Method for separating and recovering phosphonic acid from acetic acid-nitric acid-phosphonic acid waiste liquid
A technology for separation and recovery of phosphoric acid, used in ammonium orthophosphate fertilizers, chemical instruments and methods, alkaline orthophosphate fertilizers, etc., can solve problems such as incomplete compliance, achieve good production efficiency, improve extraction selectivity, and inhibit emulsification Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
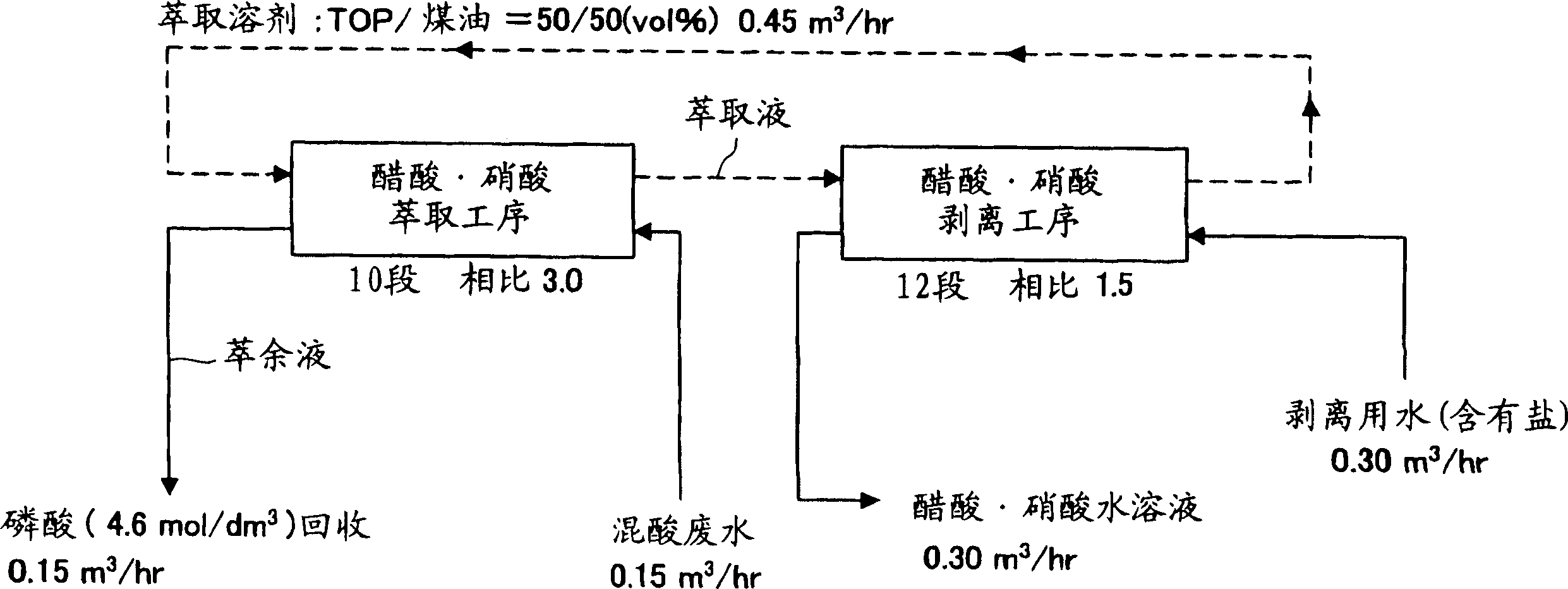
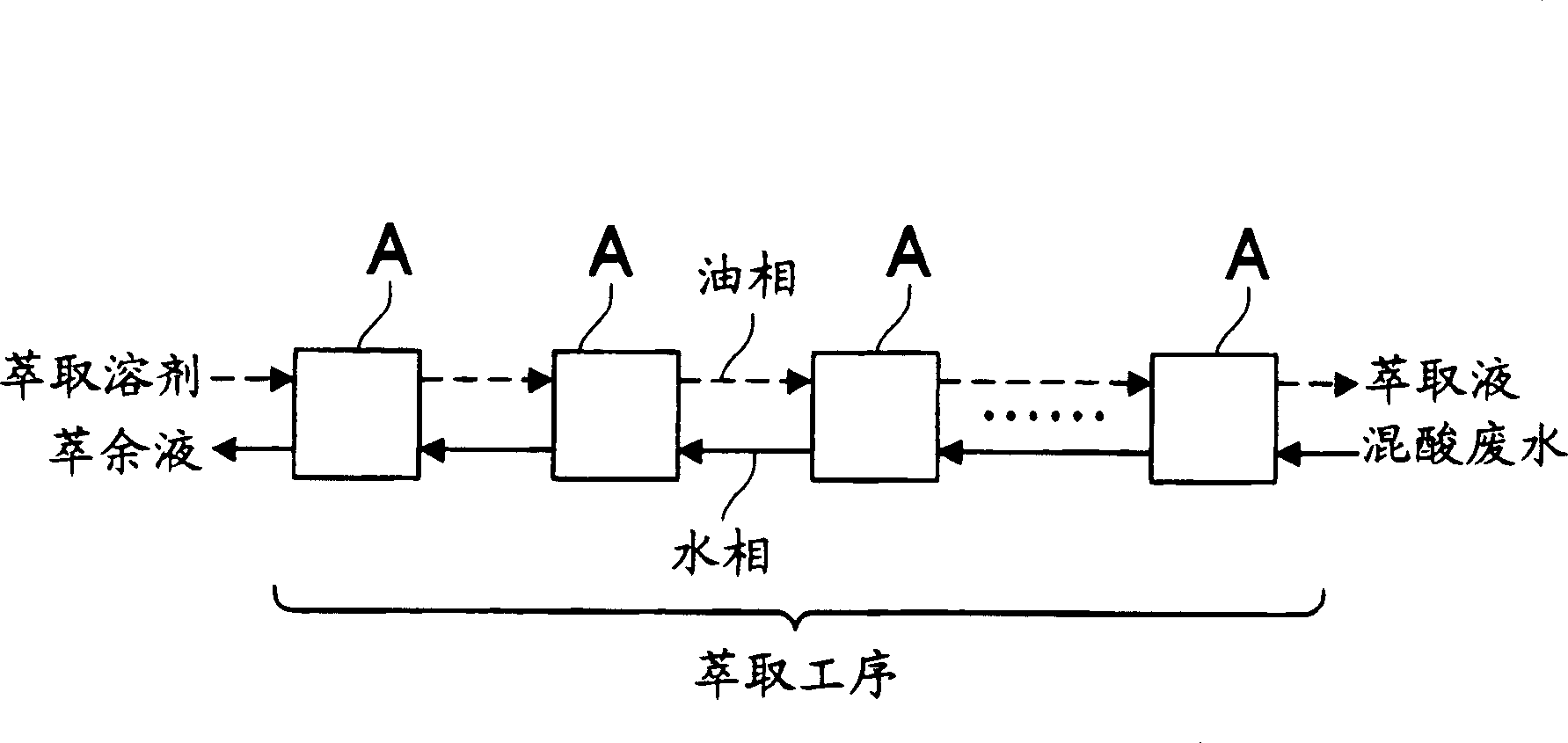
[0058] According to the separation and recovery method of the embodiment enumerated in the previous item (with reference to figure 1 ), separating and recovering phosphoric acid from mixed acid wastewater containing acetic acid, nitric acid and phosphoric acid. The mixed-acid wastewater used in this embodiment is the mixed-acid wastewater from the liquid crystal manufacturing plant, and is composed as shown in table 1 (certainly, the mixed-acid wastewater produced from the liquid crystal manufacturing plant is not completely such composition, and various factories etc. different places). Detailed conditions such as the flow rate of each part, the number of stages in each process, and comparison are shown in figure 1 middle. In addition, as an extraction solvent, an extraction solvent having a composition of tris(2-ethylhexyl)phosphate (TOP) / kerosene=50 / 50 (volume ratio) was used. As kerosene, "Solvessol 150" (trade name) manufactured by Showa Shell Oil Co., Ltd. was used. ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Except using the water that contains 2000ppm NaCl as stripping water, others are separated and recovered phosphoric acid from mixed acid wastewater containing acetic acid, nitric acid and phosphoric acid in the same manner as in Example 1. In addition, the flow rate of each part, the number of stages in each process, and the detailed conditions such as comparison are the same as in Example 1 (refer to figure 1 ).
Embodiment 3
[0063] Except using the water that contains 2000ppm KCl as stripping water, other are separated and recovered phosphoric acid from the mixed acid wastewater containing acetic acid, nitric acid and phosphoric acid in the same manner as in Example 1. In addition, detailed conditions such as the flow rate of each part, the number of stages in each process, and comparison are the same as in Example 1 (see figure 1 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com