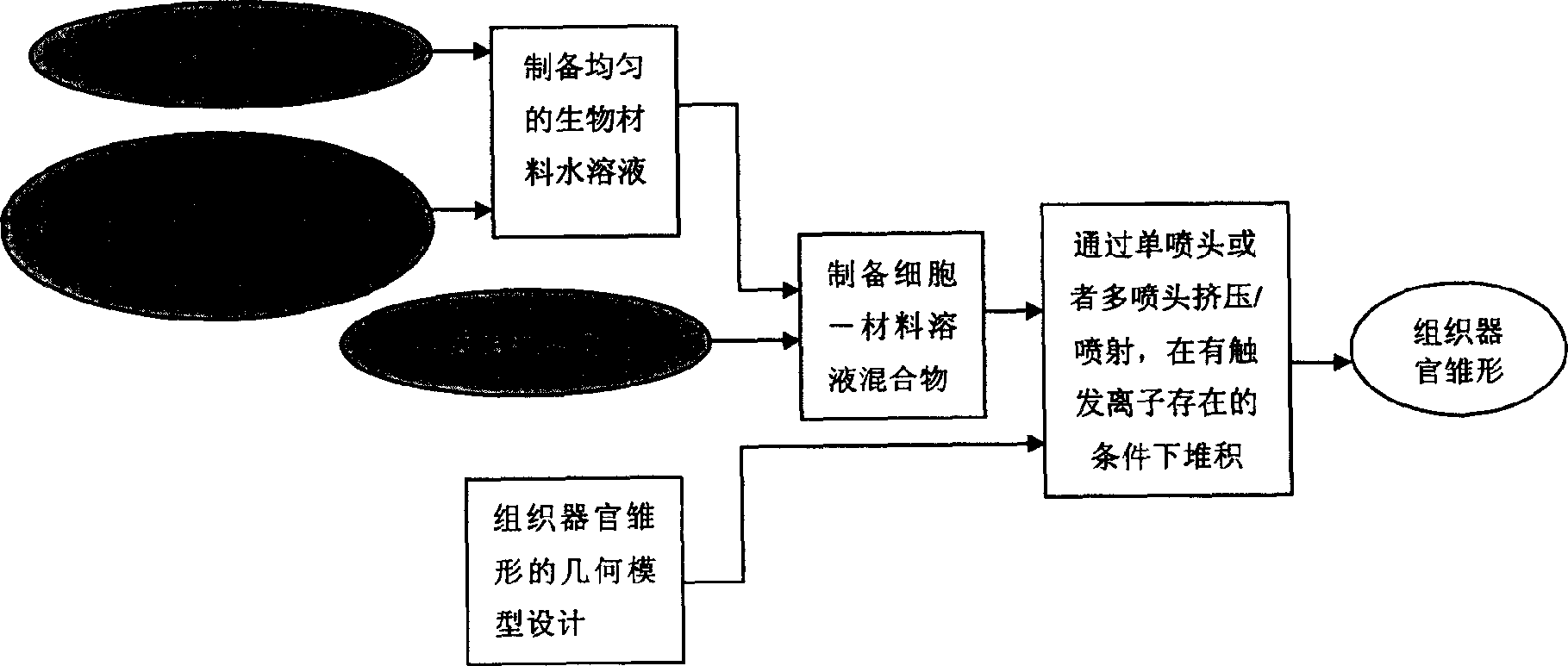
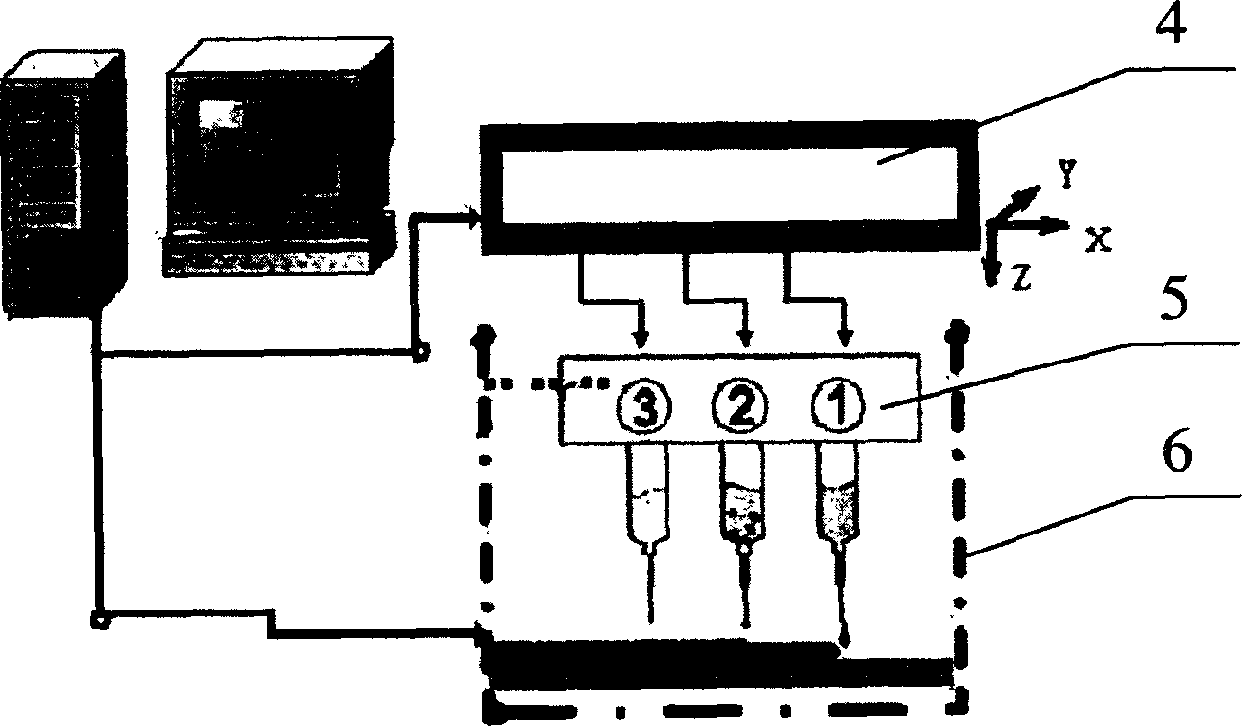
3D controlled stacking formation method of cell-material units
A cell and three-dimensional technology, applied to biochemical equipment and methods, fixed on/in organic carriers, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of different cell positioning and fixed-point placement, blood vessel growth restriction, cell migration and Reproduction is not particularly ideal and other issues, to achieve the effect of facilitating proliferation and differentiation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: The three-dimensional structure of chondrocyte-gelatin-calcium alginate manufactured by this process. The mixture of sodium alginate and gelatin that promotes cell adhesion and growth is prepared into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 100g / L, wherein the mass ratio of sodium alginate and gelatin is 1:10, and it is sterilized for use; the chondrocytes are mixed with the material solution evenly , to obtain a mixture of chondrocyte-gelatin-sodium alginate solution; prepare 10% calcium chloride solution as a trigger and make it atomized in the forming space; according to the pre-designed structure and defined planning path, the above mixture It is sprayed into a room-temperature sterile forming chamber filled with an atomization trigger by means of droplet spraying; after the solution is sprayed to a designated position, it undergoes a sol-gel transition rapidly to form a chondrocyte-gelatin-calcium alginate gel; gradually Layer stacking results in a t...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2: The three-dimensional structure of hepatocyte-gelatin-hepatocyte growth factor-calcium alginate produced by this process. The mixture of sodium alginate, gelatin and hepatocyte growth factor that promotes cell adhesion growth is prepared into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 30g / L, wherein sodium alginate: (gelatin+hepatocyte growth factor) is 1: 0.67 (mass ratio) , sterilized for later use; the hepatocytes and the material solution were evenly mixed to obtain a mixture of hepatocytes-gelatin-hepatocyte growth factor-sodium alginate solution; 5% calcium chloride solution was prepared as a trigger and input into the trigger nozzle; according to With the pre-designed structure and the defined and planned path, the above-mentioned mixture is sprayed to the designated position in the forming chamber by the method of droplet spraying, and the trigger agent sprays the calcium chloride solution at the same position, so that the cell-material unit rapidly u...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3: The three-dimensional structure of hepatocyte-endothelial cell-gelatin-calcium alginate produced by this process. The mixture of sodium alginate and gelatin that promotes cell adhesion and growth is prepared into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 10g / L, wherein the mass ratio of sodium alginate and gelatin is 1:0.5, and it is sterilized for use; liver cells and endothelial cells are mixed with Mix evenly with the material solution to obtain a mixture of two cell-gelatin-sodium alginate solutions; input the two mixtures into different nozzles respectively; prepare 20% calcium chloride solution as a trigger and input it into a special trigger nozzle; Design the structure and define the planned path. After the above mixture is sprayed to the specified position by the method of droplet injection, the trigger nozzle sprays the calcium chloride solution at the same position, and the mixture of cell-material solution undergoes a sol-gel transition rapidly. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com