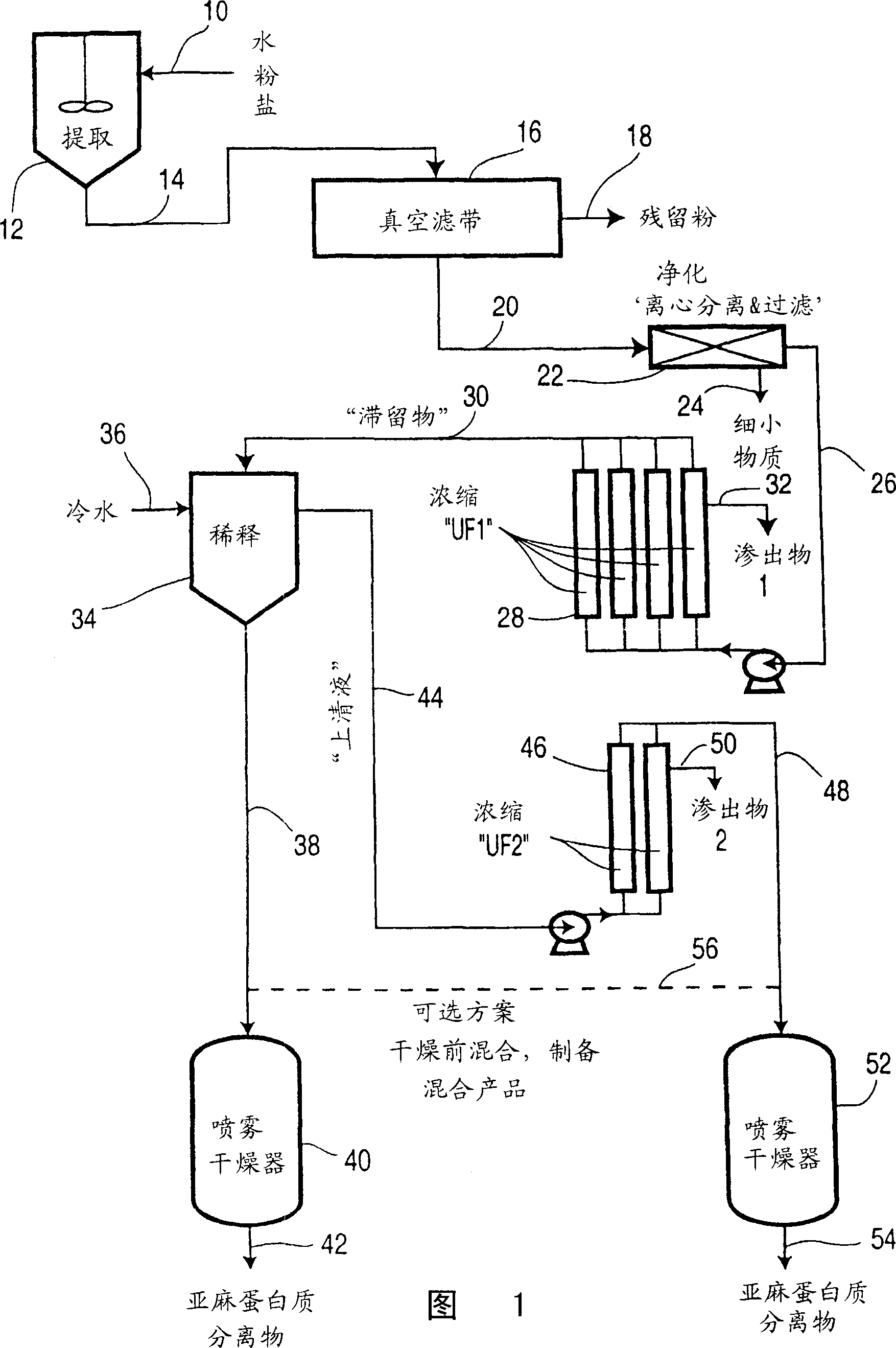
Flax protein isolate and production
A protein separation and protein technology, applied in the preparation method of peptides, protein food ingredients, plant protein processing, etc., can solve the problem of no prompt recovery of flax protein isolates, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] This example illustrates the recovery of linola protein from linola oilseed.
[0061] The linola oil seeds are cold pressed and the oil recovered. 16.8 Kg ground oilseed meal was added to 335 L of 0.15M NaCl solution (5% w / v, extraction concentration at 13°C) and the mixture was stirred for 60 minutes, followed by a 60 minute settling period. 190 L of the extract was decanted and filtered through a 20 micron filter pad to provide 180 L of an aqueous protein solution with a protein content of 6 g / L.
[0062] The volume of the aqueous solution was reduced to 11 L by concentration on an ultrafiltration system using a molecular weight cut-off of 30,000 Daltons. The resulting concentrated solution had a protein content of 6 g / L, which represented a yield of 51 wt% of the protein initially extracted from the linola powder.
[0063] The concentrated protein solution at 30°C was added to water at 4°C at a dilution ratio of 1:10. A white cloud formed immediately and was allow...
Embodiment 2
[0065] This example illustrates the recovery of flax protein from flax oilseed meal.
[0066] 17.5 Kg of commercially available linseed oil meal was added to 350 L of 0.5M NaCl solution (5% w / v) at 20°C and the mixture was stirred for 60 minutes, followed by a settling time of 60 minutes. The protein concentration of the obtained protein extract solution was 8.5 g / L. Another 17.5 Kg of commercially available linseed oil meal material was processed in the same manner, and the protein concentration of the obtained protein extract solution was 7.9 g / L. The extract solutions from both batches were decanted and filtered through a 20 micron filter plate on a filter press, and the filtrates were combined.
[0067] The filtered aqueous protein solution was concentrated on an ultrafiltration system using a molecular weight cut off of 5,000 Daltons to provide 11 L of concentrated protein aqueous solution with a protein content of 120 g / L.
[0068] The concentrated protein solution at ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] This example illustrates the effect of pH on linola extraction.
[0072] The linola oilseed meal was extracted in a 5% w / v solution and the extraction pH was adjusted to pH levels 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12 with NaOH or HCl. All extractions were performed at room temperature with shaking on an orbital shaker at 230 RPM for 30 minutes. After this mixing time, the spent oilseed meal was separated from the extract and sampled for protein content analysis.
[0073] The results obtained are shown in Table I below:
[0074] extraction pH
extract protein
12
0.942%
11
0.708%
10
0.522%
9
0.616%
8
0.514%
7
0.330%
6
0.264%
5
0.165%
4
0.188%
[0075] It can be seen that higher pH extractions yielded more protein than lower pH extractions. The extracts at pH 5.0 and 4.0 appeared rath...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com