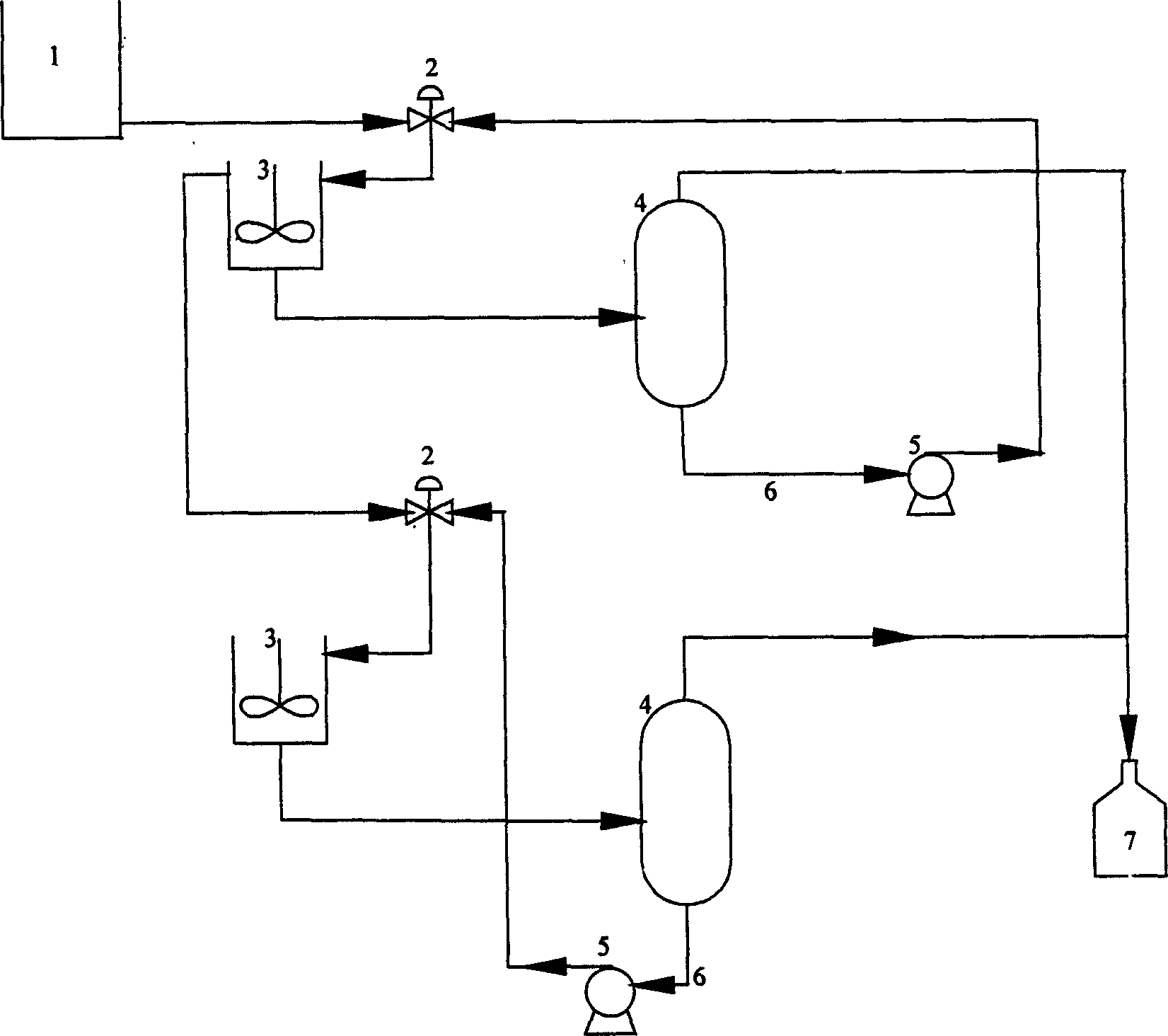
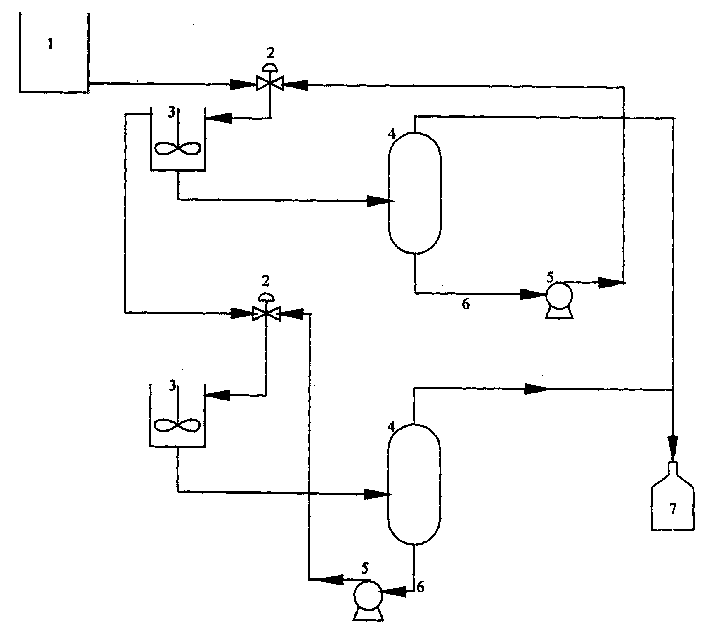
Process for separating and recovering minim organic solvent from waste water using ion liquid
A technology of ionic liquids and organic solvents, applied in the field of trace organic solvents, can solve problems such as secondary pollution, time-consuming, and unsatisfactory separation and recovery effects, and achieve reduced loss, good adaptability and operability, and increased compatibility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1, hydrophobic ionic liquid [bmim] PF 6 Synthesis
[0034] According to the literature (J.G.Huddlestion, H.D.Willauer, et al.[J].Chem.Commun., 1998, 1765), the ionic liquid was synthesized in two steps by the hydrothermal method, and the bromobutane imidazole compound was first synthesized. Re-distill methylimidazole and bromobutane respectively before the reaction, then mix them in a three-necked flask at a molar ratio of 1:1, heat and reflux in a water bath at a temperature of 70°C for 32 hours, wash with ethyl acetate after cooling 3 to 5 times to remove unreacted methylimidazole and bromobutane, and 70°C rotary evaporation to obtain bromobutane imidazole with a yield of >99.5%. Will KPF 6 After mixing with newly synthesized bromobutylimidazole in a molar ratio of 1.1:1, ion exchange occurs at a water bath temperature of 70°C, and washed with an equal volume of deionized water for 3 to 5 times until the pH is near neutral. The target product was obtaine...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2, the solubility characteristic of pure organic solvent in ionic liquid
[0037] Select five commonly used organic solvents, butyl acetate, acetic acid, ethanol, butanol, and dimethylformamide (DMF), and mix them with hydrophobic ionic liquid [bmim]PF at a volume ratio of 1:1 6 、[omim]PF 6 , [C 12 mim]PF 6 After fully mixing, it was found that no emulsification occurred. Experimental results such as figure 2 as shown, figure 2 It is the state of two-phase delamination after mixing equal volumes of organic solvents and ionic liquids (the mixing effect of the same series of ionic liquids is similar). From this result, it can be seen that butyl acetate, acetic acid and dimethylformamide (DMF) are miscible with ionic liquids , no stratification occurred; only about 30% of ethanol and butanol were dissolved in the ionic liquid. In conclusion, the above organic solvents can be enriched in ionic liquids.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3, use the ionic liquid prepared in embodiment 1 to extract butyl acetate in the aqueous solution
[0039] Under room temperature conditions, preparation concentration (wt%) is the butyl acetate aqueous solution of 0.6,0.4,0.3,0.2, the hydrophobic ionic liquid prepared with embodiment 1 is extractant, with (ionic liquid / butyl acetate aqueous solution ) in a ratio of 1 / 10, fully stirred, and left to stand, the water phase and the ionic liquid phase can be separated rapidly without emulsification.
[0040] The aqueous raffinate was extracted with n-hexane, analyzed by gas chromatography, and the residual organic solvent content of the aqueous raffinate was detected. The extraction rate of the ionic liquid was calculated according to formula (1). The results are listed in Table 1.
[0041]
[0042] Extraction rate (%)
[0043] It can be seen from Table 1 that under the condition of comparing 1:10, the primary extraction efficiency of the ionic liqui...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com