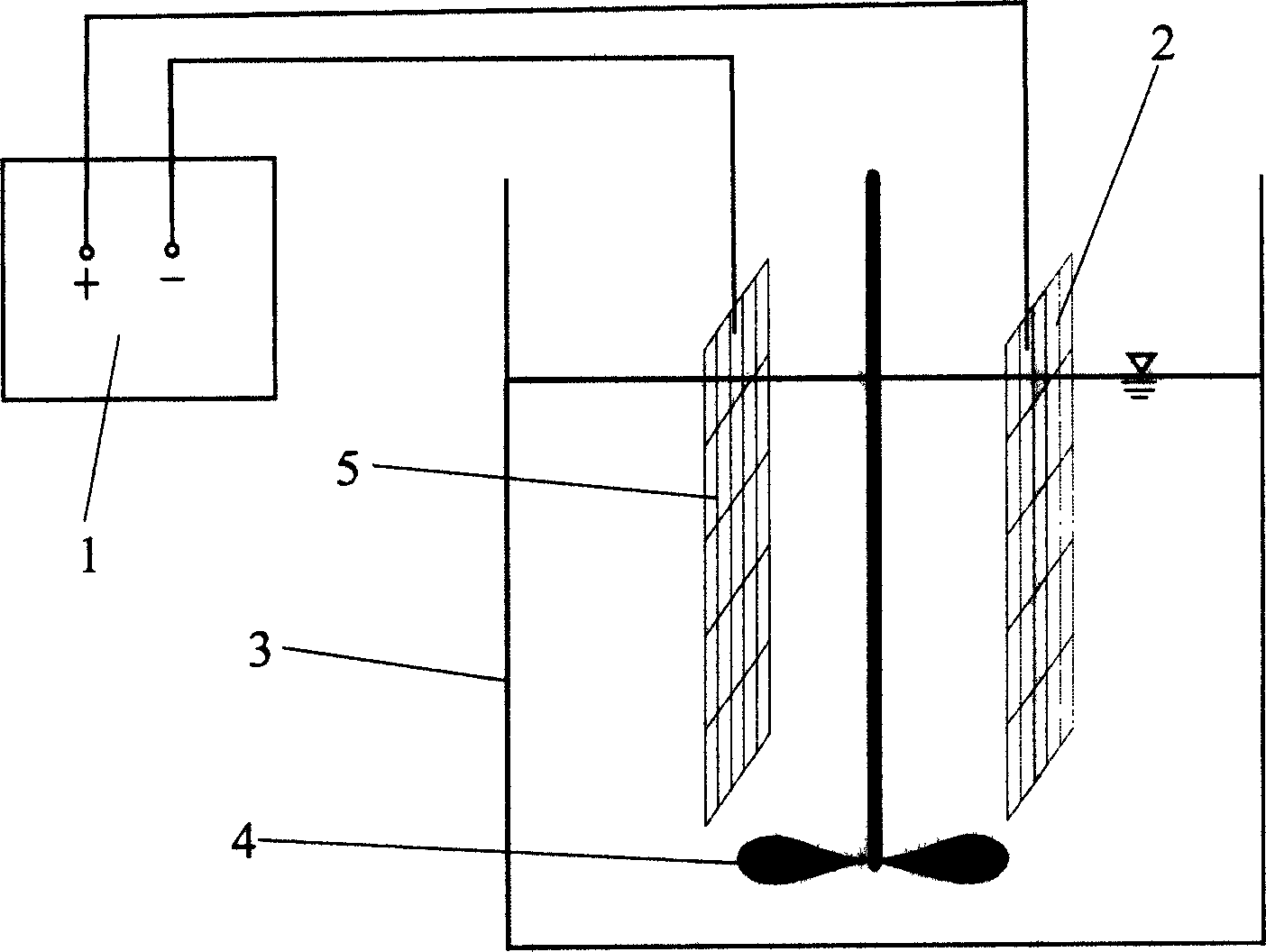
Electrochemical oxidation process for removing algae toxins from water
A technology for algal toxins and water removal, applied in chemical instruments and methods, electrochemical water/sewage treatment, separation methods, etc., can solve the problems of unreported algal toxins in water, etc. simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1. Removal of different concentrations of algae toxins in raw water by electrochemical oxidation
[0026] Use high-purity water to prepare aqueous solutions containing algae toxins of different concentrations, and perform electrochemical treatment under the following conditions:
[0027] Algal toxin concentration: MCRR 12.58, 6.29, 3.14mg / L, MCLR 8.29, 4.15, 2.07mg / LNaCl initial concentration is 1.85mmol / L
[0028] pH=7.00
[0029] Current intensity I=60mA
[0030] Table 1 shows the changes in algal toxin concentration when treated at different times.
[0031] time, min
[0032] As can be seen from Example 1, the lower the initial concentration of algal toxins, the shorter the reaction time required for complete removal.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2. Removal of algae toxins in raw water containing different concentrations of chloride ions by electrochemical oxidation
[0034] Use high-purity water to prepare algae toxin raw water containing different concentrations of chloride ions, and perform electrochemical treatment under the following conditions:
[0035] Initial concentration of chloride ion: 1.85, 20, 40mmol / L Cl -
[0036] Algal toxin concentration: MCRR 12.58mg / L, MCLR 8.29mg / L
[0037] pH=7.00
[0038] Current intensity I=60mA
[0039] After treatment for different time, the changes of algal toxin concentration are shown in Table 2.
[0040] It can be seen from Example 2 that with the increase of the concentration of chloride ions in the raw water, the reaction time required for the complete removal of algae toxins is shortened.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3. Removal of algae toxins in raw water by electrochemical oxidation under different current intensities
[0042] Use raw water with a certain concentration of algae toxins to perform electrochemical treatment under the following conditions:
[0043] Current intensity I=40, 60, 80mA
[0044] NaCl initial concentration: 1.85 mmol / L
[0045] Algal toxin concentration: MCRR 12.58mg / L, MCLR 8.29mg / L
[0046] pH=7.00
[0047] The changes in algal toxin concentration after treatment for different time are shown in Table 3.
[0048] It can be seen from Example 3 that with the increase of the current intensity, the reaction time required for the complete removal of algae toxins is shortened.
[0049]
[0050]
[0051]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com