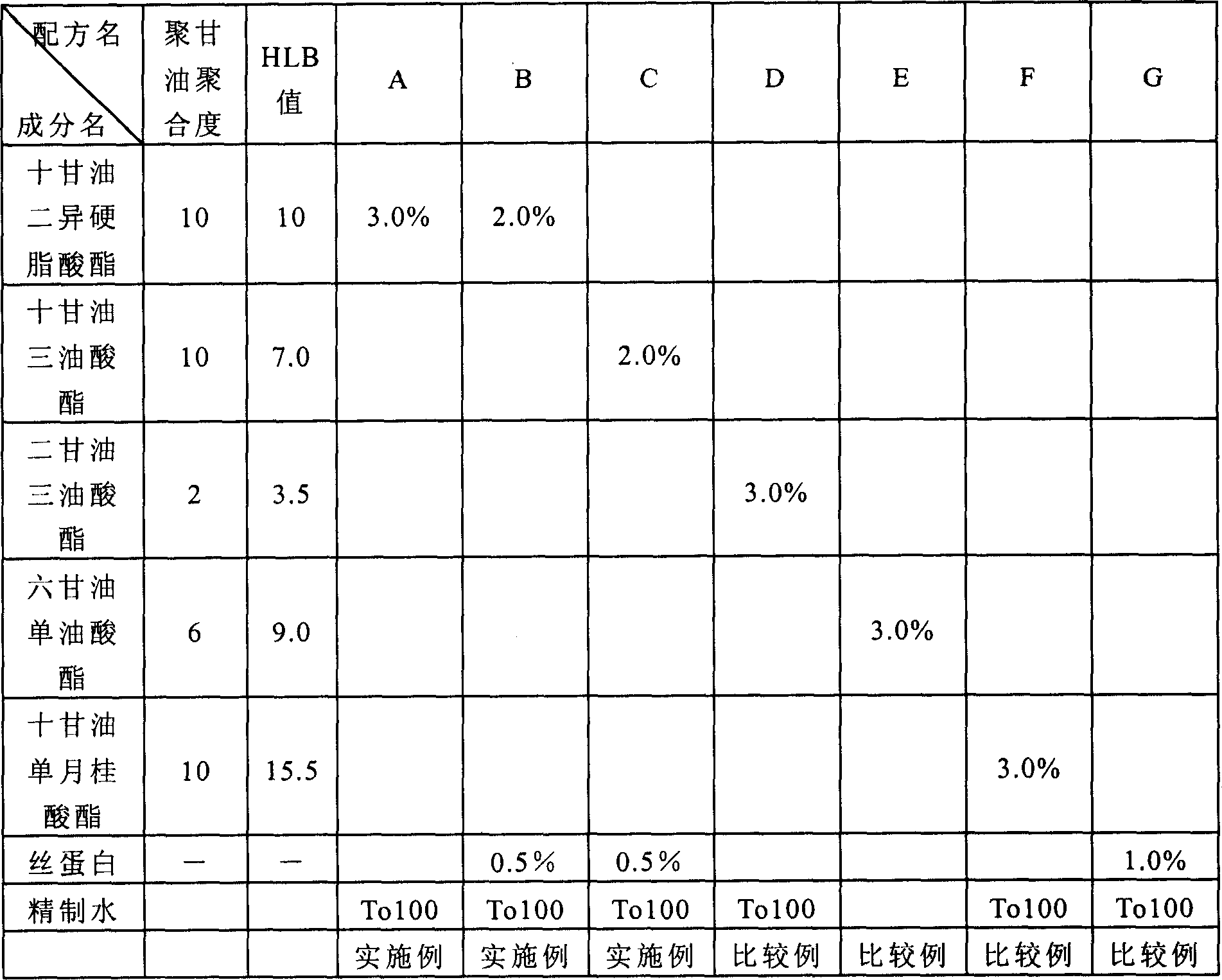
[0054] Adjust the fiber treatment agent according to the formula in Table 1, and use the exhaust dyeing method [equipment: newmatchmangle (ニユ一マツチチチングル) IPM-1 type: manufactured by Tsujii Dyeing Machinery Co., Ltd., sensitivity (pick-up) 60%, drying at 120 ° C × 2 minutes], cotton and polyester fabrics were treated as test fabrics. In addition, untreated cloth was used as a control. A moisture absorption rate test and a moisture permeability test were performed on these test cloths.
[0055] In addition, the adhesion amount of the fiber treatment agent on the fabric was 1.8% in Example 1, 1.5% in Example 2, 1.5% in Example 3, 1.8% in Example 4, 1.5% in Example 5, and 1.5% in Example 6. 1.5%, Comparative Examples 1-3 were 1.8%, Comparative Example 4 was 0.6%, Comparative Examples 5-7 were 1.8%, and Comparative Example 8 was 0.6%.
[0056] According to the results shown in Table 2, for the moisture absorption test, high moisture absorption was shown in Examples 2 and 5, and esp...
Embodiment 5、 comparative example 5
[0061] The liquid crystal structure on the surface of the fiber was confirmed using test fabrics of polyester fabrics treated according to formulation B (Example 5) and formulation D (Comparative Example 5) in Table 1. Confirmation was performed with a transmission electron microscope (60,000 magnifications). Such as figure 1 As shown, Example 5 has a layered liquid crystal structure on the surface of the fiber. Such as figure 2 As shown, in Comparative Example 5, no lamellar structure can be seen.
Embodiment 7、8
[0063] Use the decaglyceryl diisostearate of Table 1, press the formula of Table 3, utilize the exhaust dyeing method [equipment: newmatchmangle (ニユ一マツチチチングル) IPM-1 type: Tsujii dyeing machine industry Co., Ltd., sensitivity 60%, dry 120° C.×2 minutes] The polyester fabric was treated to obtain a test fabric. This test cloth was subjected to a moisture retention test. In addition, the amount of fiber adhesion on the fabric was 1.56%, respectively.
[0064] As a result, as shown in Table 4, the state of restoring the water content of cutin is shown.
[0065] ingredient name
[0066] Before silk coating
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com